Abstract
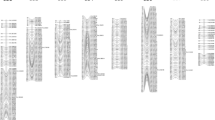
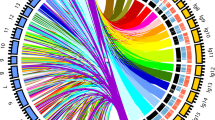
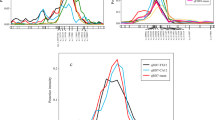
Chilling requirement (CR) for floral bud dormancy release is one of the major limiting factors for geographical adaptation of fruiting trees. Using a whole genome sequencing approach (Illumina platform), we explored polymorphism underlying phenotypic differences among individuals in a peach F2 cross segregating for chilling requirement and bloom date. Allelic configuration of individuals, which represented phenotypic extremes in the cross (300 vs. 1,100 chill hours) allowed reconstruction of low- and high-chill haplotypes within three most significant quantitative trait locus (QTL) intervals on the Prunus G1, G4, and G7. We detected single nucleotide polymorphic sites (SNPs), small deletions and insertions (DIPs), and large structural variants (SVs) associated with low-chill haplotypes and created a prioritized list of candidate genes based on functionally characterized homologs from Arabidopsis thaliana. Two dormancy associated genes PpeDAM5 and PpeDAM6 are the strongest candidate genes for the major QTL signal at the lower end of G1. Also, key functional genes involved in the Polycomb repressive mechanism, cell cycle progression, and hormone regulation were evident as strong candidate genes underlying QTL intervals in this peach cross.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandre CM, Hennig L (2008) FLC or not FLC: the other side of vernalization. J Exp Bot 59:1127–1135
Almada R, Cabrera N, Casaretto JA, Penă-Cortés H, Ruiz-Lara S, Villanueva EG (2011) Epigenetic repressor-like genes are differentially regulated during grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) development. Plant Cell Rep 30:1959–1968
Amasino RM, Michaels SD (2010) The timing of flowering. Plant Physiol 154:516–520
Aranzana MJ, Illa E, Howad W, Arús P (2012) A first insight into peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] SNP variability. Tree Genet Genomes 8(6):1359–1369. doi:10.1007/s11295-012-0523-6
Barrero JM, González-Bayón R, del Pozo JC, Ponce MR, Micol JL (2007) INCURVATA2 encodes the catalytic subunit of DNA polymerase alpha and interacts with genes involved in chromatin-mediated cellular memory in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 19:2822–2838
Bartrina I, Otto E, Strnad M, Werner T, Schmülling T (2011) Cytokinin regulates the activity of reproductive meristems, flower organ size, ovule formation, and thus seed yield in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 23:69–80
Becker A, Theißen G (2003) The major clades of MADS-box genes and their role in the development and evolution of flowering plants. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:464–489
Bielenberg DG, Wang Y, Fan S, Reighard GL, Scorza R, Abbott AG (2004) A deletion affecting several gene candidates is present in the Evergrowing peach mutant. J Hered 95:436–444
Bielenberg DG, Wang Y, Li Z, Zhebentyayeva T, Fan S, Reighard GL, Scorza R, Abbott AG (2008) Sequencing and annotation of the evergrowing locus in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] reveals a cluster of six MADS-box transcription factors as candidate genes for regulation of terminal bud formation. Tree Genet Genomes 4:495–507
Campoy JA, Ruiz D, Egea J, Rees J, Celton JM, Martínez-Gómez P (2011) Inheritance of flowering time in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) and analysis of linked quantitative trait loci (QTLs) using simple sequence repeat markers. Plant Mol Biol Report 29:404–410
Caro E, Stroud H, Greenberg MV, Bernatavichute YV, Feng S, Groth M, Vashisht AA, Wohlschlegel J, Jacobsen SE (2012) The SET-domain protein SUVR5 mediates H3K9me2 deposition and silencing at stimulus response genes in a DNA methylation-independent manner. PLoS Genet 8(10):e1002995. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002995
Chagné D, Crowhurst RN, Troggio M, Davey MW, Gilmore B, Lawley C, Vanderzande S, Hellens RP, Kumar S, Cestaro A, Velasco R, Main D, Rees JD, Iezzoni A, Mockler T, Wilhelm L, Van de Weg E, Gardiner SE, Bassil N, Peace C (2012) Genome-wide SNP detection, validation, and development of an 8 K SNP array for apple. PloS One 7(2):e31745. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0031745
Cooke JEK, Eriksson ME, Junttila O (2012) The dynamic nature of bud dormancy in trees: environmental control and molecular mechanisms. Plant Cell Environ 10:1707–1728. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02552.x
Coustham V, Li P, Strange A, Clare Lister C, Song J, Dean C (2012) Quantitative modulation of polycomb silencing underlies natural variation in vernalization. Science 337:584–587. doi:10.1126/science.1221881
Desvoyes B, Sanchez MP, Ramirez-Parra E, Gutierrez C (2010) Impact of nucleosome dynamics and histone modifications on cell proliferation during Arabidopsis development. Heredity 105:80–91
Diaz-Riquelme J, Lijavetzky D, Martinez-Zapater JM, Carmona MJ (2009) Genome-wide analysis of MIKCC-type MADS box genes in grapevine. Plant Physiol 149:354–369
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arús P (2004) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:9891–9896
Dirlewanger E, Quero-García J, Le Dantec L, Lambert P, Ruiz D, Dondini L, Illa E, Quilot-Turion B, Audergon JM, Tartarini S, Letourmy P, Arús P (2012) Comparison of the genetic determinism of two key phenological traits, flowering and maturity dates, in three Prunus species: peach, apricot and sweet cherry. Heredity 109:280–292
Dondini L, Lain O, Geuna F, Banfi R, Gaiotti F, Tartarini S, Bassi D, Testolin R (2007) Development of a new SSR-based linkage map in apricot and analysis of synteny with existing Prunus maps. Tree Genet Genomes 3:239–249
Eldredge L, Ballard R, Baird WV, Abbott A, Morgens P, Callahan A, Scorza R, Monet R (1992) Application of RFLP analysis to genetic linkage mapping in peaches. HortSci 27:160–163
Fan S, Bielenberg DG, Zhebentyayeva TN, Reighard GL, Okie WR, Holland D, Abbott AG (2010) Mapping quantitative trait loci associated with chilling requirement, heat requirement and bloom date in peach (Prunus persica). New Phytol 185:917–930
Finnegan EJ, Helliwell C, Sheldon C, Peacock JW, Dennis E S, Bagnall D, Rouse D, Talege M (2010) Vernalization. In: Encyclopedia of life sciences (ELS). Wiley: Chichester. doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0002048.pub3
Gazzani S, Gendall AR, Lister L, Dean C (2003) Analysis of the molecular basis of flowering time variation in Arabidopsis accessions. Plant Physiol 132:1107–1114
Goodstein DM, Shu S, Howson R, Neupane R, Hayes RD, Fazo J, Mitros T, Dirks W, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Rokshar D (2012) Phytozome: a comparative platform for green plant genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 40:D1178–D1186
Hadjebi O, Casas-Terradellas E, Garcia-Gonzalo FR, Rosa JL (2008) The RCC1 superfamily: from genes, to function, to disease. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 1783:1467–1479
Hecht V, Foucher F, Ferrándiz C, Macknight R, Navarro C, Morin J, Vardy ME, Ellis N, Beltrán JP, Rameau C, Weller JL (2005) Conservation of Arabidopsis flowering genes in model legumes. Plant Physiol 137:1420–1434
Hennig L, Derkacheva M (2009) Diversity of Polycomb group complexes in plants: same rules, different players? Trends Genet 25:414–423
Higgins JA, Bailey PC, Laurie DA (2010) Comparative genomics of flowering time pathways using Brachypodium distachyon as a model for the temperate grasses. PLoS One 5(4):e10065
Holec S, Berger F (2012) Polycomb group complexes mediate developmental transitions in plants. Plant Physiol 158:35–43
Horvath DP (2009) Common mechanisms regulate flowering and dormancy. Plant Sci 177:523–531
Horvath DP, Anderson JV, Chao WS, Foley M (2003) Knowing when to grow: signals regulating bud dormancy. Trends Plant Sci 11:534–540
Jiménez S, Lawton-Rauh AL, Reighard GL, Abbott AG, Bielenberg DG (2009) Phylogenetic analysis and molecular evolution of the dormancy associated MADS-box genes from peach. BMC Plant Biol 9:81
Jung J-H, Seo PJ, Ahn JH, Park C-H (2012) Arabidopsis RNA-binding protein FCA regulates microRNA172 processing in thermosensory flowering. J Biol Chem 287:16007–16016
Laudencia-Chingcuanco D, Fowler DB (2012) Genotype-dependent burst of transposable element expression in crowns of hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) during cold acclimation. Comp Funct Genomics 2012: Article ID 232530. doi:10.1155/2012/232530
Leida C, Terol J, Martí G, Agustí M, Llácer G, Badenes ML, Ríos G (2010) Identification of genes associated with bud dormancy release in Prunus persica by suppression subtractive hybridization. Tree Physiol 30:655–666
Leida C, Conesa A, LlácerG BML, Gabino Ríos G (2012) Histone modifications and expression of DAM6 gene in peach are modulated during bud dormancy release in a cultivar-dependent manner. New Phytol 193:67–80
Levy YY, Mesnage S, Mylne JS, Gendall AR, Dean C (2002) Multiple roles of Arabidopsis VRN1 in vernalization and flowering time control. Science 297:243–246
Li ZG, Reighard GL, Abbott AG, Bielenberg DG (2009) Dormancy- associated MADS genes from the EVG locus of peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] have distinct seasonal and photoperiodic expression patterns. J Exp Bot 60:3521–3530
Li ZM, Zhang JZ, Mei L, Deng XX, Hu CG, Yao JL (2010) PtSVP, an SVP homolog from trifoliate orange (Poncirus trifoliata L. Raf.), shows seasonal periodicity of meristem determination and affects flower development in transgenic Arabidopsis and tobacco plants. Plant Mol Biol 74:129–142
Liu Z, Zhu Y, Gao J, Yu F, Dong A, Shen WH (2009) Molecular and reverse genetic characterization of NUCLEOSOME ASSEMBLY PROTEIN1 (NAP1) genes unravels their function in transcription and nucleotide excision repair in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 59:27–38
Liu X, Kim YJ, Muller R, Yumul RE, Liu C, Pan Y, Cao X, Goodrich J, Chen X (2011) AGAMOUS terminates floral stem cell maintenance in Arabidopsis by directly repressing WUSCHEL through recruitment of polycomb group proteins. Plant Cell 23:3654–3670
Liu G, Li W, Zheng P, Xu T, Chen L, Liu D, Hussain S, Teng Y (2012) Transcriptomic analysis of ‘Suli’ pear (Pyrus pyrifolia white pear group) buds during the dormancy by RNA-Seq. BMC Genomics 13:700. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-13-700
Martin A, Adam H, Diaz-Mendoza M, Zurczak M, Gonzalez-Schain ND, Suarez-Lopez P (2009) Graft-transmissible induction of potato tuberization by the microRNA miR172. Development 136:2873–2881
Mathiason K, He D, Grimplet J, Venkateswari J, Galbraith DW, Or E, Fennell A (2009) Transcript profiling in Vitis riparia during chilling requirement fulfillment reveals coordination of gene expression patterns with optimized bud break. Funct Integr Genomics 9:81–96
Metzger JD (1996) A physiological comparison of vernalization and dormancy chilling requirement. In: Lang GA (ed) Plant dormancy: physiology, biochemistry and molecular biology. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 147–155
Mimida N, Kidou S-I, Kotoda N (2007) Constitutive expression of two apple (Malus × domestica Borkh.) homolog genes of LIKE HETEROCHROMATIN PROTEIN1 affects flowering time and whole-plant growth in transgenic Arabidopsis. Mol Genet Genomics 278:295–305
Naik D, Dhanaraj AL, Arora R, Rowland LJ (2007) Identification of genes associated with cold acclimation in blueberry (Vaccinium corymbosum L.) using a subtractive hybridization approach. Plant Sci 173:213–222
Nishimoto T, Eilen E, Basilico C (1978) Premature of chromosome condensation in a ts DNA-mutant of BHK cells. Cell 15:475–483
Okie WR (1998) Handbook of peach and nectarine varieties. USDA-ARS, Byron, 808 pp
Olsen JE (2010) Light and temperature sensing and signalling in induction of bud dormancy in woody plants. Plant Mol Biol 73:37–47
Olukolu BA (2010) The genetics of chilling requirement in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Dissertation, Clemson University
Olukolu BA, Trainin T, Fan S, Kole C, Bielenberg G, Reighard GL, Abbott AG, Holland D (2009) Genetic linkage mapping for molecular dissection of chilling requirement and bud break in apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). Genome 52:819–828
Pacey-Miller T, Scott K, Ablett E, Tingey S, Ching A, Henry R (2003) Genes associated with the end of dormancy in grapes. Funct Integr Genomics 3:144–152
Rodriguez J, Sherman WB, Scorza R, Wisniewski M, Okie WR (1994) Evergreen peach, its inheritance and dormant behavior. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 119:789–792
Rohde A, Ruttink T, Hostyn V, Sterck L, Driessche KV, Boerjan W (2007) Gene expression during the induction, maintenance, and release of dormancy in apical buds of poplar. J Exp Bot 58:4047–4060
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics methods and protocols: methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 365–386
Saito S, Hirai N, Matsumoto C, Ohigashi H, Ohta D, Sakata K, Mizutani M (2004) Arabidopsis CYP707As encode (+)-abscisic acid 8′-hydroxylase, a key enzyme in the oxidative catabolism of abscisic acid. Plant Physiol 134:1439–1449
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbour
Sánchez-Pérez R, Dicenta F, Martínez-Gómez P (2012) Inheritance of chilling and heat requirements for flowering in almond and QTL analysis. Tree Genet Genomes 8:379–389. doi:10.1007/s11295-011-0448-5
Santamaría ME, Rodríguez R, Cañal MJ, Toorop PE (2011) Transcriptome analysis of chestnut (Castanea sativa) tree buds suggests a putative role for epigenetic control of bud dormancy. Annu Bot 108:485–498
Sasaki R, Yamane H, Ooka T, Jotatsu H, Kitamura Y, Akagi T, Tao R (2011) Functional and expressional analyses of PmDAM genes associated with endodormancy in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). Plant Physiol 157(1):485–497. doi:10.1104/pp. 111.181982
Sasaki T, Kobayashi A, Saze H, Kakutani T (2012) RNAi-independent de novo DNA methylation revealed in Arabidopsis mutants of chromatin remodeling gene DDM1. Plant J 70:750–758. doi:10.1111/j.1365-313X.2012.04911.x
Schmitz RJ, Hong L, Michaels S, Amasino RM (2005) FRIGIDA-ESSENTIAL 1 interacts genetically with FRIGIDA and FRIGIDA-LIKE 1 to promote the winter-annual habit of Arabidopsis thaliana. Development 132:5471–5478
Smaczniak C, Immink RG, Muiño JM, Blanvillain R, Busscher M, Busscher-Lange J, Dinh QD, Liu S, Westphal AH, Boeren S, Parcy F, Xu L, Carles CC, Angenent GC, Kaufman K (2012) Characterization of MADS-domain transcription factor complexes in Arabidopsis flower development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:1560–1565
Socquet-Juglard D, Christen D, DevènesG G, Gessler C, Duffy B, Patocchi A (2012) Mapping architectural, phenological, and fruit quality QTLs in apricot. Plant Mol Biol Report. doi:10.1007/s11105-012-0511-x
Stafstrom JP, Ripley BD, Devitt ML, Drake B (1998) Dormancy-associated gene expression in pea axillary buds. Cloning and expression of PsDRM1 and PsDRM2. Planta 205:547–552
Strange A, Li P, Lister C, Anderson J, Warthmann N, Shindo C, Irwin J, Nordborg M, Dean C (2011) Major-effect alleles at relatively few loci underlie distinct vernalization and flowering variation in Arabidopsis accessions. PLoS One 6(5):e19949. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019949
Testone G, Condello E, Verde I, Nicolodi C, Caboni E, Dettori MT, Vendramin E, Bruno L, Bitonti MB, Mele G, Giannino D (2012) The peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch) genome harbours 10 KNOX genes, which are differentially expressed in stem development, and the class 1 KNOPE1 regulates elongation and lignification during primary growth. J Exp Bot 63:5417–5435
Topp BL, Sherman WB, Rasera MCB (2008) Low-chill cultivars development. In: The peach: botany, production and uses (Eds DR Layne and D. Bassi), CAB International, Wallingford, 615pp, pp106-138.
Turck F, Roudier F, Farrona S, Martin-Magniette ML, Guillaume E, Buisine N, Gagnot S, Martienssen RA, Coupland G, Colot V (2007) Arabidopsis TFL2/LHP1 specifically associates with genes marked by trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27. PLoS Genet 3:e86
Ueno S, Klopp C, Leplé JC, Derory J, Noirot C, Léger V, Prince E, Kremer A, Plomion C, Le Provost G (2013) Transcriptional profiling of bud dormancy induction and release in oak by next-generation sequencing. BMC Genomics 14:236. doi:10.1186/1471-2164-14-236
Utz HF, Melchinger AE (1996) PLABQTL: a program for composite interval mapping of QTL. J. Agric. Genomics 2(1)
Van Bel M, Proost S, Wischnitzki E, Movahedi S, Scheerlinck C, Van de Peer Y, Vandepoele K (2012) Dissecting plant genomes with the PLAZA comparative genomics platform. Plant Physiol 158:590–600
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMapÒ 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Verde I, Bassil N, Scalabrin S, Gilmore B, Lawley CT, Gasic K, Micheletti D, Rosyara UR, Cattonaro F, Vendramin E, Main D, Aramini V, Blas AL, Mocker TC, Bryan DW, Wilhelm L, Troggio M, Sosinski B, Aranzana MJ, Arus P, Iezzoni A, Morgante M, Peace C (2012) Development and evaluation of a 9K SNP array for peach by internationally coordinated SNP detection and validation in breeding germplasm. PLoS One 7(4):e35668. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0035668
Verde I, Abbott AG, Scalabrin S, Jung S, Shu S, Marroni F, Zhebentyayeva T, Dettori MT, Grimwood J et al (2013) The high quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet 45(5):487–494. doi:10.1038/ng.2586
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTL. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang D, Karle R, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1998) Genetic linkage map in sour cherry using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1217–1224
Wu R-M, Walton EF, Richardson AC, Wood M, Hellens RP, Varkonyi-Gasic E (2012) Conservation and divergence of four kiwifruit SVP-like MADS-box genes suggest distinct roles in kiwifruit bud dormancy and flowering. J Exp Bot 63:797–807
Xu L, Shen WH (2008) Polycomb silencing of KNOX genes confines shoot stem cell niches in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 18:1966–1971
Yamane H, Kashiwa Y, Ooka T, Tao R, Yonemori K (2008) Suppression subtractive hybridization and differential screening reveals endodormancy-associated expression of an SVP/AGL24-type MADS- box gene in lateral vegetative buds of Japanese apricot. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 133:708–716
Yamane H, Ooka T, Jotatsu H, Hosaka Y, Sasaki R, Tao R (2011a) Expressional regulation of PpDAM5 and PpDAM6, peach (Prunus persica) dormancy-associated MADS-box genes, by low temperature and dormancy-breaking reagent treatment. J Exp Bot 62:3481–3488
Yamane H, Tao R, Ooka T, Jotatsu H, Sasaki R, Yonemori K (2011b) Comparative analyses of dormancy-associated MADS-box genes, PpDAM5 and PpDAM6, in low- and high-chill peaches (Prunus persica L.). J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 80:276–283
Yamane H, Ooka T, Jotatsu H, Sasaki R, Tao R (2011c) Expression analysis of PpDAM5 and PpDAM6 during flower bud development in peach (Prunus persica). Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 129:844–848
Zhebentyayeva TN, Reighard GL, Gorina VM, Abbott AG (2003) Simple sequence repeats (SSR) analysis for assessment of genetic variability in apricot germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 106:435–444
Acknowledgments
The study was carried out with financial support from the Robert and Lois Coker Trustees Chair in Molecular Genetics at the Department of Genetics and Biochemistry, Clemson University. We also are thankful to Kathy Brock for maintaining plants used in this study and Dr. Mike Wang at the David H. Murdock Research Institution (Kannapolis, NC) for guidance with Illumina Sequencing applications.
Data Archiving Statement
We followed standard Tree Genetics and Genomes policy. The GDR accession number for QTL data is tfGDR1004. Sequences submitted to GenBank have accession numbers KF218189–KF218196 which are also listed in the Supplemental File S7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by D. Neale
Supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Fig. S1
Size distribution of the paired-end reads in the “4ind” assembly (DOCX 132 kb)
Supplemental Table S1
The SSR haplotypes of the C × Fla individuals A209, A318, A323 and A340 within QTL intervals on G1, G4 and G7 (DOCX 18 kb)
Supplemental Table S2
Gene targeted SSRs used for saturation QTL intervals in the C × Fla cross (XLSX 15 kb)
Supplemental Table S3
List of primers used for SNP/DIP verification in peach germplasm (XLSX 15 kb)
Supplemental Table S4
List of the PcG homologs in peach genome (XLSX 14 kb)
Supplemental Table S5
SNP/DIP validation in peach germplasm. Chilling requirement in hours is shown (XLS 43 kb)
Supplemental Table S6
The SNP/DIP polymorphic sites within annotated gene models underlying 3 strongest CR/BD QTLs on G1, G4 and G7 in the C × Fla cross (XLSX 255 kb)
Supplemental File S7
Verification of the low-chill polymorphic sites resolved using Sanger sequencing (DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhebentyayeva, T.N., Fan, S., Chandra, A. et al. Dissection of chilling requirement and bloom date QTLs in peach using a whole genome sequencing of sibling trees from an F2 mapping population. Tree Genetics & Genomes 10, 35–51 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-013-0660-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-013-0660-6