Abstract
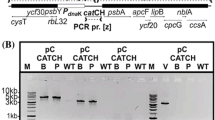
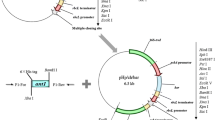
On the basis of fundamental genetic transformation technologies, the goal of this study was to optimize Tetraselmis subcordiformis chloroplast transformation through the use of endogenous regulators. The genes rrn16S, rbcL, psbA, and psbC are commonly highly expressed in chloroplasts, and the regulators of these genes are often used in chloroplast transformation. For lack of a known chloroplast genome sequence, the genome-walking method was used here to obtain full sequences of T. subcordiformis endogenous regulators. The resulting regulators, including three promoters, two terminators, and a ribosome combination sequence, were inserted into the previously constructed plasmid pPSC-R, with the egfp gene included as a reporter gene, and five chloroplast expression vectors prepared. These vectors were successfully transformed into T. subcordiformis by particle bombardment and the efficiency of each vector tested by assessing EGFP fluorescence via microscopy. The results showed that these vectors exhibited higher efficiency than the former vector pPSC-G carrying exogenous regulators, and the vector pRFA with Prrn, psbA-5′RE, and TpsbA showed the highest efficiency. This research provides a set of effective endogenous regulators for T. subcordiformis and will facilitate future fundamental studies of this alga.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apt KE, Kroth-Pancic PG, Grossman AR (1996) Stable nuclear transformation of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mol Gen Genet 252:572–579. doi:10.1007/s004380050264
Chiyoda S, Linley PJ, Yamato KT, Fukuzawa H, Yokota A, Kohchi T (2007) Simple and efficient plastid transformation system for the liverwort Marchantia polymorpha L. suspension-culture cells. Transgenic Res 16:41–49. doi:10.1007/s11248-006-9027-1
Cui YL, Qin S, Jiang P (2014) Chloroplast transformation of Platymonas (Tetraselmis) subcordiformis with the bar gene as selectable maker. PLoS One 9(6):e98607. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098607
De Cosa B, Moar W, Lee SB, Miller M, Daniell H (2001) Overexpression of the Bt cry2Aa2 operon in chloroplasts leads to formation of insecticidal crystals. Nat Biotechnol 19:71–74. doi:10.1038/83559
Doetsch NA, Favreau MR, Kuscuoglu N, Thompson MD, Hallick RB (2001) Chloroplast transformation in Euglena gracilis: splicing of a group III twintron transcribed from a transgenic psbK operon. Curr Genet 39:49–60. doi:10.1007/s002940000174
Fukuda S, Mikami K, Uji T, Park E-J, Ohba T, Asada K, Kitade Y, Endo H, Kato I, Saga N (2008) Factors influencing efficiency of transient gene expression in the red macrophyte Porphyra yezoensis. Plant Sci 174:329–339. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2007.12.006
Guan YF, Zhang W, Deng MC, Jin MF, Yu XJ (2004) Significant enhancement of photobiological H2 evolution by carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone in the marine green alga Platymonas subcordiformis. Biotechnol Lett 26:1031–1035. doi:10.1023/B:BILE.0000032961.71564.00
Guo Z, Chen ZA, Zhang W, Yu XJ, Jin MF (2008) Improved hydrogen photoproduction regulated by carbonylcyanide m-chlorophenylhrazone from marine green alga Platymonas subcordiformis grown in CO2-supplemented air bubble column bioreactor. Biotechnol Lett 30:877–883. doi:10.1007/s10529-008-9637-1
Jiang P, Qin S, Zseng CK (2002) Expression of hepatitis B surface antigen gene (HBsAg) in Laminaria japonica (Laminariales, Phaeophyta). Chin Sci Bull 47(17):1438–1440. doi:10.1360/02tb9317
Kuroda H, Maliga P (2001) Complementarity of the 16S rRNA penultimate stem with sequences downstream of the AUG destabilizes the plastid mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 29:970–975. doi:10.1093/nar/29.4.970
Lescot M, Déhais P, Moreau Y, De Moor B, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE: a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30(1):325–327. doi:10.1093/nar/30.1.325
Li D, Han XX, Zuo J, Xie LL, He RH, Gao J, Chang L, Yuan LP, Cao ML (2011) Construction of rice site-specific chloroplast transformation vector and transient expression EGFP gene in Dunaliella Salina. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7:801–806. doi:10.1166/jbn.2011.1339
Quesada-Vargas T, Ruiz ON, Daniell H (2005) Characterization of heterologous multigene operons in transgenic chloroplasts: transcription, processing, and translation. Plant Physiol 138:1746–1762. doi:10.1104/pp.105.063040
Ruhlman T, Ahangari R, Devine A, Samsam M, Daniell H (2007) Expression of cholera toxin B-proinsulin fusion protein in lettuce and tobacco chloroplasts-oral administration protects against development of insulitis in non-obese diabetic mice. Plant Biotechnol J 5:495–510. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00259.x
Ruhlman T, Verma D, Samson N, Daniell H (2010) The role of heterologous chloroplast sequence elements in transgene integration and expression. Plant Physiol 152:2088–2104. doi:10.1104/pp.109.152017
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual (3-volumeset). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, NewYork
Sidorov VA, Kasten D, Pang SZ, Hajdukiewicz PT, Staub JM, Nehra NS (1999) Stable chloroplast transformation in potato: use of green fluorescent protein as a plastid marker. Plant J 19:209–216. doi:10.1046/j.1365-313X.1999.00508.x
Svab Z, Maliga P (1993) High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:913–917. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.3.913
Verma D, Daniell H (2007) Chloroplast vector systems for biotechnology applications. Plant Physiol 145:1129–1143. doi:10.1104/pp.107.106690
Wei M, Kong ZY, Zhong L, Qiu LQ, Li YS, Zhao L, Li XZ, Zhong WH (2012) Construction of a native promoter-containing transposon vector for stable monitoring the denitrifying bacterium Pseudomonas stutzeri LYS-86 by chromosomal integrated gfp. Plasmid 68:61–68. doi:10.1016/j.plasmid.2012.02.002
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 41406192, 41176144, and 41376139), the Science Foundation of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDA1102040300).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yulin Cui and Jialin Zhao are co-first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cui, Y., Zhao, J., Hou, S. et al. Enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) gene expression in Tetraselmis subcordiformis chloroplast with endogenous regulators. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32, 83 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2039-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-016-2039-y