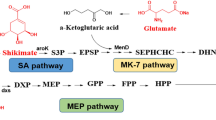
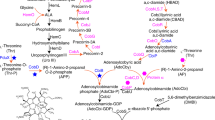
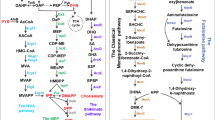
Abstract
Menaquinone-7 (MK-7), a highly valuable member of the vitamin K2 series, is an essential nutrient for humans. In this study, to develop engineered Escherichia coli strains for MK-7 production, heterogeneous heptaprenyl pyrophosphate synthetase (HepPPS) was introduced, and MK-7 production was first achieved in engineered E. coli by overexpression of Bacillus subtilis-derived HepPPS (BsHepPPS). Then, by optimizing the enzyme expression of the heterogenous mevalonic acid (MVA) pathway and the BsHepPPS, the titre of MK-7 increased to 2.3 μM, which was 22-fold higher than that of the original strain. The competitive pathways of MK-7 were further investigated by deletion of ubiCA or ispB. Finally, the scale-up fermentation of the engineered E. coli in a 5-L fermenter was studied under aerobic conditions using glucose, and 13.6 μM (8.8 mg/L) MK-7 was achieved. Additionally, metabolite analysis revealed a new bottleneck in the MK-7 pathway at ubiE, suggesting an avenue for further optimization. This report is the first to describe the metabolic engineering of MK-7 in E. coli, which provides a new perspective for MK-7 production.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files]. The authors agree that any materials newly described in the study are available to members of the scientific community for noncommercial purposes, if necessary, via an appropriate Materials Transfer Agreement between the interested parties.
References
Berenjian A, Mahanama R, Kavanagh J, Dehghani F (2015) Vitamin K series: current status and future prospects. Crit Rev Biotechnol 35:199–208. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2013.832142
Beulens JWJ et al (2009) High dietary menaquinone intake is associated with reduced coronary calcification. Atherosclerosis 203:489–493
Chen X, Zhou L, Tian K, Kumar A, Singh S, Prior BA, Wang Z (2013) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli: a sustainable industrial platform for bio-based chemical production. Biotechnol Adv 31:1200–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.02.009
Desai J, Liu YL, Wei HL, Liu WD, Ko TP, Guo RT, Oldfield E (2016) Structure function, and inhibition of Staphylococcus aureus heptaprenyl diphosphate synthase. ChemMedChem 11:1915–1923
Kong MK, Lee PC (2011) Metabolic engineering of menaquinone-8 pathway of Escherichia coli as a microbial platform for vitamin K production. Biotechnol Bioeng 108:1997–2002. https://doi.org/10.1002/bit.23142
Lee PT, Hsu AY, Ha HT, Clarke CF (1997) A C-methyltransferase involved in both ubiquinone and menaquinone biosynthesis: isolation and identification of the Escherichia coli ubiE gene. J Bacteriol 179:1748–1754. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.179.5.1748-1754.1997
Liu N, Liu B, Wang G, Soong Y-HV, Tao Y, Liu W, Xie D (2020) Lycopene production from glucose, fatty acid and waste cooking oil by metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Biochem Eng J 155:107488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2020.107488
Ma Y, McClure DD, Somerville MV, Proschogo NW, Dehghani F, Kavanagh JM, Coleman NV (2019) Metabolic engineering of the MEP pathway in Bacillus subtilis for increased biosynthesis of menaquinone-7. ACS Synth Biol. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.9b00077
Mahdinia E, Demirci A, Berenjian A (2017) Production and application of menaquinone-7 (vitamin K2): a new perspective. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 33:2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2169-2
Mahdinia E, Demirci A, Berenjian A (2019) Biofilm reactors as a promising method for vitamin K (menaquinone-7) production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 103:5583–5592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-019-09913-w
Rad SA, Zahiri HS, Noghabi KA, Rajaei S, Heidari R, Mojallali L (2012) Type 2 IDI performs better than type 1 for improving lycopene production in metabolically engineered E. coli strains. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:313–321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0821-4
Ren LJ, Peng C, Hu XC, Han YW, Huang H (2020) Microbial production of vitamin K2: current status and future prospects. Biotechnol Adv 39:107453
Shukal S, Chen X, Zhang C (2019) Systematic engineering for high-yield production of viridiflorol and amorphadiene in auxotrophic Escherichia coli. Metab Eng 55:170–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2019.07.007
Soballe B, Poole RK (1997) Aerobic and anaerobic regulation of the ubiCA operon, encoding enzymes for the first two committed steps of ubiquinone biosynthesis in Escherichia coli. FEBS Lett 414:373–376. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0014-5793(97)01041-7
Song J et al (2014) Enhanced production of vitamin K2 from Bacillus subtilis (natto)by mutation and optimization of the fermentation medium. Braz Arch Biol Technol 57:606–612. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-8913201402126
Studier FW (2005) Protein production by auto-induction in high-density shaking cultures. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):207–234
Yang S et al (2019) Modular Pathway Engineering of Bacillus subtilis To Promote De Novo Biosynthesis of Menaquinone-7. ACS Synth Biol 8:70–81. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssynbio.8b00258
Zahiri HS, Yoon SH, Keasling JD, Lee SH, Won Kim S, Yoon SC, Shin YC (2006) Coenzyme Q10 production in recombinant Escherichia coli strains engineered with a heterologous decaprenyl diphosphate synthase gene and foreign mevalonate pathway. Metab Eng 8:406–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymben.2006.05.002
Zhang C, Seow VY, Chen X, Too HP (2018) Multidimensional heuristic process for high-yield production of astaxanthin and fragrance molecules in Escherichia coli. Nat Commun 9:1858. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04211-x
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFA0901400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant (31670051).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Key Research and Development Project of China (2018YFA0901400) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China Grant (31670051).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
QG carried out the main work, collected and analysed the data, and drafted the manuscript. HC, WW and BL participated in the research. BL supervised the work and participated in data analysis and revised the manuscript. YT and JH participated in the conception and finalized the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. Informed consent was obtained from all the authors included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Q., Chen, H., Wang, W. et al. Menaquinone-7 production in engineered Escherichia coli. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 132 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02880-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-020-02880-9