Abstract
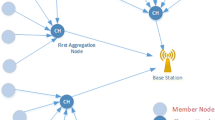
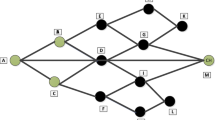
In Wireless Sensor Networks (WSN), one of the major issues is to maximize the network lifetime. Since all sensor nodes directly send the data to the Base station, the energy requirement is very high. This reduces the lifetime of the network. One of the solutions is to partition the network into various clusters which avoids direct communication. In this paper we propose an Energy efficient Cluster Based Data Aggregation (ECBDA) scheme for sensor networks. In this algorithm, Cluster members send the data only to its corresponding local cluster head, there by communication overhead is reduced. Data generated from neighboring sensors are often redundant and highly correlated. So the cluster head performs data aggregation to reduce the redundant packet transmission. In our approach, clusters are formed in a non-periodic manner to avoid unnecessary setup message transmissions. Re-clustering is performed only when CH needs to balance the load among the nodes. The simulation results show that our approach effectively reduces the energy consumption and hence the network lifetime is also increased.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dressler, F. (2007). Self-organization in sensor and actor, networks (pp. 185–202). New York: Wiley.
Rajagopalan, R., & Pramod, K. V. (2006). Data aggregation techniques in sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 8(4), 48–63.
Abbasi, A. A., & Younis, M. (2007). A survey on clustering algorithms for wireless sensor networks. Computer Communications, 30(14–15), 2826–2841.
Tarng, W., Ou, K. L., Huang, K. J., Deng, L. Z., & Lin, H. W. (2011). Applying cluster merging and dynamic routing mechanisms to extend the lifetime of wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 3(1), 8–16.
Hussaini, M., Bello-Salau, H., Salami, A. F., Anwar, F., Abdalla, A. H., & Islam, M. R. (2012). Enhanced clustering routing protocol for power-efficient gathering in wireless sensor network. International Journal of Communication Networks and Information Security (IJCNIS), 4(1), 18–28.
Karl, H., & Willig, A. (2007). Protocols and architectures for wireless sensor networks. New York: Wiley.
Bajaber, F., & Awan, I. (2008). Dynamic/static clustering protocol for wireless sensor network. Second UKSIM European symposium on computer modeling and simulation (pp. 524–529)
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol for wireless microsensor, networks. In Proceedings of the 33rd international conference on system sciences (HICSS’00) (pp 1–10).
Heinzelman, W., Chandrakasan, A., & Balakrishnan, H. (2002). An application-specific protocol architecture for wireless microsensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 1(4), 660–669.
Yoon, S., & Shahabi, C. (2007). The clustered AGgregation (CAG) technique leveraging spatial and temporal correlations in wireless sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks (TOSN), 3(1), Article 3.
Chang, R.-S., & Kuo, C.-J. (2006). An energy efficient routing mechanism for wireless sensor networks. In 20th international conference on advanced information networking and applications (Vol. 2 (AINA’06), pp. 308–312).
Sivrikaya, F., & Yener, B. (2004). Time synchronization in sensor networks: A survey. IEEE Network, 18(4), 45–50.
Wu, Y.-C., Chaudhari, Q. M., & Serpedin, E. (2011). Clock synchronization of wireless sensor networks. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 28(1), 124–138.
Kim, H., Kim, D., & Yoo, S. (2006). Cluster-based hierarchical time synchronization for multi-hop wireless sensor networks. In 20th international conference on advanced information networking and applications (Vol. 2, pp. 318–322).
Jabbarifar, M., Sendi, A. S., Pedram, H., Dehghan, M., & Dagenais, M. R. (2010). L-SYNC: Larger degree clustering based time-synchronisation for wireless sensor network. SERA, 2010, 171–178.
Jabbarifar, M., Sendi, A. S., Sadighian, A., Jivan, N. E., & Dagenais, M. (2010). A reliable and efficient time synchronization protocol for heterogeneous wireless sensor network. Wireless sensor networks, 2(12), 910–918.
Hua, M., Ki Lau, J., & Pei, K. Wu. (2009). Continuous K-means monitoring with low reporting cost in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(12), 1679–1691.
Hui Li, X., & Ling Fang, K. (2009). A clustering algorithm based on K-means for wireless indoor monitoring system. International Conference on Information Technology and Computer Science, 1, 488–492.
Datta, S., Giannella, C. R., & Kargupta, H. (2009). Approximate distributed K-means clustering over a peer-to-peer network. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 21(10), 1372–1388.
Patel, R. B., Aseri, T. C., & Kumar, D. (2009). EEHC: Energy efficient heterogeneous clustered scheme for wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Computer Communications, Elsevier, 32(4), 662–667.
Younis, O., & Fahmy, S. (2004). HEED: A hybrid, energy-efficient, distributed clustering approach for ad hoc sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 3(4), 366–379.
Ishmanov, F., & Kim, S. W. (2009). Distributed clustering algorithm with load balancing in wireless sensor networks. WRI World Congress on Computer Science and Information Engineering, CSIE 2009 (Vol. 1, pp. 19–23).
Min, X., Wei-ren, S., Chang-jiang, J., & Ying, Z. (2010). Energy efficient clustering algorithm for maximizing lifetime of wireless sensor networks. AEU-International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 64(4), 289–298.
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., Rivest, R. L., & Stein, C. Introduction to algorithms (2nd ed. pp. 658–664). The MIT Press: Cambridge.
Alrajeh, N. A., Khan, S., Lloret, J., & Loo, J. (2013). Secure routing protocol using cross-layer design and energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2013, 11 pp. Article ID 374796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Siva Ranjani, S., Radha Krishnan, S., Thangaraj, C. et al. Achieving Energy Conservation by Cluster Based Data Aggregation in Wireless Sensor Networks. Wireless Pers Commun 73, 731–751 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1213-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-013-1213-x