Abstract
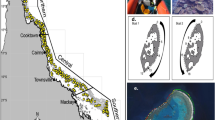
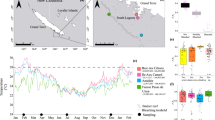
Summer bleaching of corals has been prevalent in the coastal waters of India in recent years before the onset of monsoon. Repeated bleaching of shallow water corals has changed the benthic dynamics of reef ecosystems. In the present study two locations, Wandoor and Burmanullah in South Andaman, were identified where such changes have occurred. After 3 years of study, the shift from coral domination to macroalgae and sponge is evident. In Wandoor, fleshy macroalgae (28.80%) have become a dominated benthic substrate and in Burmanullah, sponges (19.50%) have taken over much of reef space. Observation of multispecies domination of macroalgae in Wandoor and single species domination of sponges in Burmanullah has been established through this study of shallow reefs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ainsworth CH, Mumby PJ (2015) Coral–algal phase shifts alter fish communities and reduce fisheries production. Glob Change Biol 21:165–172
Bell JJ, Smith D (2004) Ecology of sponge assemblages (Porifera) in the Wakatobi region, south-east Sulawesi, Indonesia: richness and abundance. J Mar Biol Assoc 84(3):581–591
Bell JJ, Davy SK, Jones T, Taylor MW, Webster NS (2013) Could some coral reefs become sponge reefs as our climate changes? Glob Change Biol 19:2613–2624
Bell JJ, Rovellini A, Davy SK, Taylor MW, Fulton EA, Dunn MR, Bennett HM, Kandler NM, Luter HM, Webster NS (2018) Climate change alterations to ecosystem dominance: how might sponge-dominated reefs function? Ecology 99(9):1920–1931
Bennett HM, Altenrath C, Woods L, Davy SK, Webster NS, Bell JJ (2017) Interactive effects of temperature and pCO2 on sponges: from the cradle to the grave. Glob Change Biol 23:2031–2046
Bennett H, Bell JJ, Davy SK, Webster NS, Francis DS (2018) Elucidating the sponge stress response; lipids and fatty acids can facilitate survival under future climate scenarios. Glob Change Biol 24(7):3130–3144
Berkelmans R (2001) Bleaching, upper thermal limits and temperature adaptation in reef corals. James Cook University, Townsville, p 179
Birrell CL, McCook LJ, Willis BL, Diaz-Pulido GA (2008) Effects of benthic algae on the replenishment of corals and the implications for the resilience of coral reefs. Oceanogr Mar Biol Annu Rev 46:25–63
Bruno JF, Sweatman H, Precht WF, Selig ER, Schutte VGW (2009) Assessing evidence of phase shifts from coral to macroalgal dominance on coral reefs. Ecology 90(6):1478–1484
De'ath G, Fabricius K (2010) Water quality as a regional driver of coral biodiversity and macroalgae on the great barrier reef. Ecol Appl 20(3):840–850
Duckworth AR, West L, Vansach T, Stubler A, Hardt M (2012) Effects of water temperature and pH on growth and metabolite biosynthesis of coral reef sponges. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 462:67–77
English S, Wilkinson C, Baker V (1997) Survey manual for tropical marine resources, 2nd edn. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, p 390
Enochs IC, Manzello DP, Donham EM, Kolodziej G, Okano R, Johnston L, Young C, Iguel J, Edwards CB, Fox MD, Valentino L, Johnson S, Benavente D, Clark SJ, Carlton R, Burton T, Eynaud Y, Price NN (2015) Shift from coral to macroalgae dominance on a volcanically acidified reef. Nat Clim Change 5:1083–1089
Fabricius K, De’ath G, McCook L, Turak E, Williams DM, (2005) Changes in algal, coral and fish assemblages along water quality gradients on the inshore Great Barrier Reef. Mar Pollut Bull 51(1):384–398
Hill J, Wilkinson C (2004) Methods for ecological monitoring of coral reefs. Australian Institute of Marine Science, Townsville, p 117
Hoegh-Guldberg O, Mumby PJ, Hooten AJ, Steneck RS, Greenfield P, Gomez E, Harvell CD, Sale PF, Edwards AJ, Caldeira K, Knowlton N (2007) Coral reefs under rapid climate change and ocean acidification. Science 318(5857):1737–1742
Hughes TP, Rodrigues MJ, Bellwood DR, Ceccarelli D, Hoegh-Guldberg O, McCook L, Moltschaniwskyj N, Pratchett MS, Steneck RS, Willis B (2007) Phase shifts, herbivory, and the resilience of coral reefs to climate change. Curr Biol 17(4):360–365
Immanuel T, Krishnan P, Raghunathan C (2015) An updated report on the diversity of marine sponges of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. In: Venkataraman K, Sivaperuman C (eds) Marine faunal diversity in India: taxonomy, ecology and conservation. Academic, Elsevier Inc, pp 3–13
Knapp ISS, Williams GJ, Bell JJ (2016) Temporal dynamics and persistence of sponge assemblages in a Central Pacific atoll lagoon. Mar Ecol 37(5):1147–1153
Krishnan P, Roy SD, George G, Srivastava RC, Anand A, Murugesan S, Kaliyamoorthy M, Vikas N, Soundararajan S (2011) Elevated sea surface temperature during May 2010 induces mass bleaching of corals in the Andaman. Curr Sci 100(1):111–117
Kuffner IB, Walters LJ, Becerro MA, Paul VJ, Ritson-Williams R, Beach KS (2006) Inhibition of coral recruitment by macroalgae and cyanobacteria. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 323:107–117
Marimuthu N, Wilson JJ, Vinithkumar NV, Kirubagaran R (2013) Coral reef recovery status in South Andaman Islands after the bleaching event 2010. J Ocean Univ China 12(1):91–96
McManus JW, Meńez LAB, Kesner-Reyes KN, Vergara SG, Ablan MC (2000) Coral reef fishing and coral-algal phase shifts: implications for global reef status. ICES J Mar Sci 57:572–578
Nugues MM, Smith GW, Hooidonk RJ, Seabra MI, Bak RP (2004) Algal contact as a trigger for coral disease. Ecol Lett 7(10):919–923
Powell AL, Hepburn LJ, Smith DJ, Bell JJ (2010) Patterns of sponge abundance across a gradient of habitat quality in the Wakatobi Marine National Park, Indonesia. Open Mar Biol J 4:31–38
Smith JE, Shaw M, Edwards RA, Obura D, Pantos O, Sala E, Sandin SA, Smriga S, Hatay M, Rohwer FL (2006) Indirect effects of algae on coral: algae-mediated, microbe-induced coral mortality. Ecol Lett 9(7):835–845
Funding
No funding source for this study as this study was a part of PhD work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malakar, B., Venu, S., Samuel, V.D. et al. Increasing signs of degradation of shallow water coral reefs due to repeated bleaching and spatial competition among benthic substrates. Wetlands Ecol Manage 29, 669–675 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-020-09744-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11273-020-09744-x