Abstract
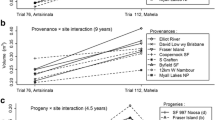
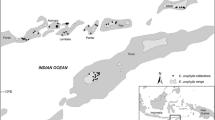
Genetic parameters for growth, stem straightness, pilodyn penetration, relative bark thickness and survival were estimated in a base-population of five open-pollinated provenance/progeny trials of Eucalyptus viminalis. The trials, located in northern, central and southern Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, comprised 148 open-pollinated families from 13 Australian native provenances and eight local Argentinean seedlots. The Australian native provenances come from a limited range of the natural distribution. Overall survival, based on the latest assessment of each trial, was 62.4%. Single-site analyses showed that statistically significant provenances differences (p < 0.05) for at least one of the studied traits in three out of the five trials analyzed. The local land race performed inconsistently in this study. The average narrow-sense individual-tree heritability estimate \( \left( {{{\hat{h}}^2}} \right) \) was 0.27 for diameter and 0.17 for total height. Values of \( {\hat{h}^2} \) also increased with age. Pilodyn penetration, assessed at only one site, was more heritable \( \left( {{{\hat{h}}^2} = 0.32} \right) \) than the average of growth traits. Estimated individual-tree heritabilities were moderate to low for stem straightness (average of 0.20) and relative bark thickness (0.16). The estimated additive genetic correlations \( \left( {{{{r}}_{{A}}}} \right) \) between diameter and height were consistently high and positive (\( {{r}_{^A}} \)average of 0.90). High additive genetic correlations were observed between growth variables and pilodyn penetration (\( {{r}_{^A}} \)average of 0.58). Relative bark thickness showed a negative correlation with diameter \( \left( {{{{r}}_{^A}} = - 0.39} \right) \) and height \( \left( {{{{r}}_{^A}} = - 0.51} \right) \). The average estimated additive genetic correlation between sites was high for diameter (0.67). The implications of all these parameter estimates for genetic improvement of E. viminalis in Argentina are discussed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnes RD (1995) The breeding seedling seed orchard in the multiple population breeding strategy. Silvae Genet 44:81–88
Boland DJ, Brooker MIH, Chippendale GM, Hall N, Hyland BPM, Johnston DA, Kleinig DA, McDonald MW, Turner JD (2006) Forest trees of Australia. CSIRO, Australia
Borralho NMG, Cotterill PP, Kanowski PJ (1993) Breeding objectives for pulp production of Eucalyptus globulus under different industrial cost structures. Can J For Res 23:648–656
Bouvet JM, Vigneron P (1995) Age trends in variances and heritabilities in Eucalyptus factorial mating designs. Silvae Genet 44:206–216
Chambers PGS, Borralho NMG (1997) Importance of survival in short-rotation tree breeding programs. Can J For Res 27:911–917
Chambers PGS, Borralho NMG, Potts BM (1996) Genetic analysis of survival in Eucalyptus globulus ssp. globulus. Silvae Genet 45:107–112
Cockerham CC (1984) Additive by additive variance with inbreeding and linkage. Genetics 108:487–500
Cornelius JP (1994) Heritabilities and additive genetic coefficients of variation in forest trees. Can J For Res 24:372–379
Costa e Silva J, Potts BM, Dutkowski GW (2006) Genotype by environment interaction for growth of Eucalyptus globulus in Australia. Tree Genet Genom 2:61–75
Costa e Silva J, Borralho NMG, Araújo JA, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM (2009) Genetic parameters for growth, wood density and pulp yield in Eucalyptus globulus. Tree Genet Genom 5:291–305
Dutkowski G, Potts BM (1999) Geographical patterns of genetic variation in Eucalyptus globulus ssp. globulus and a revised racial classification. Aust J Bot 47:237–263
Eldridge KG (1995) Eucalypt base populations for selection. In: Potts BM, Borralho NMG, Reid JB, Cromer RN, Tibbits WN, Raymond CA (eds) Eucalypt plantations: improving fibre yield and quality. Proceedings, CRCTHF-IUFRO Conference, Hobart, 19–24 Feb. CRC for Temperate Hardwood Forestry, Hobart, pp 204–207
Eldridge K, Davidson J, Hardwood C, van Wyk G (1993) Eucalyptus domestication and breeding. Oxford University Press, New York
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Longman Group Ltd, New York
Gea LD, Alliani RC (1988) Origenes de Eucalyptus viminalis Labill. para el centro y norte de la provincia de Buenos Aires. Congreso Forestal Argentino V. 2. Santiago del Estero, Argentina, pp 257–260
Gilmour AR, Thompson R, Cullis BR (1995) Average information REML, an efficient algorithm for variance parameter estimation in linear mixed models. Biometrics 51:1440–1450
Gilmour A, Dutkowski G (2004) Pedigree options in ASReml. Available at: www.animalgenome.org/bioinfo/resources/manuals/ASReml/pedigree.pdf. Accessed on: 19 Jan 2010.
Gilmour AR, Gogel BJ, Cullis BR, Thompson R (2006) ASReml User Guide Release 2.0 VSN International Ltd, Hemel Hempstead, HP1 1ES, UK. p 267
Greaves BL, Borralho NMG, Raymond CA (1997) Age-age correlations in and relationship between basic density and growth in Eucalyptus nitens. Silvae Genet 46:264–270
Griffin AR, Cotterill PP (1988) Genetic variation in growth of outcrossed, selfed and open-pollinated progenies of Eucalyptus regnans and some implications for breeding strategy. Silvae Genet 37:124–131
Hamilton MG, Potts BM (2008) Review of Eucalyptus nitens genetic parameters. New Zeal J For Sci 38:102–119
Henderson CR (1984) Applications of linear models in animal breeding. University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
Hodge GR, Volker PW, Potts BM, Owen JV (1996) A comparison of genetic information from open-pollinated and control-pollinated progeny tests in two eucalypt species. Theor Appl Genet 92:53–63
Houle D (1992) Comparing evolvability and variability of quantitative traits. Genetics 130:195–204
Kien ND, Jansson G, Harwood C, Almqvist C, Thinh HH (2008) Genetic variation in wood basic density and pilodyn penetration and their relationships with growth, stem straightness, and branch size for Eucalyptus urophylla in Northern Vietnam. New Zeal J For Sci 38:160–174
Ladiges PY, Ashton DH (1974) Variation in some central Victorian populations of Eucalyptus viminalis Labill. Aust J Bot 22:81–102
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA, USA
Lopez GA, Potts BM, Dutkowski GW, Rodriguez Traverso JM (2001) Quantitative genetics of Eucalyptus globulus: affinities of land race and native stand localities. Silvae Genet 50(5–6):244–252
Lopez GA, Potts BM, Dutkowski GW, Apiolaza LA, Gelid P (2002) Genetic variation and inter-trait correlations in Eucalyptus globulus base population trials in Argentina. Forest Gen 9:223–237
McDonald AC, Borralho NMG, Potts BM (1997) Genetic variation for growth and wood density in Eucalyptus globulus ssp. globulus in Tasmania (Australia). Silvae Genet 46:236–241
Marcó M, White T (2002) Genetic parameter estimates and genetic gains for Eucalyptus grandis and E. dunnii in Argentina. Forest Gen 9:205–215
Mendonza LA (1974) Ensayos de procedencias de Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehn. y E. viminalis Labill., en el norte de la provincia de Buenos Aires. IDIA Suplemento Forestal 8:53–60
Mendonza L, Alliani R (1983) Preliminary trial of some Eucalyptus in the north of the province of Buenos Aries. pp. 440-47. In: Colloque International Sur Les Eucalyptus Resistants Au Froid. Proceedings of the IUFRO symposium, 26–30 September 1983, Bordeaux. AFOCEL, France
Moschini RC, Conti HA, Alonso M, Rodríguez Traverso JM, Nakama V, Alfieri A (2000) Delimitación de áreas de aptitud climática para el cultivo de eucaliptos en la región pampeana. Revista SAGPyA Forestal 15:2–11
Muneri A, Raymond CA (2000) Genetic parameters and genotype-by-environment interactions for basic density, pilodyn penetration and diameter in Eucalyptus globulus. Forest Gen 7:321–332
Otegbeye GO, Kellison RC (1980) Genetics of wood and bark characteristics of Eucalyptus viminalis. Silvae Genet 29:27–31
Patterson HD, Thompson R (1971) Recovery of inter-block information when block sizes are unequal. Biometrika 58:545–554
Raymond CA (2002) Genetics of Eucalyptus wood properties. Ann For Sci 59:525–531
Resende MDV, Oliveira EB, Higa AR (1990) Utilização de índices de seleção no melhoramento de eucalipto. Boletim de Pesquisa Florestal 21:1–13
Soria F, Basurco F, Toval G, Silió L, Rodriguez MC, Toro M (1998) An application of Bayesian techniques to the genetic evaluation of growth traits in Eucalyptus globulus. Can J For Res 28:1286–1294
Tripiana V, Bourgeois M, Verhaegen D, Vigneron P, Bouvet JM (2007) Combining microsatellites, growth, and adaptive traits for managing in situ genetic resources of Eucalyptus urophylla. Can J For Res 37:773–785
Volker PW, Dean CA, Tibbits WN, Ravenwood IC (1990) Genetic parameters and gains expected from selection in Eucalyptus globulus in Tasmania. Silvae Genet 39:18–21
Volker PW, Potts BM, Borralho NMG (2008) Genetic parameters of intra- and inter-specific hybrids of Eucalyptus globulus and E. nitens. Tree Genet Genom 4:445–460
Wei X, Borralho NMG (1997) Genetic control of wood basic density and bark thickness and their relationship with growth traits of Eucalyptus urophylla in South East China. Silvae Genet 46:245–249
Wei X, Borralho NMG (1998) Genetic control of growth traits of Eucalyptus urophylla S.T. Blake in South East China. Silvae Genet 47:158–165
White TL (1996) Genetic parameter estimates and breeding value predictions: issues and implications in tree improvement programs. In: Dieters MJ, Matheson AC, Nikles DG, Harwood CE, Walker SM (eds) Proceedings of the QFRI-IUFRO Conference Tree Improvement for Sustainable Tropical Forestry. Caloundra, Queensland, Australia, pp 110–117
Acknowledgements
Trials and data collection were partially supported by the Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria and the Proyecto Forestal de Desarrollo. Thanks are due to all the landowner associated with field trials involved in this study. Particular thanks to Pedro Gelid for help in establishing, maintaining, and assessing the trials. The authors are grateful to Vicente Nakama, Adelqui Alfieri, Ricardo Moschini, and Graciela Cazenave from the Instituto Nacional de Tecnología Agropecuaria, for providing information about the soil and climate of the trial sites. Finally, we also wish to thank Alvin Yanchuk and Professor Brad Potts for their comments and suggestions and to the Associate Editor Dr. R. Burdon and two anonymous referees for their insightful comments on an earlier version of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Burdon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cappa, E.P., Pathauer, P.S. & Lopez, G.A. Provenance variation and genetic parameters of Eucalyptus viminalis in Argentina. Tree Genetics & Genomes 6, 981–994 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0307-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0307-9