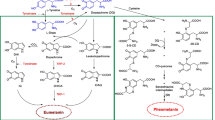
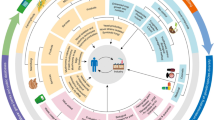
Abstract
Melanin is a secondary metabolite composed of complex heterogeneous polymers. Fungal melanin is considered to be a sustainable and biodegradable natural pigment and has a variety of functional properties and biological activities. On one hand, due to its own specific properties it can play the role of antioxidant, anti-radiation, adsorption, and photoprotection. On the other hand, it has good biological activities such as hepatoprotective effect, hypolipidemic effect and anti-cancer. Therefore, it is widely used in various fields of daily life, including dyeing, food, biomedical and commercial industry. It is conducive to environmental protection and human health. However, the insolubility of fungal melanin in water, acids and organic solvents has been an obstacle to its commercial applications. Thus, the chemical modification methods of fungal melanin are summarized to increase its solubility and expand the application fields. Although fungal melanin has been used in many industries, as the structure and function of fungal melanin and modified melanin are further studied, more functional properties and bioactivities are expected to be discovered for a wide range of applications in the future.
Graphic abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida-Paes R, Borba-Santos LP, Rozental S, Marco S, Zancopé-Oliveira RM, da Cunha MML (2017) Melanin biosynthesis in pathogenic species of Sporothrix. Fungal Biol Rev 31:50–59. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2016.09.001
Ban Y, Tang M, Chen H, Xu Z, Zhang H, Yang Y (2012) The response of dark septate endophytes (DSE) to heavy metals in pure culture. PLoS ONE 7:e47968. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0047968
Bayram S (2022) A comparative characterization study between fungal and bacterial eumelanin pigments. Indian J Microbiol doi. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-022-01012-1
Burmasova MA, Utebaeva AA, Sysoeva EV, Sysoeva MA (2019) Melanins of Inonotus obliquus: bifidogenic and antioxidant properties. Biomolecules 9:248. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9060248
Camacho E, Vij R, Chrissian C, Prados-Rosales R, Gil D, O’Meally RN, Cordero RJB, Cole RN, McCaffery JM, Stark RE, Casadevall A (2019) The structural unit of melanin in the cell wall of the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans. J Biol Chem 294:10471–10489. doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.008684
Cao W, Zhou X, McCallum NC, Hu Z, Ni QZ, Kapoor U, Heil CM, Cay KS, Zand T, Mantanona AJ, Jayaraman A, Dhinojwala A, Deheyn DD, Shawkey MD, Burkart MD, Rinehart JD, Gianneschi NC (2021) Unraveling the structure and function of melanin through synthesis. J Am Chem Soc 143:2622–2637. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c12322
Casadevall A, Cordero RJB, Bryan R, Nosanchuk J, Dadachova E, Heitman J, Gow NAR (2017) Melanin, radiation, and energy transduction in fungi. Microbiol Spectr 5:5.2.05. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/microbiolspec.FUNK-0037-2016
Chatragadda R, Dufossé L (2021) Ecological and biotechnological aspects of pigmented microbes: a way forward in development of food and pharmaceutical grade pigments. Microorganisms 9:637. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms9030637
Chen Y, Xu M, Wang X, Shan X, Ji L, Zhang Y (2021) Preparation of wood ear medicinal mushroom, Auricularia auricula-judae (Agaricomycetes), melanin and its antioxidant properties: evaluation in vitro and in vivo. Int J Med Mushrooms 23:89–100. doi: https://doi.org/10.1615/IntJMedMushrooms.v23.i6.90
Chornenka N, Raetska Y, Grebinyk D, Dranitsina A, Savchuk O, Beregova T, Ostapchenko L (2018) Protective antioxidant effect of melanin against chemical burn-induced esophageal injury. Biomed Res Ther 5:2712–2718. doi: https://doi.org/10.15419/bmrat.v5i10.484
Chrissian C, Camacho E, Fu MS, Prados-Rosales R, Chatterjee S, Cordero RJB, Lodge JK, Casadevall A, Stark RE (2020) Melanin deposition in two Cryptococcus species depends on cell-wall composition and flexibility. J Biol Chem 295:1815–1828. doi: https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA119.011949
Coelho E, Reis TA, Cotrim M, Mullan TK, Corrêa B (2020) Resistant fungi isolated from contaminated uranium mine in Brazil shows a high capacity to uptake uranium from water. Chemosphere 248:126068. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126068
Cohrs KC, Simon A, Viaud M, Schumacher J (2016) Light governs asexual differentiation in the grey mould fungus Botrytis cinerea via the putative transcription factor BcLTF2. Environ Microbiol 18:4068–4086. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13431
Cordero RJB, Casadevall A (2017) Functions of fungal melanin beyond virulence. Fungal Biol Rev 31:99–112. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbr.2016.12.003
Cordero RJB, Casadevall A (2020) Melanin. Curr Biol 30:142–143. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2019.12.042
Cordero RJB, Vij R, Casadevall A (2017) Microbial melanins for radioprotection and bioremediation. Microb Biotechnol 10:1186–1190. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12807
Cordero RJB (2017) Melanin for space travel radioprotection. Environ Microbiol 19:2529–2532. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13753
Cunha MM, Franzen AJ, Seabra SH, Herbst MH, Vugman NV, Borba LP, de Souza W, Rozental S (2010) Melanin in Fonsecaea pedrosoi: a trap for oxidative radicals. BMC Microbiol 10:80. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2180-10-80
Cuzzubbo S, Carpentier AF (2021) Applications of melanin and melanin-like nanoparticles in cancer therapy: a review of recent advances. Cancers 13:1463. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13061463
D’Mello SAN, Finlay GJ, Baguley BC, Askarian-Amiri ME (2016) Signaling pathways in melanogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 17:1144. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17071144
Dadachova E, Casadevall A (2008) Ionizing radiation: how fungi cope, adapt, and exploit with the help of melanin. Curr Opin Microbiol 11:525–531. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2008.09.013
DeSouza RA, Kamat NM, Nadkarni VS (2018) Purification and characterisation of a sulphur rich melanin from edible mushroom Termitomyces albuminosus Heim. Mycology 9:296–306. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/21501203
d’Ischia M, Wakamatsu K, Napolitano A, Briganti S, Garcia-Borron JC, Kovacs D, Meredith P, Pezzella A, Picardo M, Sarna T, Simon JD, Ito S (2013) Melanins and melanogenesis: methods, standards, protocols. Pigm Cell Melanoma Res 26:616–633. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/pcmr.12121
Eisenman HC, Casadevall A (2012) Synthesis and assembly of fungal melanin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:931–940. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3777-2
Eisenman HC, Greer EM, McGrail CW (2020) The role of melanins in melanotic fungi for pathogenesis and environmental survival. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:4247–4257. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-020-10532-z
El-Naggar NEA, Saber WIA (2022) Natural melanin: current trends, and future approaches, with especial reference to microbial source. Polymers 14:1339. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym14071339
Fernandes C, Mota M, Barros L, Dias MI, Ferreira ICFR, Piedade AP, Casadevall A, Gonçalves T (2021) Pyomelanin synthesis in Alternaria alternata inhibits DHN-melanin synthesis and decreases cell wall chitin content and thickness. Front Microbiol 12:691433. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2021.691433
Fogarty RV, Tobin JM (1996) Fungal melanins and their interactions with metals Enzyme and Microb Tech19: 311–317. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0141-0229(96)00002-6
Fonseca CS, da Silva NR, Ballesteros LF, Basto B, Abrunhosa L, Teixeira JA, Silvério SC (2022) Penicillium brevicompactum as a novel source of natural pigments with potential for food applications. Food Bioproc Tech 132:188–199. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fbp.2022.01.007
Gadd GM, de Rome L (1988) Biosorption of copper by fungal melanin. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:610–617. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF0026099
Geib E, Gressler M, Viediernikova I, Hillmann F, Jacobsen ID, Nietzsche S, Hertweck C, Brock MA (2016) Non-canonical melanin biosynthesis pathway protects Aspergillus terreus conidia from environmental stress. Cell Chem Biol 23:587–597. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2016.03.014
Ghadge V, Kumar P, Maity TK, Prasad K, Shinde PB (2022) Facile alternative sustainable process for the selective extraction of microbial melanin. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:2681–2688. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.1c07135
Henson JM, Butler MJ, Day AW (1999) The dark side of the mycelium: melanins of phytopathogenic fungi. Annu Rev Phytopathol 37:447–471. doi: https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.phyto.37.1.447
Hou R, Liu X, Wu X, Zheng M, Fu J (2021) Therapeutic effect of natural melanin from edible fungus Auricularia auricula on alcohol-induced liver damage in vitro and in vivo. Food Sci Hum Well 10:514–522. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fshw.2021.04.014
Howell RC, Schweitzer AD, Casadevall A, Dadachova EA (2008) Chemosorption of radiometals of interest to nuclear medicine by synthetic melanins. Nucl Med Biol 35:353–357. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2007.12.006
Ito S, Wakamatsu K, Sarna T (2018) Photodegradation of eumelanin and pheomelanin and its pathophysiological implications. Photochem Photobiol 94:409–420. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12837
Jacobson ES, Hove E, Emery HS (1995) Antioxidant function of melanin in black fungi. Infect Immun 63:4944–4945. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/iai.63.12.4944-4945.1995
Jeon JR, Le TT, Chang YS (2016) Dihydroxynaphthalene-based mimicry of fungal melanogenesis for multifunctional coatings. Microb Biotechnol 9:305–315. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-7915.12347
Jia SL, Chi Z, Chen L, Liu GL, Hu Z, Chi ZM (2021) Molecular evolution and regulation of DHN melanin-related gene clusters are closely related to adaptation of different melanin-producing fungi. Genomics 113:1962–1975. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2021.04.034
Kalra R, Conlan XA, Goel M (2020) Fungi as a potential source of pigments: harnessing filamentous fungi. Front Chem 8:369. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.00369
Koehler A, Heidrich D, Pagani DM, Corbellini VA, Scroferneker ML (2021) Melanin and chromoblastomycosis agents: characterization, functions, and relation with antifungals. J Basic Microbiol 61:203–211. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/jobm.202000664
Kothamasi D, Wannijn J, Van Hees M, Nauts R, Van Gompel A, Vanhoudt N, Vandenhove H (2019) Exposure to ionizing radiation affects the growth of ectomycorrhizal fungi and induces increased melanin production and increased capacities of reactive oxygen species scavenging enzymes. J Environ Radioact 197:16–22. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvrad.2018.11.005
Kumari S, Tien Guan Thng S, Kumar Verma N, Gautam HK (2018) Melanogenesis inhibitors. Acta Derm Venereol 98:924–931. doi: https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-3002
Lee D, Jang EH, Lee M, Kim SW, Lee Y, Lee KT, Bahn YS, Lorenz M (2019) Unraveling melanin biosynthesis and signaling networks in Cryptococcus neoformans. mBio 10:e02267–e02219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.02267-19
Lee JH, Hyun CK (2014) Insulin-sensitizing and beneficial lipid-metabolic effects of the water-soluble melanin complex extracted from Inonotus obliquus. Phytother Res 28:1320–1328. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.5131
Li B, Li W, Chen XH, Jiang M, Dong MS (2012) In vitro antibiofilm activity of the melanin from Auricularia auricula, an edible jelly mushroom. Ann Microbiol 62:1523–1530. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13213-011-0406-3
Li L, Shi F, Li J, Huang Q, Xu C, Yang L, Yang Q, Shaikh F, Ye M (2017) Immunoregulatory effect assessment of a novel melanin and its carboxymethyl derivative. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 27:1831–1834. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2017.02.046
Li L, Yuan H, Li S, Ye M (2016) Molecular modifications of melanin from Lachnum and their antioxidative activities. Hefei University of Technology 39:404–409. doi: https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1003-5060.2016.03.022 (in Chinese with an English Abstract)
Li S, Yang L, Li J, Chen T, Ye M (2019) Structure, molecular modification, and anti-radiation activity of melanin from Lachnum YM156 on ultraviolet b-induced injury in mice. Appl Biochem 188:555–567. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2898-9
Lim W, Konings M, Parel F, Eadie K, Strepis N, Fahal A, Verbon A, van de Sande WWJ (2022) Inhibiting DHN- and DOPA-melanin biosynthesis pathway increased the therapeutic value of itraconazole in Madurella mycetomatis infected Galleria mellonella. Med Mycol 60:2. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/mmy/myac003
Lin L, Xu J (2020) Fungal pigments and their roles associated with human health. J Fungi 6:280. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6040280
Lin Y, Chen H, Cao Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Guo W, Lv X, Rao P, Ni L, Liu P (2021) Auricularia auricula melanin protects against alcoholic liver injury and modulates intestinal microbiota composition in mice exposed to alcohol intake. Foods 10:2436. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10102436
Liu D, Sun X, Yan B, Ma A (2022) Alternative oxidase is involved in oxidative stress resistance and melanin synthesis in Annulohypoxylon stygium, a companion fungus of Tremella fuciformis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 115:365–374. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-021-01705-5
Łopusiewicz Ł, Jędra F, Mizielińska M (2018) New poly (lactic acid) active packaging composite films incorporated with fungal melanin. Polymers 10:386. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10040386
Łopusiewicz Ł, Kwiatkowski P, Drozłowska E, Trocer P, Kostek M, Śliwiński M, Polak-Śliwińska M, Kowalczyk E, Sienkiewicz M (2021) Preparation and characterization of carboxymethyl cellulose-based bioactive composite films modified with fungal melanin and carvacrol. Polymers 13:499. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13040499
Lu M, Yu M, Shi T (2020) Optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of melanin and its hypoglycemic activities from Sporisorium reilianum. J Food Process Preserv 44:e14707. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ifset.2010.07.002
Lu Y, Ye M, Song S, Li L, Shaikh F, Li J (2014) Isolation, purification, and anti-aging activity of melanin from Lachnum singerianum. Appl Biochem Biotech 174:762–771. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1110-0
Luo Q, Feng H, Sun S (2019) Effects of different conditions on mycelial growth and melanin formation of Hypoxylon sp. North Hortic 16:130–135. doi:https://doi.org/10.11937/bfyy.20190533(in Chinese with an English abstract)
Ma S, Cao K, Liu N, Meng C, Cao Z, Dai D, Jia H, Zang J, Li Z, Hao Z, Gu S, Dong J (2017) The StLAC2 gene is required for cell wall integrity, DHN-melanin synthesis and the pathogenicity of Setosphaeria turcica. Fungal Biol 121:589–601. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funbio.2017.04.003
Manap A, Lum Y, Ong L, Tang Y, Gew L, Chia A (2021) Perspective approaches on melanogenesis inhibition. Dermatologica Sin 39:1–12. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/ds.ds_46_20
Maranduca MA, Branisteanu D, Serban DN, Branisteanu DC, Stoleriu G, Manolache N, Serban IL (2019) Synthesis and physiological implications of melanic pigments (Review). Oncol Lett 17:4183–4187. doi: https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2019.10071
Marcovici I, Coricovac D, Pinzaru I, Macasoi IG, Popescu R, Chioibas R, Zupko I, Dehelean CA (2022) Melanin and melanin-functionalized nanoparticles as promising tools in cancer research-a review. Cancers 14:1838. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071838
Mavridi-Printezi A, Guernelli M, Menichetti A, Montalti M (2020) Bio-applications of multifunctional melanin nanoparticles: from nanomedicine to nanocosmetics. Nanomaterials 10:2276. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano10112276
McCallum NC, Son FA, Clemons TD, Weigand SJ, Gnanasekaran K, Battistella C, Barnes BE, Abeyratne-Perera H, Siwicka ZE, Forman CJ, Zhou X, Moore MH, Savin DA, Stupp SI, Wang Z, Vora GJ, Johnson BJ, Farha OK, Gianneschi NC (2021) Allomelanin: A Biopolymer of Intrinsic Microporosity. J Am Chem Soc 143:4005–4016. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c00748
Mesías M, Delgado-Andrade C (2017) Melanoidins as a potential functional food ingredient. Curr Opin Food Sci 14:37–42. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cofs.2017.01.007
Nosanchuk JD, Stark RE, Casadevall A (2015) Fungal melanin: what do we know about structure? Front Microbiol 6:1463. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb
Oh JJ, Kim JY, Kim YJ, Kim S, Kim GH (2021a) Utilization of extracellular fungal melanin as an eco-friendly biosorbent for treatment of metal-contaminated effluents. Chemosphere 272:129884. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021a.129884
Oh JJ, Kim JY, Son SH, Jung WJ, Kim DH, Seo JW, Kim GH (2021b) Fungal melanin as a biocompatible broad-spectrum sunscreen with high antioxidant activity. RSC Adv 11:19682–19689. doi: 10.1039/d1ra02583j
Pacelli C, Bryan RA, Onofri S, Selbmann L, Shuryak I, Dadachova E (2017) Melanin is effective in protecting fast and slow growing fungi from various types of ionizing radiation. Environ Microbiol 19:1612–1624. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13681
Pak S, Chen F, Ma L, Hu X, Ji J (2021) Functional perspective of black fungi (Auricularia auricula): Major bioactive components, health benefits and potential mechanisms. Trends Food Sci Technol 114:245–261. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.013
Panzella L, Ebato A, Napolitano A, Koike K (2018) The late stages of melanogenesis: exploring the chemical facets and the application opportunities. Int J Mol Med 19:1753. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061753
Perez-Cuesta U, Aparicio-Fernandez L, Guruceaga X, Martin-Souto L, Abad-Diaz-de-Cerio A, Antoran A, Buldain I, Hernando FL, Ramirez-Garcia A, Rementeria A (2020) Melanin and pyomelanin in Aspergillus fumigatus: from its genetics to host interaction. Int J Microbiol 23:55–63. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10123-019-00078-0
Pierce JA, Rast DM (1995) A comparison of native and synthetic mushroom melanins by fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. Phytochemistry 39:49–55. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/0031-9422(94)00837-J
Pillaiyar T, Manickam M, Jung SH (2017) Recent development of signaling pathways inhibitors of melanogenesis. Cell Signal 40:99–115. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2017.09.004
Pillaiyar T, Namasivayam V, Manickam M, Jung SH (2018) Inhibitors of melanogenesis: an updated review. J Med Chem 61:7395–7418. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.7b00967
Prados-Rosales R, Toriola S, Nakouz A, Chatterjee S, Stark R, Gerfen G, Tumpowsky P, Dadachova E, Casadevall A (2015) Structural characterization of melanin pigments from commercial preparations of the edible mushroom Auricularia auricula. J Agric Food Chem 63:7326–7332. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.5b02713
Pralea IE, Moldovan RC, Petrache AM, Ilieș M, Hegheș SC, Ielciu I, Nicoară R, Moldovan M, Ene M, Radu M, Uifălean A, Iuga CA (2019) From extraction to advanced analytical methods: the challenges of melanin analysis. Int J Mol Sci 20:3943. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163943
Qi C, Fu LH, Xu H, Wang TF, Lin J, Huang P (2019) Melanin/polydopamine-based nanomaterials for biomedical applications. Sci China Chem 62:162–188. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-018-9392-6
Revskaya E, Chu P, Howell RC, Schweitzer AD, Bryan RA, Harris M, Gerfen G, Jiang Z, Jandl T, Kim K, Ting LM, Sellers RS, Dadachova E, Casadevall A (2012) Compton scattering by internal shields based on melanin-containing mushrooms provides protection of gastrointestinal tract from ionizing radiation. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 27:570–576. doi: https://doi.org/10.1089/cbr.2012.1318
Riley PA (1997) Melanin. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 29:1235–1239. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1357-2725(97)00013-7
Sansinenea E, Ortiz A (2015) Melanin: a photoprotection for Bacillus thuringiensis based biopesticides. Biotechnol Lett 37:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-014-1726-8
Sarna T, Swartz HM, Zadlo A (2022) Interaction of melanin with metal ions modulates their cytotoxic potential. Appl Magn Reson 53:105–121. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00723-021-01386-3
Schumacher J (2016) DHN melanin biosynthesis in the plant pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea is based on two developmentally regulated key enzyme (PKS)-encoding genes. Mol Microbiol 99:729–748. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13262
Schumacher J, Simon A, Cohrs KC, Viaud M, Tudzynski P (2014) The transcription factor BcLTF1 regulates virulence and light responses in the necrotrophic plant pathogen Botrytis cinerea. PLoS Genet 10:e1004040. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004040
Shi F, Li J, Yang L, Hou G, Ye M (2018a) Hypolipidemic effect and protection ability of liver-kidney functions of melanin from Lachnum YM226 in high-fat diet fed mice. Food Funct 9:880–889. doi: 10.1039/C7FO01294B
Shi F, Li J, Ye Z, Yang L, Chen T, Chen X, Ye M (2018b) Antitumor effects of melanin from Lachnum YM226 and its derivative in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Med Chem Commun 9:1059–1068. doi: 10.1039/C8MD00035B
Singh S, Nimse SB, Mathew DE, Dhimmar A, Sahastrabudhe H, Gajjar A, Ghadge VA, Kumar P, Shinde PB (2021) Microbial melanin: recent advances in biosynthesis, extraction, characterization, and applications. Biotechnol Adv 53:107773. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2021.107773
Singla S, Htut KZ, Zhu R, Davis A, Ma J, Ni QZ, Burkart MD, Maurer C, Miyoshi T, Dhinojwala A (2021) Isolation and characterization of allomelanin from pathogenic black knot fungus-a sustainable source of melanin. ACS Omega 6:35514–35522. doi: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.1c05030
Solano F (2016) Photoprotection versus photodamage: updating an old but still unsolved controversy about melanin. Polym Int 65:1276–1287. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/pi.5117
Song S, Li S, Su N, Li J, Shi F, Ye M (2016a) Structural characterization, molecular modification and hepatoprotective effect of melanin from Lachnum YM226 on acute alcohol-induced liver injury in mice. Food Funct 7:3617–3627. doi: 10.1039/c6fo00333h
Song S, Yang L, Ye M, Chen X, Shi F, Shaikh F (2016b) Antioxidant activity of a Lachnum YM226 melanin-iron complex and its influence on cytokine production in mice with iron deficiency anemia. Food Funct 7:1508–1514. doi: 10.1039/c5fo01274k
Strycker BD, Han Z, Bahari A, Pham T, Lin X, Shaw BD, Sokolov AV, Scully MO (2021) Raman characterization of fungal DHN and DOPA melanin biosynthesis pathways. J Fungi 7:841. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7100841
Surendirakumar K, Pandey RR, Muthukumar T, Sathiyaseelan A, Loushambam S, Seth A (2022) Characterization and biological activities of melanin pigment from root endophytic fungus, Phoma sp. RDSE17. Arch Microbiol 204:171. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-02788-y
Suryanarayanan TS, Ravishankar JP, Venkatesan G, Murali TS (2004) Characterization of the melanin pigment of a cosmopolitan fungal endophyte. Mycol Res 108:974–978. doi: https://doi.org/10.1017/S0953756204000619
Toledo AV, Franco MEE, Yanil Lopez SM, Troncozo MI, Saparrat MCN, Balatti PA (2017) Melanins in fungi: types, localization and putative biological roles. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 99:2–6. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.04.004
Tran-Ly AN, Ribera J, Schwarze FWMR, Brunelli M, Fortunato G (2020) Fungal melanin-based electrospun membranes for heavy metal detoxification of water. Sustain Mater Technol 23:e00146. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.susmat.2019.e00146
Vasanthakumar A, DeAraujo A, Mazurek J, Schilling M, Mitchell R (2015) Pyomelanin production in Penicillium chrysogenum is stimulated by l-tyrosine. Microbiology 161:1211–1218. doi: https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000030
Venil CK, Velmurugan P, Dufossé L, Devi PR, Ravi AV (2020) Fungal pigments: potential coloring compounds for wide ranging applications in textile dyeing. J Fungi 6:68. doi: https://doi.org/10.3390/jof6020068
Vitiello G, Melone P, Silvestri B, Pezzella A, Di Donato P, D’Errico G, Di Napoli M, Zanfardino A, Varcamonti M, Luciani G (2019) Titanium based complexes with melanin precursors as a tool for directing melanogenic pathways. Pure Appl Chem 91:1605–1616. doi: https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2018-1210
Wang Z, Zou Y, Li Y, Cheng Y (2020) Metal-containing polydopamine nanomaterials: catalysis, energy, and theranostics. Small 16:1907042. doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201907042
Williamson PR (1994) Biochemical and molecular characterization of the diphenol oxidase of Cryptococcus neoformans: identification as a laccase. J Bacteriol 176:656–664. doi: https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.176.3.656-664.1994
Wu X, Guan W, Yan R, Lei J, Xu L, Wang Z (2016) Effects of UV-C on antioxidant activity, total phenolics and main phenolic compounds of the melanin biosynthesis pathway in different tissues of button mushroom. Postharvest Biol Tec 118:51–58. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2016.03.017
Wu Y, Shan L, Yang S, Ma A (2008a) Identification and antioxidant activity of melanin isolated from Hypoxylon archeri, a companion fungus of Tremella fuciformis. J Basic Microbiol 48:217–221. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200700366
Wu Y, Wang X, Ma A, Xie B (2008b) Effects of melanin extracted from Hypoxylon sp. on fungal growth and polyphenol oxidase activity. Nat Prod Res Dev 3:501–504. doi:10.16333/j.1001-6880.2008b.03.002(in Chinese with an English abstract)
Xiao M, Chen W, Li W, Zhao J, Hong YL, Nishiyama Y, Miyoshi T, Shawkey MD, Dhinojwala A (2018) Elucidation of the hierarchical structure of natural eumelanins. J R Soc Interface 15:45. doi: https://doi.org/10.1098/rsif.2018.0045
Xu C, Chen T, Li J, Jin M, Ye M (2020a) The structural analysis and its hepatoprotective activity of melanin isolated from Lachnum sp. Process Biochem 90:249–256. doi: 10.1016/J.PROCBIO.2019.08.022
Xu C, Li J, Yang L, Shi F, Yang L, Ye M (2017) Antibacterial activity and a membrane damage mechanism of Lachnum YM30 melanin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Staphylococcus aureus. Food Control 73:1445–1451. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.10.048
Xu L, Li J, Chang M (2020b) Comparison on physicochemical and biochemical properties of natural and arginine-modified melanin from medicinal mushroom Ganoderma lucidum. J Basic Microbiol 60:1014–1028. doi: 10.1002/jobm.2020b00430
Ye M, Wang Y, Qian M, Chen X, Hu X (2011) Preparation and Properties of the Melanin from Lachnum singerianum. Int J of Basic & Appl Sci 11:51–58
Ye Z, Lu Y, Zong S, Yang L, Shaikh F, Li J, Ye M (2019) Structure, molecular modification and anti-tumor activity of melanin from Lachnum singerianum. Process Biochem 76:203–212. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-018-2898-9
Yu X, Huo L, Liu H, Chen L, Wang Y, Zhu X (2015) Melanin is required for the formation of the multi-cellular conidia in the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis microspora. Microbiol Res 179:1–11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2015.06.004
Zhou M, Li Z, Liu Y, Zhang P, Hao X, Zhu X (2022a) Transcription factors pmr1 and pmr2 cooperatively regulate melanin biosynthesis, conidia development and secondary metabolism in Pestalotiopsis microspora. J Fungi 8:38. doi: 10.3390/jof8010038
Zhou Y, Song J, Wang Y, Yang L, Wu M, Li G, Zhang J (2022b) Biological characterization of the melanin biosynthesis gene Bcscd1 in the plant pathogenic fungus Botrytis cinerea. Fungal Genet Biol 160:103693. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2022b.103693
Zong S, Li L, Li J, Shaikh F, Yang L, Ye M (2017) Structure characterization and lead detoxification effect of carboxymethylated melanin derived from Lachnum sp. Appl Biochem 182:669–686. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2353-8
Zou Y, Hu W, Ma K, Tian M (2015) Physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of melanin and fractions from Auricularia auricula fruiting bodies. Food Sci Biotechnol 24:15–21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0003-5
Zou Y, Hu W, Ma K, Tian M (2017) Fermentative production of melanin by the fungus Auricularia auricula using wheat bran extract as major nutrient source. Food Sci Technol Res 23:23–29. doi:https://doi.org/10.3136/fstr.23.23
Funding
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31,572,182; 31,772,375) to Aimin Ma.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to this study. RL and AM had the ideas for the article and performed the literature search and data analysis. RL wrote the manuscript. XM, CM, XW and AM critically reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclaimer
The views stated here are ours and ours only. We apologize if we failed to mention other significative researches of fungal melanin and if our interpretation of the data is not accepted by other researchers.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, R., Meng, X., Mo, C. et al. Melanin of fungi: from classification to application. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 38, 228 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03415-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-022-03415-0