Abstract
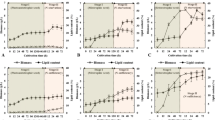
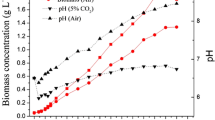
Microalgae possess higher photosynthetic efficiency and accumulate more neutral lipids when supplied with high-dose CO2. However, the nature of lipid accumulation under conditions of elevated CO2 has not been fully elucidated so far. We now revealed that the enhanced lipid accumulation of Chlorella in high-dose CO2 was as efficient as under heterotrophic conditions and this may be attributed to the driving of enlarged carbon source. Both photoautotrophic and heterotrophic cultures were established by using Chlorella sorokiniana CS-1. A series of changes in the carbon fixation, lipid accumulation, energy conversion, and carbon-lipid conversion under high-dose CO2 (1–10 %) treatment were characterized subsequently. The daily carbon fixation rate of C. sorokiniana LS-2 in 10 % CO2 aeration was significantly increased compared with air CO2. Correspondingly, double oil content (28 %) was observed in 10 % CO2 aeration, close to 32.3 % produced under heterotrophic conditions. In addition, with 10 % CO2 aeration, the overall energy yield (Ψ) in Chlorella reached 12.4 from 7.3 % (with air aeration) because of the enhanced daily carbon fixation rates. This treatment also improved the energetic lipid yield (Ylipid/Es) with 4.7-fold, tending to the heterotrophic parameters. More significantly, 2.2 times of carbon-lipid conversion efficiency (ηClipid/Ctotal, 42.4 %) was observed in 10 % CO2 aeration, towards to 53.7 % in heterotrophic cultures, suggesting that more fixed carbon might flow into lipid synthesis under both 10 % CO2 aeration and heterotrophic conditions. Taken together, all our evidence showed that 10 % CO2 may push photoautotrophic Chlorella to display heterotrophic-like efficiency at least in lipid production. It might bring us an efficient model of lipid production based on microalgal cells with high-dose CO2, which is essential to sustain biodiesel production at large scales.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Es:
-
The total energy supplied to the reactor
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- CCD:
-
Central composite design
- Xmax:
-
The maximum biomass
- Pmax:
-
The maximum productivity
- μ:
-
Specific growth rate
- qmax :
-
Specific formation rate of lipid
- Es:
-
The total energy supplied to the reactor
- Ylipid/Es :
-
Energetic lipid yield
- Qb and Qs:
-
The heat of combustion of C. sorokiniana and glucose
- Ψ:
-
Energy yield
- ηClipid/Ctotal :
-
Carbon-lipid conversion efficiency
- FDavg and FDmax:
-
The average and maximum carbon fixation
- CCMs:
-
CO2 concentrating mechanisms
- DIC:
-
Dissolved inorganic carbon
- CBB:
-
The Calvin–Benson–Bassham
References
Amin S (2009) Review on biofuel oil and gas production processes from microalgae. Energy Convers Manag 50(7):1834–1840
Axelsson L, Beer S (2001) Carbon Limitations. In: Rai LC, Gaur JP (eds) Algal adaptation to environmental stresses. Springer, Berlin, pp 21–43
Boelen P, van Dijk R, Damsté JSS, Rijpstra WIC, Buma AG (2013) On the potential application of polar and temperate marine microalgae for EPA and DHA production. AMB Express 3:1–9
Chen Y-F, Wu Q (2011) Production of biodiesel from algal biomass: current perspectives and future. In: Pandey A, Larroche C, Ricke SC, Dussap CG, Gnansounou E (eds) Biofuels: alternative feedstocks and conversion processes. Elsevier, pp 399–413
Chen CY, Yeh KL, Aisyah R, Lee DJ, Chang JS (2011) Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: a critical review. Bioresour Technol 102(1):71–81
Chisti Y (2007) Biodiesel from microalgae. Biotechnol Adv 25:294–306
Chiu S, Kao C, Chen C, Kuan T, Ong S, Lin C (2008) Reduction of CO2 by a high-density culture of Chlorella sp. in a semicontinuous photobioreactor. Bioresour Technol 99:3389–3396
DaHai T, Wei H, PengLin L, XiaoLing M, JianJiang Z (2011) CO2 biofixation and fatty acid composition of Scenedesmus obliquus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa in response to different CO2 levels. Bioresour Technol 102:3071–3076
Demirbas A (2011) Biodiesel from oilgae, biofixation of carbon dioxide by microalgae: a solution to pollution problems. Appl Energy 88(10):3541–3547
Doucha J, Straka F, Lívanský K (2005) Utilization of flue gas for cultivation of microalgae Chlorella sp.) in an outdoor open thin-layer photobioreactor. J Appl Phycol 17(5):403–412
Douskova I, Doucha J, Livansky K, Machat J, Novak P, Umysova D, Zachleder V, Vitova M (2009) Simultaneous flue gas bioremediation and reduction of microalgal biomass production costs. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:179–185
Dragone G, Fernandes B, Vicente A, Teixeira JA (2010) Third generation biofuels from microalgae. In: Vilas AM (ed) Current research, technology and education topics in applied microbiology and microbial biotechnology. Formatex Research Center, Badajoz, pp 1355–1366
Ducharme NA, Bickel PE (2008) Minireview: lipid droplets in lipogenesis and lipolysis. Endocrinology 149:942–949
Goudriaan J, Ajtay G (1979) The possible effect of increased CO2 on photosynthesis. In: Bolin B, Degens ET, Kempe S, Ketner P (eds) The global carbon cycle. Wiley, Chichester, pp 237–249
Guedes AC, Amaro HM, Malcata FX (2011) Microalgae as sources of carotenoids. Mar Drugs 9:625–644
Halim R, Gladman B, Danquah MK, Webley PA (2011) Oil extraction from microalgae for biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 102:178–185
Ho K, Payne W (1979) Assimilation efficiency and energy contents of prototrophic bacteria. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:787–802
Ho SH, Chen WM, Chang JS (2010) Scenedesmus obliquus CNW-N as a potential candidate for CO2 mitigation and biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 101:8725–8730
Huang G, Chen F, Wei D, Zhang X, Chen G (2010) Biodiesel production by microalgal biotechnology. Appl Energy 87:38–46
Khataee AR, Dehghan G, Ebadi E, Pourhassan M (2010) Central composite design optimization of biological dye removal in the presence of macroalgae Chara sp. Clean Soil Air Water 38:750–757
Kumar A, Ergas S, Yuan X, Sahu A, Zhang Q, Dewulf J, Van Langenhove H (2010) Enhanced CO2 fixation and biofuel production via microalgae: recent developments and future directions. Trends Biotechnol 28(7):371–380
Li X, Xu H, Wu Q (2007) Large-scale biodiesel production from microalga Chlorella protothecoides through heterotrophic cultivation in bioreactors. Biotechnol Bioeng 98:764–771
Liang Y, Sarkany N, Cui Y (2009) Biomass and lipid productivities of Chlorella vulgaris under autotrophic, heterotrophic and mixotrophic growth conditions. Biotechnol Lett 31:1043–1049
Long SP, Zhu XG, Naidu SL, Ort DR (2006) Can improvement in photosynthesis increase crop yields? Plant Cell Environ 29(3):315–330
Miao X, Wu Q (2006) Biodiesel production from heterotrophic microalgal oil. Bioresour Technol 97(6):841–846
Nakkash N, Wang Z, Naterer G (2013) Solar thermal energy-based high purity CO2 release from carbonate sorbents. http://www3.aiche.org/Proceedings/content/Annual-2013/extended-abstracts/P319102.pdf
O’Neill BF, Zangerl AR, Dermody O, Bilgin DD, Casteel CL, Zavala JA, DeLucia EH, Berenbaum MR (2010) Impact of elevated levels of atmospheric CO2 and herbivory on flavonoids of soybean (Glycine max Linnaeus). J Chem Ecol 36:35–45
Parsaeimehr A, Sun Z, Dou X, Chen Y-F (2015) Simultaneous improvement in production of microalgal biodiesel and high-value alpha-linolenic acid by a single regulator acetylcholine. Biotechnol Biofuels 8:11. doi:10.1186/s13068-015-0196-0
Qiao H, Wang G, Zhang X (2009) Isolation and characterization of Chlorella sorokiniana Gxnn01 (Chlorophyta) with the properties of heterotrophic and microaerobic growth. J Phycol 45:1153–1162
Rodolfi L, Chini Zittelli G, Bassi N, Padovani G, Biondi N, Bonini G, Tredici MR (2009) Microalgae for oil: strain selection, induction of lipid synthesis and outdoor mass cultivation in a low-cost photobioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng 102(1):100–112
Rosa APCD, Carvalho LF, Goldbeck L, Costa JAV (2011) Carbon dioxide fixation by microalgae cultivated in open bioreactors. Energy Convers Manag 52:3071–3073
Sforza E, Bertucco A, Morosinotto T, Giacometti GM (2012) Photobioreactors for microalgal growth and oil production with Nannochloropsis salina: from lab-scale experiments to large-scale design. Chem Eng Res Des 90:1151–1158
Sun X, Cao Y, Xu H, Liu Y, Sun J, Qiao D, Cao Y (2014) Effect of nitrogen-starvation, light intensity and iron on triacylglyceride/carbohydrate production and fatty acid profile of Neochloris oleoabundans HK-129 by a two-stage process. Bioresour Technol 155:204–212
Sydney EB, Sturm W, de Carvalho JC, Thomaz-Soccol V, Larroche C, Pandey A, Soccol CR (2010) Potential carbon dioxide fixation by industrially important microalgae. Bioresour Technol 101:5892–5896
Wang B, Li Y, Wu N, Lan CQ (2008) CO2 bio-mitigation using microalgae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(5):707–718
Westerhoff P, Hu Q, Esparza-Soto M, Vermaas W (2010) Growth parameters of microalgae tolerant to high levels of carbon dioxide in batch and continuous-flow photobioreactors. Environ Technol 31:523–532
Xiong W, Li X, Xiang J, Wu Q (2008) High-density fermentation of microalga Chlorella protothecoides in bioreactor for microbio-diesel production. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 78:29–36
Xiong W, Gao C, Yan D, Wu C, Wu Q (2010) Double CO2 fixation in photosynthesis–fermentation model enhances algal lipid synthesis for biodiesel production. Bioresour Technol 101(7):2287–2293
Xu H, Miao X, Wu Q (2006) High quality biodiesel production from a microalga Chlorella protothecoides by heterotrophic growth in fermenters. J Biotechnol 126(4):499–507
Yang C, Hua Q, Shimizu K (2000) Energetics and carbon metabolism during growth of microalgal cells under photoautotrophic, mixotrophic and cyclic light-autotrophic/dark-heterotrophic conditions. Biochem Eng J 6:87–102
Yemm EW, Willis AJ (1954) The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem J 57(3):508–514
Yoo C, Jun SY, Lee JY, Ahn CY, Oh HM (2010) Selection of microalgae for lipid production under high levels carbon dioxide. Bioresour Technol 101:S71–S74
Yuan JP, Peng J, Yin K, Wang JH (2011) Potential health-promoting effects of astaxanthin: a high-value carotenoid mostly from microalgae. Mol Nutr Food Res 55:150–165
Zeng X, Danquah MK, Chen XD, Lu Y (2011) Microalgae bioengineering: from CO2 fixation to biofuel production. Renew Sust Energy Rev 15:3252–3260
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Jiangsu Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Funds (CX (12) 3041), the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (BK20130712), and the Open Foundation of Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Microbes and Functional Genomics Key Laboratory (164070303402). Dr. Ali Parsaeimehr and Dr. Sitwat Aman critically read the manuscript. Undergraduate student Dongling Liang assisted in the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Z., Dou, X., Wu, J. et al. Enhanced lipid accumulation of photoautotrophic microalgae by high-dose CO2 mimics a heterotrophic characterization. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 32, 9 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1963-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1963-6