Abstract
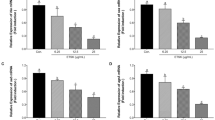
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) causes a wide variety of infections, which are of major concern worldwide. S. aureus produces multiple virulence factors, resulting in food infection and poisoning. These virulence factors include hyaluronidases, proteases, coagulases, lipases, deoxyribonucleases and enterotoxins. Among the extracellular proteins produced by S. aureus that contribute to pathogenicity, the exotoxins α-hemolysin, staphylococcal enterotoxin A (SEA) and staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) are thought to be of major significance. Totarol, a plant extract, has been revealed to inhibit the proliferation of several pathogens effectively. However, there are no reports on the effects of totarol on the production of α-hemolysin, SEA or SEB secreted by S. aureus. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of totarol on these three exotoxins. Hemolysis assay, western blotting and real-time reverse transcriptase-PCR assay were performed to identify the influence of graded subinhibitory concentrations of totarol on the production of α-hemolysin and the two major enterotoxins, SEA and SEB, by S. aureus in a dose-dependent manner. Moreover, an enzyme linked immunosorbent assay showed that the TNF-α production of RAW264.7 cells stimulated by S. aureus supernatants was inhibited by subinhibitory concentrations of totarol. Form the data, we propose that totarol could potentially be used as a promising natural compound in the food and pharmaceutical industries.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajpai VK, Rahman A, Kang SC (2008) Chemical composition and inhibitory parameters of essential oil and extracts of Nandina domestica Thunb. to control food-borne pathogenic and spoilage bacteria. Int J Food Microbiol 15:117–122
Balaban N, Rasooly A (2000) Staphylococcal enterotoxins. Int J Food Microbiol 61:1–10
Bernardo K, Pakulat N, Fleer S, Schnaith A, Utermöhlen O, Krut O (2004) Subinhibitory concentrations of linezolid reduce Staphylococcus aureus virulence factor expression. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 48:546–555
Bronner S, Monteil H, Prévost G (2004) Regulation of virulence determinants in Staphylococcus aureus: complexity and applications. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:183–200
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) (2009) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, vol 8., Approved Standard M7-A8CLSI, Wayne, PA
Constantine GH, Karchesy JJ, Franzblau SG, LaFleur LE (2001) (+)-Totarol from Chamaecyparis nootkatensis and activity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Fitoterapia 72:572–574
Dinges MM, Orwin PM, Schlievert PM (2000) Exotoxins of Staphylococcus aureus. Clin Microbiol Rev 13:16–34
Dufour M, Simmonds RS, Bremer PJ (2003) Development of a method to quantify in vitro the synergistic activity of “natural” antimicrobials. Int J Food Microbiol 85:249–258
Gordien AY, Gray A, Franzblau SG, Seidel V (2009) Antimycobacterial terpenoids from Juniperus communis L. (Cuppressaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 126:500–505
Haraguchi H, Ishikawa H, Kubo I (1996) Mode of antibacterial action of totarol, a diterpene from Podocarpus nagi. Planta Med 62:122–125
Hatano T, Shintani Y, Aga Y, Shiota S, Tsuchiya T, Yoshida T (2000) Phenolic constituents of licorice. VIII. Structures of glicophenone and glicoisoflavanone, and effects of licorice phenolics on methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 48:1286–1292
Hoffman D (1987) The herb user’s guide. Thorsons Publishing Group, Wellingborough
Huang H, Kang R, Wang J, Luo G, Yang W, Zhao Z (2013) Hepatitis C virus inhibits AKT-tuberous sclerosis complex (TSC), the mechanistic target of rapamycin (MTOR) pathway, through endoplasmic reticulum stress to induce autophagy. Autophagy 9:175–195
Jaiswal R, Beuria TK, Mohan R, Mahajan SK, Panda D (2007) Totarol inhibits bacterial cytokinesis by perturbing the assembly dynamics of FtsZ. Bioche 46:4211–4220
Kawate T, Gouaux E (2003) Arresting and releasing Staphylococcal α-hemolysin at intermediate stages of pore formation by engineered disulfide bonds. Protein Sci 12:997–1006
Kim MB, Shaw JT (2010) Synthesis of antimicrobial natural products targeting FtsZ: (+)-totarol and related totarane diterpenes. Org Lett 12:3324–3327
Koszczol C, Bernardo K, Kronke M, Krut O (2006) Subinhibitory quinupristin/dalfopristin attenuates virulence of Staphylococcus aureus. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:564–574
Koszczol C, Bernardo K, Kronke M, Krut L (2010) Staphylococcal enterotoxins, toxic shock syndrome toxin and streptococcal pyrogenic exotoxins: a comparative study of their molecular biology. Chem Immunol 55:1–35
Kubo I, Muroi H, Himejima M (1992) Antibacterial activity of totarol and its potentiation. J Nat Prod 55:1436–1440
Larkin E, Carman R, Krakauer T, Stiles B (2009) Staphylococcus aureus: the toxic presence of a pathogen extraordinaire. Curr Med Chem 16:4003–4019
Le Loir Y, Baron F, Gautier M (2003) Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet Mol Res 2:63–76
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Micol V, Mateo CR, Shapiro S, Aranda FJ, Villalain J (2001) Effects of (+)-totarol, a diterpenoid antibacterial agent, on phospholipid model membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1511:281–290
Muroi H, Kubo I (1996) Antibacterial activity of anacardic acid and totarol, alone and in combination with methicillin, against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Appl Bacteriol 80:387–394
Novick RP, Christie GE, Penadés JR (2010) The phage-related chromosomal islands of gram-positive bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:541–551
Ohlsen K, Koller K-P, Hacker J (1997) Analysis of expression of the alpha-toxin gene (hla) of Staphylococcus aureus by using a chromosomally encoded hla:lacZ gene fusion. Infect Immun 65:3606–3614
Oliveira DC, Milheirico C, Vinga S, de Lencastre H (2006) Assessment of allelic variation in the ccrAB locus in methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones. J Antimicrob Chemother 58:23–30
Qiu J, Wang D, Xiang H, Feng H, Jiang Y, Xia L et al (2010) Subinhibitory concentrations of thymol reduce enterotoxins A and B and alpha-hemolysin production in Staphylococcus aureus isolates. PLoS ONE 5:e9736
Qiu J, Xiang H, Hu C, Wang Q, Dong J, Li H (2011) Subinhibitory concentrations of farrerol reduce alpha-toxin expression in Staphylococcus aureus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 315:129–133
Qiu J, Niu X, Dong J, Wang D, Wang J, Li H (2012) Baicalin protects mice from Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia via inhibition of the cytolytic activity of α-hemolysin. Infect Immun 75:1040–1044
Rowe GE, Welch RA (1994) Assays of hemolytic toxins. Methods Enzymol 235:657–667
Sambanthamoorthy K, Smeltzer M, Elasri M (2006) Identification and characterization of msa (SA1233), a gene involved in expression of SarA and several virulence factors in Staphylococcus aureus. Microbiology 152:2559–2572
Sato K, Sugawara K, Takeuchi H, Park HS, Akiyama T, Koyama T et al (2008) Antibacterial novel phenolic diterpenes from Podocarpus macrophyllus D. Don. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 56:1691–1697
Shapiro S, Guggenheim B (1998) Inhibition of oral bacteria by phenolic compounds.1. QSAR analysis using molecular connectivity. Quant Struct Act Relationsh 17:327–337
Smith EC, Kaatz GW, Seo SM, Wareham N, Williamson EM, Gibbons S (2007) The phenolic diterpene totarol inhibits multidrug efflux pump activity in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 51:4480–4483
Smith-Palmer A, Stewart J, Fyfe L (2004) Influence of subinhibitory concentrations of plant essential oils on the production of enterotoxins A and B and α-toxin by Staphylococcus aureus. J Med Microbiol 53:1023–1027
Sun SQ, Guo HC, Sun DH, Yin SH, Shang YJ, Cai XP (2010) Development and validation of an ELISA using a protein encoded by ORF2 antigenic domain of porcine circovirus type 2. Virol J 7:274–280
Wardenburg JB, Patel RJ, Schneewind O (2007) Surface proteins and exotoxins are required for the pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. Infect Immun 75:1040–1044
Worlitzsch D, Kaygin H, Steinhuber A, Dalhoff A, Botzenhart K, Döring G (2001) Effects of amoxicillin, gentamicin, and moxifloxacin on the hemolytic activity of Staphylococcus aureus in vitro and in vivo. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 45:196–202
Yeh CT, Yen GC (2006) Induction of hepatic antioxidant enzymes by phenolic acids in rats is accompanied by increased levels of multidrug resistance-associated protein 3 mRNA expression. J Nutr 136:11–15
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this work came from the following sources: the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 31271951 and No. 31172364), China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2013M530142), the Important National Science and Technology Specific Projects (2012ZX10003002), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (NCET-09-0434; NCET-13-0245).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, C., Zhao, X., Li, W. et al. Inhibitory effect of totarol on exotoxin proteins hemolysin and enterotoxins secreted by Staphylococcus aureus . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 1565–1573 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1905-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1905-3