Abstract
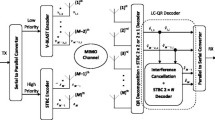
Among popular multi-transmit and multi-receive antennas techniques, the VBLAST (Vertical Bell Laboratories Layered Space-Time) architecture has been shown to be a good solution for wireless communications applications that require the transmission of data at high rates. Recently, the application of efficient error correction coding schemes such as low density parity-check (LDPC) codes to systems with multi-transmit and multi-receive antennas has shown to significantly improve bit error rate performance. Although irregular LDPC codes with non-structure are quite popular due to the ease of constructing the parity check matrices and their very good error rate performance, the complexity of the encoder is high. Simple implementation of both encoder and decoder can be an asset in wireless communications applications. In this paper, we study the application of Euclidean geometry LDPC codes to the VBLAST system. We assess system performance using different code parameters and different numbers of antennas via Monte-Carlo simulation and show that the combination of Euclidean geometry LDPC codes and VBLAST can significantly improve bit error rate performance. We also show that interleaving data is necessary to improve performance of LDPC codes when a higher number of antennas is, used in order to mitigate the effect of error propagation. The simplicity of the implementation of both encoder and decoder makes Euclidean geometry LDPC codes with VBLAST system attractive and suitable for practical applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Shannon C.E., Weaver W. (1949) The mathematical theory of communication. University of Illinois Press, Urbana, Illinois
Gallager R.G. (1963) Low density parity check codes. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
MacKay D.J.C. (1999) Good error-correcting codes based on very sparse matrices. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 45: 399–431. doi:10.1109/18.748992
Kou Y., Lin S., Fossorier M.P.C. (2001) Low -density parity-check codes based on finite geometries: a rediscovery and new results. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 47: 2711–2736. doi:10.1109/18.959255
Richardson T.J., Shokrollahi A., Urbanke R. (2001) Design of capacity-approaching low-density parity-check codes. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory 47: 619–637
Chung S.-Y., Forney J.G.D., Richardson T., Urbanke R. (2001) On the design of low-density parity-check codes within 0.0045 dB of the Shannon limit. IEEE Communications Letters 5: 58–60. doi:10.1109/4234.905935
Foschini G.J., Gans M.J. (1998) On limits of wireless communication in a fading environment when using multiple antennas. Wireless Personal Communications 6(3): 311–335. doi:10.1023/A:1008889222784
Telatar, E. (2001). Capacity of multi-antenna Gaussian channels. In Proceedings on 2001 IEEE International Symposium Information Theory, June 24–29, 2001.
Hottinen A., Tirkkonen O., Wichman R. (2003) Multi-antenna transceiver techniques for 3G and Beyond. Wiley, UK
Wolniansky, P. W., Foschini, G. J., Golden, G. D., & Valenzuela, R. A. (1998). V-BLAST : An architecture for realizing very high data rates over the rich-scattering wireless channel. URSI International Symposium on Signals, Systems and Electronics (pp. 295–300), 1998.
Noh, M., Kim, N., Park, H., & Lee, H. (2004). A variable rate LDPC coded V-BLAST system. In Proceeding of VTC2004 (Vol. 4, pp. 2540–2543), Sept 26–29, 2004.
Noh, M., Kim, N., Park, H., & Lee, H. (2005). A variable rate LDPC coded V-BLAST system using the MMSE QR decomposition. In Proceeding of the VTC2005 (Vol. 3, pp. 1672–1675), May 30–June 1, 2005.
Peterson W.W., Weldon E.J. Jr. (1972) Error-correcting codes, 2nd ed. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Kasami T., Lin S., Peterson W.W. (1968) Polynomial codes. IEEE Transcations Information Theory IT- 14: 807–814. doi:10.1109/TIT.1968.1054226
Proakis J.G. (2000) Digital communications, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, NY
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poocharoen, P., Magaña, M.E. Euclidean Geometry LDPC-VBLAST System Design and Performance Evaluation. Wireless Pers Commun 50, 401–416 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-008-9612-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-008-9612-0