Abstract
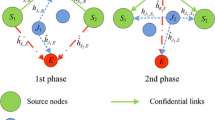
Physical layer security is an efficient technique to realize security in wireless network without relying on conventional cryptographic techniques. In cooperative networks with secrecy constraints, joint relay and jammer selection is a promising approach for improving the security of wireless communications. We need to apply more techniques in order to achieve more effective security in contrast to the mentioned method. In this paper, we propose three techniques to increase the secrecy as follows: Firstly, we introduce a new criterion which decreases the rate at the eavesdroppers. Next, a new relay selection schemes are proposed, where two of the available relays are selected for data transmission. Therefore, the secrecy rate is increased considerably. Finally, we propose a sub-optimal power allocation solution for jammer nodes. Sub-optimal power of the jammer nodes vary according to the type of scenario, location of the eavesdroppers, and the destination. The sub-optimal power allocation to the jammer nodes causes more eavesdroppers confusion. As a result, the total secrecy rate is increased. Simulation and analytical results demonstrate the performance improvement of the proposed techniques.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silva, E., Dos Santos, A., Albini, L. C. P., & Lima, M. N. (2008). Identity-based key management in mobile ad hoc networks: techniques and applications. IEEE Wireless Communications, 15(5), 46–52.
Barros, J., & Rodrigues, M. R. (2006). Secrecy capacity of wireless channels. In 2006 IEEE International Symposium on Information Theory (pp. 356–360). IEEE.
Bloch, M., Barros, J., Rodrigues, M. R., & McLaughlin, S. W. (2008). Wireless information-theoretic security. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(6), 2515–2534.
Liu, R., Maric, I., Spasojevic, P., & Yates, R. D. (2008). Discrete memoryless interference and broadcast channels with confidential messages: Secrecy rate regions. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(6), 2493–2507.
Csiszár, I., & Korner, J. (1978). Broadcast channels with confidential messages. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 24(3), 339–348.
Wyner, A. D. (1975). The wire-tap channel. Bell Labs Technical Journal, 54(8), 1355–1387.
Vicario, J. L., Bel, A., Lopez-Salcedo, J. A., & Seco, G. (2009). Opportunistic relay selection with outdated CSI: Outage probability and diversity analysis. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(6), 2872–2876.
Zhang, W., Duan, D., & Yang, L. (2009). Relay selection from a battery energy efficiency perspective. In Military Communications Conference, MILCOM 2009, IEEE (pp. 1–7). IEEE.
Seyfi, M., Muhaidat, S., & Liang, J. (2011). Performance analysis of relay selection with feedback delay and channel estimation errors. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 18(1), 67–70.
Krikidis, I., Thompson, J., McLaughlin, S., & Goertz, N. (2008). Amplify-and-forward with partial relay selection. IEEE Communications Letters, 12(4), 235–237.
Bletsas, A., Shin, H., & Win, M. Z. (2007). Outage analysis for co-operative communication with multiple amplify-and-forward relays. Electronics Letters, 43(6), 353–355.
Kim, J., Ikhlef, A., & Schober, R. (2012). Combined relay selection and cooperative beamforming for physical layer security. Journal of Communications and Networks, 14(4), 364–373.
Liu, Y., & Petropulu, A. P. (2012). Relay selection and scaling law in destination assisted physical layer secrecy systems. In Statistical Signal Processing Workshop (SSP), IEEE (pp. 381–384). IEEE.
Wang, L., Ke, T., Song, M., Wei, Y., & Teng, Y. (2011). Research on secrecy capacity oriented relay selection for mobile cooperative networks. In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing and Intelligence Systems (CCIS) (pp. 443–447). IEEE.
Cai, C., Cai, Y., & Yang, W. (2011). Secrecy rates for relay selection in OFDMA networks. In CMC (pp. 158–160).
Yan, S., Mugen, P., Wenbo, W., Dong, L., & Manzoor, A. (2012). Relay self-selection for secure cooperative in amplify-and-forward netowrks. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Communications and Networking in China (CHINACOM’12) (pp. 581–585).
Sakran, H., Shokair, M., Nasr, O., El-Rabaie, S., & El-Azm, A. A. (2012). Proposed relay selection scheme for physical layer security in cognitive radio networks. IET Communications, 6(16), 2676–2687.
Luo, S., Godrich, H., Petropulu, A., & Poor, H. V. (2011). A knapsack problem formulation for relay selection in secure cooperative wireless communication. In 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) (pp. 2512–2515). IEEE.
Bassily, R., & Ulukus, S. (2013). Deaf cooperation and relay selection strategies for secure communication in multiple relay networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 61(6), 1544–1554.
Krikidis, I., Thompson, J. S., & McLaughlin, S. (2009). Relay selection for secure cooperative networks with jamming. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 8(10), 5003–5011.
Krikidis, I. (2010). Opportunistic relay selection for cooperative networks with secrecy constraints. IET Communications, 4(15), 1787–1791.
Al-nahari, A. Y., Krikidis, I., Ibrahim, A. S., Dessouky, M. I., & Abd El-Samie, F. E. (2014). Relaying techniques for enhancing the physical layer secrecy in cooperative networks with multiple eavesdroppers. Transactions on Emerging Telecommunications Technologies, 25(4), 445–460.
Li, J., Petropulu, A. P., & Weber, S. (2010). Optimal cooperative relaying schemes for improving wireless physical layer security. arXiv preprint arXiv:1001.1389.
Lai, L., & El Gamal, H. (2008). The relay–eavesdropper channel: Cooperation for secrecy. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 54(9), 4005–4019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saeidi-Khabisi, FS., Vakili, V.T. & Abbasi-Moghadam, D. Improving the Physical Layer Security in Cooperative Networks with Multiple Eavesdroppers. Wireless Pers Commun 95, 3295–3320 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-3998-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-3998-5