Abstract
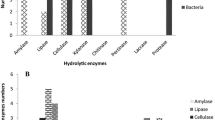
Tuz Lake is a hypersaline lake located in Central Anatolia, Turkey. The lake and its salterns, Kaldirim and Kayacik, are the major sources of solar salt for industrial applications in Turkey, especially in the food and leather industries. Use of the crude solar salt often results in microbial deterioration of the products. We therefore initiated a thorough characterization of the microbial communities in Tuz Lake and its adjacent salterns, and we present here the results of investigations on diversity of extremely halophilic Archaea. Twenty-seven colonies of aerobic red or pink Archaea (family Halobacteriaceae) were selected according to colony shape, size, consistency and pigmentation, and characterized according to their phenotypic characteristics, polar lipid contents, and antibiotic sensitivities. Furthermore, 16S rRNA genes of the isolates were screened by DGGE analysis and partially sequenced. Phylogenetic analysis showed that most isolates belonged to the genera Haloarcula, Halorubrum and Halobacterium. Haloarcula was found to be dominant both in Tuz Lake and in the saltern samples. Halorubrum species were isolated from Tuz Lake and from the Kaldirim saltern, and Halobacterium species were recovered from Tuz Lake and from the Kayacik saltern. All strains showed various activities of hydrolytic enzymes (proteases, amylases, cellulases, and others), activities which are responsible for the detrimental effects of the crude salt in food and leather products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller M, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Arahal DR, Dewhirst FE, Paster BJ, Volcani BE, Ventosa A (1996) Phylogenetic analyses of some extremely halophilic archaea isolated from Dead Sea water determined on the basis of their 16S rRNA sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3779–3786
Bailey DG, Birbir M (1993) A study of the extremely halophilic microorganisms found on commercially brine-cured cattle hides. J Am Leather Chem Association 88:285–293
Bailey DG, Birbir M (1996) The impact of halophilic organisms on the grain quality of brine cured hides. J Am Leather Chem Association 91:47–51
Bauer MW, Driskill LE, Callen W, Snead MA, Mathur FJ, Kelly RM (1999) An endoglucanase, EglA, from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus hydrolyzes β-1,4 bonds in mixed linkage (1-3)(1-4)-β-D-glucans and cellulose. J Bacteriol 181:284–290
Birbir M (2004) Examination of amylase, caseinase and cellulase enzyme production of extremely halophilic strains isolated from Tuz Lake, Kaldırım and Kayacık Salterns and Tuzköy salt mine. In: Altuğ G, Onaç-Içöz I (eds) Marine Bacteriology, 25–27 November, Istanbul 2004; Congress Proceedings, pp. 25–28. Istanbul, The Scientific and Technical Research Council of Turkey; Istanbul University, Faculty of Fisheries
Birbir M, Ilgaz A (1996) Isolation and identification of bacteria adversely affecting hide and leather quality. J Soc Leather Technologists Chem 80:147–153
Birbir M, Sesal C (2003) Extremely halophilic bacterial communities in Sereflikochisar Salt Lake in Turkey. Turkish J Biol 27(7):7–21
Birbir M, Kallenberger W, Ilgaz A, Bailey DG (1996) Halophilic bacteria isolated from brine-cured cattle hides. J Soc Leather Technologists Chem 80:87–90
Birbir M, Kalli N, Johansson C (2002) The examination of salt quality of Sereflikochisar lake used in Turkish leather industry. J Soc Leather Technologists Chem 86:112–117
Birbir M, Ogan A, Calli B, Mertoglu B (2004) Enzymatic characteristics of extremely halophilic archaeal community in Tuzkoy Salt Mine, Turkey. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:613–621
Burns DG, Camakaris HM, Janssen PH, Dyall-Smith ML (2004) Combined use of cultivation-dependent and cultivation-independent methods indicates that members of most haloarchaeal groups in an Australian crystallizer pond are cultivable. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:5258–5265
Calli B, Mertoglu B, Tas N, Inanc B, Yenigun O, Ozturk I (2003) Investigation of variations in microbial diversity in anaerobic reactors treating landfill leachate. Water Sci Technol 48:105–112
Elevi R, Assa P, Birbir M, Ogan A, Oren A (2004) Characterization of extremely halophilic Archaea isolated from the Ayvalik saltern, Turkey. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 20:719–725
Ficker M, Krastel K, Orlicky S, Edwards E (1999) Molecular characterization of a toluene-degrading methanogenic consortium. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:5576–5585
Gónzalez C Gutierrez C, Ramirez C (1978) Halobacterium vallismortis sp. nov. An amylolytic and carbohydrate-metabolizing, extremely halophilic bacterium. Can J Microbiol 24:710–715
Gozuacık A, Ogan A, Birbir M (2004) Immobilization of halophilic Archaea to various polymeric supports and determination of their cellulase activity. In: International Workshop on Bioengineering; Problems and Perspectives. Yıldız Technical University, TUBITAK, October 20–23, Istanbul, Turkey
Grant WD, Gemmell RT, McGenity TJ (1998) Halophiles. In: Horikoshi K, Grant WD (eds) Extremophiles: microbial life in extreme environments, pp. 93–132. Wiley-Liss, Inc., New York. ISBN 0-471-02618-2
Grosskopf R, Janssen PH, Liesack W (1998) Diversity and structure of the methanogenic community in anoxic rice paddy soil microcosms as examined by cultivation and direct 16S rRNA gene sequence retrieval. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:960–969
Jukes TH, Cantor CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro HN (ed) Mammalian protein metabolism, pp 21–132. Academic Press, New York. ISBN 0-125-10604-1
Kallenberger EW (1984) Halophilic bacteria in brine curing. J Am Leather Chem Association 79:104–111
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA 2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Lane DJ (1991) 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In: Stackebrandt E, Goodfellow M (eds) Nucleic acid techniques in bacterial systematics, pp. 115–147. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester. ISBN 0-471-92906-9
Limauro D, Cannio R, Fiorentino G, Rossi M, Bartolucci S (2001) Identification and molecular characterization of an endoglucanase gene, celS, from the extremely thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus solfaraticus. Extremophiles 5:213–219
Nübel U, Engelen B, Felske A, Snaidr J, Wieshuber A, Amann RI, Ludwig W, Backhaus H (1996) Sequence heterogeneities of genes encoding 16S rRNAs in Paenibacillus polymyxa detected by temperature gradient gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol 178:5636–5643
Oren A (2000) The Order Halobacteriales. In: Dworkin M, Falkow S, Rosenberg E, Schleifer K-H, Stackebrandt E (eds) The prokaryotes: an evolving electronic resource for the microbiological community, 3rd edn, release 3.2. 25 July 2001. Springer, New York
Oren A, Gurevich P (1993) Characterization of the dominant halophilic Archaea in a bacterial bloom in the Dead Sea. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 12:249–256
Oren A, Litchfield CD (1999) A procedure for the enrichment and isolation of Halobacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 173:353–358
Oren A, Duker S, Ritter S (1996) The polar lipid composition of␣Walsby’s square bacterium. FEMS Microbiol Lett 138:135–140
Oren A, Ventosa A, Grant WD (1997) Proposed minimal standards for description of new taxa in the order Halobacteriales. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:233–238
Quesada E, Ventosa A, Rodriguez-Valera F, Ramos-Cormenzana A (1982) Types and properties of some bacteria isolated from hypersaline soils. J Appl Bacteriol 53:155–161
Rodriguez-Valera F, Ventosa A, Juez G, Imhoff F (1985) Variation of environmental features and microbial populations with salt concentrations in a multi-pond saltern. Microb Ecol 11:107–115
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) A neighbor-joining method: new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 44:406–425
Sanguinetti CJE, Dias N, Simpson AJ (1994) Rapid silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. Biotechniques 17:914–921
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ (1994) Clustal W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignments through sequence weighing position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res 22:4673–4680
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the Scientific Research Project Commission of Marmara University, Project No: 2005 FEN BSE-072/171001. We thank the Scientific Research Project Commission and the Center for Wild Plants and Water Products of Marmara University for supporting this research. Assistant Prof. Yasar Birbir, Assistant Prof. Musa. Sahin Ugur and Mr. Yemilhan Atilgan are acknowledged for supply of the samples. We express our appreciation to Mr. Hüseyin Çimen, Mrs. Didem Berber, Miss SelÇen Durmaz and Miss Hüsniye Hacioglu for their assistance. We thank also Sigma Co. (St Louis, USA) for donating the lipid detection spray reagents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birbir, M., Calli, B., Mertoglu, B. et al. Extremely halophilic Archaea from Tuz Lake, Turkey, and the adjacent Kaldirim and Kayacik salterns. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 309–316 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9223-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-006-9223-4