Abstract
This study identified eight S-haplotype-specific F-box genes (SFB alleles) and one S-haplotype-specific F-box-like gene (SFB-like gene) from genomic DNA by PCR combined with cleaved amplified polymorphic sequence markers in Prunus pseudocerasus and Prunus speciosa. The unknown sequences of C-termini were obtained by thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR. The whole nucleotide sequences of these genes were submitted to the EMBL/GenBank database. The SFBs shared typical structural features with SFBs from other Prunus species exhibiting gametophytic self-incompatibility. The deduced amino acid identity ranged from 77.1% to 82.4% among the four PpsSFBs and from 70.4% to 80.2% among the four PspeSFBs. The typical structural features were also detected in the PpsFB, but the sequence polymorphism was lower. The nucleotide identities ranged from 71.3% to 90.3% among the eight introns of the SFBs, the length of these introns varied from 95 to 121 bp and showed few polymorphisms. The distance between these SFBs and the corresponding S-RNases (S-ribonucleases) varied from 33 to 956 bp. Moreover, sequence analysis showed that interspecific amino acid identities in comparison with some other Prunus species were often higher than intraspecific identities, similar to S-RNase alleles. In addition, a similarity comparison found that the deduced amino acid identities among SFB alleles were higher than among S-RNase alleles, and the similarity data showed that the relationships among SFB alleles differed among S-RNase alleles, suggesting that the S-RNase and SFB alleles were separated but correlated during the coevolutionary process.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Pps :
-
Prunus pseudocerasus
- Pspe :
-
Prunus speciosa
- Pa :
-
Prunus avium
- Par :
-
Prunus armeniaca
- Pcer :
-
Prunus Cerasus
- Pd :
-
Prunus dulcis
- Pm :
-
Prunus mume
- Ps :
-
Prunus salicina
- PaxiF1 :
-
Petunia axillaris
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389
Anderson MA, Cornish EC, Mau SL, Williams EG, Hoggart R, Bonig I, Grego B, Simpson R, Roche PJ, Haley JD (1986) Cloning of cDNA for a stylar glycoprotein associated with expression of self-incompatibility in Nicotiana alata. Nature 321:38–44
Chung BY, Simons C, Firth AE, Brown CM, Hellens RP (2006) Effect of 5′UTR introns on gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 7:120
De Nettancourt D (2001) Incompatibility and incongruity in wild and cultivated plants. Springer, Berlin
Deshaies RJ (1999) SCF and Cullin/Ring H2-based ubiquitin ligases. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:435–467
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochemistry 19:11–15
Entani T, Iwano M, Shiba H, Che FS, Isogai A, Takayama S (2003) Comparative analysis of the self-incompatibility (S-) locus region of Prunus mume: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with allelic diversity. Genes Cells 8:203–213
Gu C, Zhang SL, Huang SX, Heng W, Liu QZ, Wu HQ, Wu J (2010) Identification of S-genotypes in Chinese cherry cultivars (Prunus pseudocerasus LindI.). Tree Genet Genomes 6:579–590
Huang SX, Wu HQ, Li YR, Wu J, Zhang SJ, Heng W, Zhang SL (2008) Competitive interaction between two functional S-haplotypes confer self-compatibility on tetraploid Chinese cherry (Prunus pseudocerasus Lindl. CV. Nanjing Chuisi). Plant Cell Rep 27:1075–1085
Ikeda K, Igic B, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Hauck NR, Nakano R, Sassa H, Iezzoni AF, Kohn JR, Tao R (2004) Primary structural features of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein, SFB, in Prunus. Sex Plant Reprod 16:235–243
Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Yamane H, Tao R, Hauck N, Sebolt AM, Iezzoni AF (2005) Linkage and physical distances between S-haplotype S-RNase and SFB genes in sweet cherry. Sex Plant Reprod 17:289–296
Kato S, Iwata H, Tsumura Y, Mukai Y (2007) Distribution of S-alleles in island populations of flowering cherry, Prunus lannesiana var. speciosa. Genes Genet Syst 82:65–75
Lai Z, Ma W, Han B, Liang L, Zhang Y, Hong G, Xue Y (2002) An F-box gene linked to the self-incompatibility (S) locus of Antirrhinum is expressed specifically in pollen and tapetum. Plant Mol Biol 50:29–42
Li Q, Yin H, Li D, Zhu H, Zhang Y, Zhu W (2007) Isolation and characterization of CMO gene promoter from halophyte Suaeda liaotungensis K. J Genet Genomics 34:355–361
McClure BA, Haring V, Ebert PR, Anderson MA, Simpson RJ, Sakiyama F, Clarke AE (1989) Style self-incompatibility gene products of Nicotlana alata are ribonucleases. Nature 342:955–957
Moriya Y, Yamamoto K, Okada K, Iwanami H, Bessho H, Nakanishi T, Takasaki T (2007) Development of a CAPS marker system for genotyping European pear cultivars harboring 17 S alleles. Plant Cell Rep 26:345–354
Newbigin E, Paape T, Kohn JR (2008) RNase-based self-incompatibility: puzzled by pollen S. Plant Cell 20:2286–2292
Romero C, Vilanova S, Burgos L, Martinez-Calvo J, Vicente M, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2004) Analysis of the S-locus structure in Prunus armeniaca L. Identification of S-haplotype specific S-RNase and F-box genes. Plant Mol Biol 56:145–157
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Sassa H, Nishio T, Kowyama Y, Hirano H, Koba T, Ikehashi H (1996) Self-incompatibility (S) alleles of the Rosaceae encode members of a distinct class of the T 2/S ribonuclease superfamily. Mol Gen Genet 250:547–557
Sonneveld T, Robbins TP, Bošković, R, Tobutt KR (2001) Cloning of six cherry self-incompatibility alleles and development of allele-specific PCR detection. Theor Appl Genet 102:1046–1055
Sonneveld T, Tobutt KR, Vaughan SP, Robbins TP (2005) Loss of pollen-S function in two self-compatible selections of Prunus avium is associated with deletion/mutation of an S haplotype-specific F-box gene. Plant Cell 17:37–51
Šurbanovski N, Tobutt KR, Konstantinović M, Maksimović V, Sargent DJ, Stevanović V, Bošković RI (2007) Self-incompatibility of Prunus tenella and evidence that reproductively isolated species of Prunus have different SFB alleles coupled with an identical S-RNase allele. Plant J 50:723–734
Sutherland BG, Tobutt KR, Robbins TP (2008) Trans-specific S-RNase and SFB alleles in Prunus self-incompatibility haplotypes. Mol Genet Genomics 279:95–106
Tao R, Yamane H, Sassa H, Mori H, Gradziel TM, Dandekar AM, Sugiura A (1997) Identification of stylar RNases associated with gametophytic self-incompatibility in almond (Prunus dulcis). Plant Cell Physiol 38:304
Thomson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive sequence alignment through sequence weighting, positions-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876
Tsukamoto T, Ando T, Watanabe H, Marchesi E, Kao TH (2005) Duplication of the S-locus F-box gene is associated with breakdown of pollen function in an S-haplotype identified in a natural population of self-incompatible Petunia axillaris. Plant Mol Biol 57:141–153
Ushijima K, Sassa H, Dandekar AM, Gradziel TM, Tao R, Hirano H (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of the self-incompatibility locus of almond: identification of a pollen-expressed F-box gene with haplotype-specific polymorphism. Plant Cell 15:771–781
Ushijima K, Yamane H, Watari A, Kakehi E, Ikeda K, Hauck NR, Iezzoni AF, Tao R (2004) The S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, is defective in self-compatible haplotypes of Prunus avium and P. mume. Plant J 39:573–586
Vaughan SP, Russell K, Sargent DJ, Tobutt KR (2006) Isolation of S-locus F-box alleles in Prunus avium and their application in a novel method to determine self-incompatibility genotype. Theor Appl Genet 112:856–866
Vieira J, Teles E, Santos RA, Vieira CP (2008) Recombination at Prunus S-locus region SLFL1 gene. Genetics 180:483–491
Vilanova S, Badenes ML, Burgos L, Martinez-Calvo J, Llacer G, Romero C (2006) Self-compatibility of two apricot selections is associated with two pollen-part mutations of different nature. Plant Physiol 142:629
Wang Y, Wang X, McCubbin AG, Kao TH (2003) Genetic mapping and molecular characterization of the self-incompatibility (S) locus in Petunia inflata. Plant Mol Biol 53:565–580
Wu J, Gu C, Zhang SL, Zhang SJ, Wu HQ, Heng W (2009) Identification of S-haplotype-specific S-RNase and SFB alleles in native Chinese apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.). J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 84:645–652
Xue Y, Carpenter R, Dickinson HG, Coen ES (1996) Origin of allelic diversity in Antirrhinum S locus RNases. Plant Cell 8:805
Yamane H, Ikeda K, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003a) A pollen-expressed gene for a novel protein with an F-box motif that is very tightly linked to a gene for S-RNase in two species of cherry, Prunus cerasus and P. avium. Plant Cell Physiol 44:764
Yamane H, Ushijima K, Sassa H, Tao R (2003b) The use of the S haplotype-specific F-box protein gene, SFB, as a molecular marker for S-haplotypes and self-compatibility in Japanese apricot (Prunus mume). Theor Appl Genet 107:1357–1361
Zhang SL, Huang SX, Kitashiba H, Nishio T (2007) Identification of S-haplotype-specific F-box gene in Japanese plum (Prunus salicina Lindl.). Sex Plant Reprod 20:1–8
Zhou J, Wang F, Ma W, Zhang Y, Han B, Xue Y (2003) Structural and transcriptional analysis of S-locus F-box genes in Antirrhinum. Sex Plant Reprod 16:165–177
Acknowledgment
We thank American Journal Experts for helping to improve our manuscript. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31071759) and the National Department Public Benefit Research Foundation (2009030044).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Communicated by A. Abbott
Chao Gu and Jun Wu contributed to this paper equally.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Fig. S 1
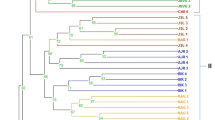
Phylogenetic trees of eight S-RNase and eight SFB genes identified in this study based on the multiple alignment of the nucleotide sequences using the neighbor-joining method. a Phylogenetic tree of four PpsS-RNase genes, b phylogenetic tree of four PpsSFB genes, c phylogenetic tree of four PspeS-RNase genes, d phylogenetic tree of four PspeSFB genes, e phylogenetic tree of four PpsS-RNase and four PspeS-RNase genes, and f phylogenetic tree of four PpsSFB and four PspeSFB genes (JPEG 90 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gu, C., Wu, J., Zhang, SJ. et al. Molecular analysis of eight SFB alleles and a new SFB-like gene in Prunus pseudocerasus and Prunus speciosa . Tree Genetics & Genomes 7, 891–902 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0382-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-011-0382-6