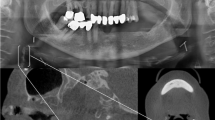
Abstract
Atherosclerosis, a progressive inflammatory disorder, may lead to coronary artery disease or stroke. The prevalence of atherosclerosis associated with mortality and morbidity is very high in developed countries, and is the underlying cause of approximately 50% of all deaths in Western societies. Panoramic radiographs (PRs) are an indispensable diagnostic tool used by dental practitioners. In the general dental population, the prevalence of positive incidental carotid artery calcifications (CACs) is reported to range from 2 to 5%. Therefore, incidental findings of CAC on PRs taken during routine dental evaluation may be useful for detecting asymptomatic patients at risk of stroke and could provide life-saving information. In this case report, we present radiological findings and follow-up of three patients with severe atherosclerosis that was incidentally detected on PRs, and discuss the role and importance of PRs in the detection of CACs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mintz BL, Hobson RW 2nd. Diagnosis and treatment of carotid artery stenosis. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2000;100:22–6.
Beneficial effects of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high-grade carotid stenosis. North American Symptomatic Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators. N Engl J Med. 1991;325:445–53.
Gokce C, Sisman Y, Sipahioglu M, Ertas ET, Akgunlu F, Unal A, et al. The prevalence of carotid artery calcification on the panoramic radiographs of end-stage renal disease patients with peritoneal dialysis: do incidental findings provide life-saving information? J Int Med Res. 2008;36:47–53.
Lusis AJ. Atherosclerosis. Nature. 2000;407:233–41.
Ross R. Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:115–26.
Prime Ministry Republic of Turkey: Turkish Statistical Institute (Turkstat) report. 2005, http://www.turkstat.gov.tr.
Yoon SJ, Yoon W, Kim OS, Lee JS, Kang BC. Diagnostic accuracy of panoramic radiography in the detection of calcified carotid artery. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2008;37:104–8.
Bayram B, Uckan S, Acikgoz A, Müderrisoglu H, Aydinalp A. Digital panoramic radiography: a reliable method to diagnose carotid artery atheromas? Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006;35:266–70.
Friedlander AH, Lande A. Panoramic radiographic identification of carotid arterial plaques. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1981;52:102–4.
Cohen SN, Friedlander AH, Jolly DA, Date L. Carotid calcification on panoramic radiographs: an important marker for vascular risk. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:510–4.
Friedlander AH, Federico M, Yueh R, Norman KM, Chin EE. Radiation-associated carotid artery atherosclerosis: case report and review of contemporaneous literature. Spec Care Dentist. 2009;29:75–9. Review.
Dorresteijn LD, Kappelle AC, Boogerd W, Klokman WJ, Balm AJ, Keus RB, et al. Increased risk of ischemic stroke after radiotherapy on the neck in patients younger than 60 years. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:282–8.
Tsai CF, Jeng JS, Lu CJ, Yip PK. Clinical and ultrasonographic manifestations in major causes of common carotid artery occlusion. J Neuroimaging. 2005;15:50–6.
Ohba T, Takata Y, Ansai T, Morimoto Y, Tanaka T, Kito S, et al. Evaluation of calcified carotid artery atheromas detected by panoramic radiograph among 80-year-olds. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2003;96:647–50.
Adachi B. Das arteriensystem der Japaner. Bd. 1. Kyoto: Maruzen; 1928. p. 47–57.
Romano-Sousa CM, Krejci L, Medeiros FM, Graciosa-Filho RG, Martins MF, Guedes VN, Fenyo-Pereira M. Diagnostic agreement between panoramic radiographs and color Doppler images of carotid atheroma. J Appl Oral Sci. 2009;17:45–8.
Lewis DA, Brooks SL. Carotid artery calcification in a general dental population: a retrospective study of panoramic radiographs. Gen Dent. 1999;47:98–103.
Almog DM. Utility of panoramic radiographs in detecting cervical calcified carotid atheroma (Letter to editor). Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;104:451–2.
Sisman Y, Ertas ET, Gokce C, Menku A, Ulker M, Akgunlu F. The prevalence of carotid artery calcification on the panoramic radiographs in Cappadocia Region population. Eur J Dent. 2007;1:132–8.
Friedlander AH, Freymiller EG. Detection of radiation-accelerated atherosclerosis of the carotid artery by panoramic radiography. A new opportunity for dentists. J Am Dent Assoc. 2003;134:1361–5.
Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstall PJ, Hoffman A, Grobbee DE. Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction. Circulation. 1997;96:1432–7.
Biller J, Feinberg WM, Castaldo JE, Whittemore AD, Harbaugh RE, Dempsey RJ. Guidelines for carotidendarterectomy: a statement for healthcare professionals from a special writing group of the Stroke Council, American Heart Association. Circulation. 1998;97:501–9.
Friedlander AH, Garrett NR, Chin EE, Baker JD. Ultrasonographic confirmation of carotid artery atheromas diagnosed via panoramic radiography. J Am Dent Assoc. 2005;136:635–40. quiz 682–3.
Madden RP, Hodges JS, Salmen CW, Rindal DB, Tunio J, Michalowicz BS, et al. Utility of panoramic radiographs in detecting cervical calcified carotid atheroma. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2007;103:543–8.
Almog DM, Horev T, Illig KA, Green RM, Carter LC. Correlating carotid artery stenosis detected by panoramic radiography with clinically relevant carotid artery stenosis determined by duplex ultrasound. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2002;94:768–73.
Almog DM, Illig KA, Khin M, Green RM. Unrecognized carotid artery stenosis discovered by calcifications on a panoramic radiograph. J Am Dent Assoc. 2000;131:1593–7.
Moneta GL, Edwards JM, Papanicolaou G, Hatsukami T, Taylor LM Jr, Strandness DE Jr, et al. Screening for asymptomatic internal carotid artery stenosis: duplex criteria for discriminating 60 percent to 90 percent stenosis. J Vasc Surg. 1995;21:989–94.
Neale ML, Chambers JL, Kelly AT, Connard S, Lawton MA, Roche J, et al. Reappraisal of duplex criteria to assess significant carotid stenosis with special reference to reports from the North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial and the European Carotid Surgery Trial. J Vasc Surg. 1994;20:642–9.
Erdoes LS, Marek JM, Mills JL, Berman SS, Whitehill T, Hunter GC, et al. The relative contributions of carotid duplex scanning, magnetic resonance angiography, and cerebral angiography to clinical decision making: a prospective study in patients with carotid occlusive disease. J Vasc Surg. 1996;23:950–6.
Py MO, André C, Azevedo FS, Domingues RC, Salomão RF. Internal carotid artery stenosis: comparison of duplex scan and magnetic resonance angiography with digital subtraction angiography. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2001;59:665–71.
Ringelstein EB. Skepticism toward carotid ultrasonography: a virtue, an attitude, or fanaticism? Stroke. 1995;26:1743–6.
Droste DW, Jürgens R, Nabavi DG, Schuierer G, Weber S, Ringelstein EB. Echocontrast-enhanced ultrasound of extracranial internal carotid artery high-grade stenosis and occlusion. Stroke. 1999;30:2302–6.
Culebras A, Kase CS, Masdeu JC, Fox AJ, Bryan RN, Grossman CB, et al. Practice guidelines for the use of imaging in transient ischemic attacks and acute stroke. Stroke. 1997;28:1480–97.
Riles TS, Eidelman EM, Litt AW, Pinto RS, Oldford F, Schwartzenberg GWST. Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography, conventional angiography, and duplex scanning. Stroke. 1992;23:341–6.
Sameshima T, Futami S, Morita Y, Yokogami K, Miyahara S, Sameshima Y, et al. Clinical usefulness of and problems with three-dimensional CT angiography for the evaluation of arteriosclerotic stenosis of the carotid artery: comparison with conventional angiography, MRA, and ultrasound sonography. Surg Neurol. 1999;51:301–8. discussion 308–9.
Wessels T, Harrer JU, Stetter S, Mull M, Klötzsch C. Three-dimensional assessment of extracranial Doppler sonography in carotid artery stenosis compared with digital subtraction angiography. Stroke. 2004;35:1847–51.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarım Ertas, E., Mavili, E., Sisman, Y. et al. Incidental findings of carotid artery stenosis detected by calcifications on panoramic radiographs: report of three cases. Oral Radiol 26, 116–121 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0047-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-010-0047-4