Abstract
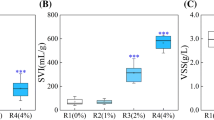
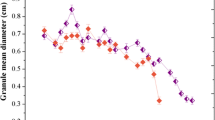
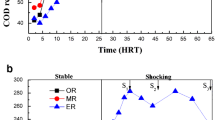
Effects of sludge retention times (SRTs) on system performance, microbial structure and quorum sensing in an activated sludge bioreactor were investigated. SRTs significantly (ANOVA, p < 0.05) affected the total inorganic nitrogen (TIN) removal. Significant (Tukey's HSD, p < 0.05) higher TIN removal efficiency was achieved at the SRT of 5 days (72.3%) than at SRTs of 15 (71.3%) and 25 (67.7%) days, respectively. This could be partially explained by the effect of SRT on the sludge properties, abundance of denitrifying bacterium and genes, and quorum sensing (QS) signals (e.g., N‐acyl‐L‐homoserine lactones (AHLs)). Specifically, a short SRT resulted in a high protein content in tightly bound extracellular polymeric substances (TEPS), which could be an indicator for compact sludge structure. Furthermore, denitrifying bacterium including Candidatus Competibacter, Thauera and Zoogloea and denitrifying genes including napAB, nirS, norB and nosZ were enriched at a short SRT. Moreover, N-decanoyl-L-homoserine lactone and N-3-(oxododecanoyl)-homoserine lactone were the dominating AHLs in the water, EPS and biomass phases of activated sludge and a particular high content of these AHLs was found in sludge at a short SRT. Based on the metagenomic results, functional microorganisms carried both nitrogen metabolism genes and AHLs synthesis genes, allowing their interactions with other autotrophs or heterotrophs through nitrogen conversion and QS signal exchange. Identification of QS and its possible roles in activated sludge systems under different operational conditions may provide potential strategies through QS regulation for enhancing system performance and microbial aggregation capability.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Apha, A. (1998). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. American Public Health Association Inc.
Cao, R., Ji, Y., Han, T., Deng, J., Zhu, L., & Xu, X. (2021). The stability of aerobic granular sludge under low energy consumption: Optimization of the granular size distribution by a novel internal component. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 7, 1125–1136.
Chen, H., Li, A., Cui, C., Ma, F., Cui, D., Zhao, H., Wang, Q., Ni, B., & Yang, J. (2019). AHL-mediated quorum sensing regulates the variations of microbial community and sludge properties of aerobic granular sludge under low organic loading. Environment International, 130, 104946.
Cui, X., Ruan, X., Yin, J., Wang, M., Li, N., & Shen, D. (2021). Regulation of las and rhl Quorum Sensing on Aerobic Denitrification in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. Current Microbiology, 78, 659–667.
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Rebers, P., & t. & Smith, F. (1956). Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry, 28, 350–356.
Feng, Z., Gu, M., Sun, Y., & Wu, G. (2021). Potential microbial functions and quorum sensing systems in partial nitritation and anammox processes. Water Environment Research, 93, 1562–1575.
Feng, Z., Sun, Y., Li, T., Meng, F., & Wu, G. (2019). Operational pattern affects nitritation, microbial community and quorum sensing in nitrifying wastewater treatment systems. Science of the Total Environment, 677, 456–465.
Figdore, B. A., Stensel, H. D., & Winkler, M.-K.H. (2018). Bioaugmentation of sidestream nitrifying-denitrifying phosphorus-accumulating granules in a low-SRT activated sludge system at low temperature. Water Research, 135, 241–250.
Han, H., Li, J., Zhang, J., Peng, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, K., Zhang, Y., Wei, P. & Luo, R. (2021). Enhancing the treatment performance of partial denitrification/Anammox process at high nitrogen load: Effects of immobilized strain HFQ8C/N on the sludge characteristics. Bioresource Technology, 125870.
Hatree, E. (1972). Determination of protein: A modification of the Lowry method that gives a linear photometric response. Analytical Biochemistry., 48, 422–427.
Huang, J., Yi, K., Zeng, G., Shi, Y., Gu, Y., Shi, L., & Yu, H. (2019). The role of quorum sensing in granular sludge: Impact and future application: A review. Chemosphere, 236, 124310.
Li, T., Guo, F., Lin, Y., Li, Y., & Wu, G. (2019). Metagenomic analysis of quorum sensing systems in activated sludge and membrane biofilm of a full-scale membrane bioreactor. Journal of Water Process Engineering, 32, 100952.
Li, Y.-C., & Zhu, J.-R. (2014). Role of N-acyl homoserine lactone (AHL)-based quorum sensing (QS) in aerobic sludge granulation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 98, 7623–7632.
Lin, H., Ma, R., Hu, Y., Lin, J., Sun, S., Jiang, J., Li, T., Liao, Q., & Luo, J. (2020). Reviewing bottlenecks in aerobic granular sludge technology: Slow granulation and low granular stability. Environmental Pollution, 263, 114638.
Liu, X., Liu, R., Yang, Q., Cui, B., Wu, W., Zhao, X., & Wang, Y. (2021). Achieving and control of partial denitrification in anoxic-oxic process of real municipal wastewater treatment plant. Bioresource Technology, 341, 125765.
Lücker, S., Schwarz, J., Gruber-Dorninger, C., Spieck, E., Wagner, M., & Daims, H. (2015). Nitrotoga-like bacteria are previously unrecognized key nitrite oxidizers in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. The ISME Journal, 9, 708–720.
Ma, H., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Hu, H., Ren, H., Geng, J., & Ding, L. (2018). The diversity, distribution and function of N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) in industrial anaerobic granular sludge. Bioresource Technology, 247, 116–124.
Mellbye, B. L., Giguere, A. T., Bottomley, P. J., & Sayavedra-Soto, L. A. (2016). Quorum quenching of Nitrobacter winogradskyi suggests that quorum sensing regulates fluxes of nitrogen oxide(s) during nitrification. MBio, 7(5), e01753–16.
Moreno-Gámez, S., Sorg, R. A., Domenech, A., Kjos, M., Weissing, F. J., van Doorn, G. S., & Veening, J.-W. (2017). Quorum sensing integrates environmental cues, cell density and cell history to control bacterial competence. Nature Communications, 8, 1–12.
Ni, B. J., Xie, W. M., Chen, Y. P., Fang, F., Liu, S. Y., Ren, T. T., Sheng, G. P., Yu, H. Q., Liu, G., & Tian, Y. C. (2011). Heterotrophs grown on the soluble microbial products (SMP) released by autotrophs are responsible for the nitrogen loss in nitrifying granular sludge. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 108, 2844–2852.
Redfield, R. J. (2002). Is quorum sensing a side effect of diffusion sensing? Trends in Microbiology, 10, 365–370.
Ruan, X., Yin, J., Cui, X., Li, N., & Shen, D. (2020). Bioaugmentation and quorum sensing disruption as solutions to increase nitrate removal in sequencing batch reactors treating nitrate-rich wastewater. Journal of Environmental Sciences, 98, 179–185.
Sakuragi, Y., & Kolter, R. (2007). Quorum-sensing regulation of the biofilm matrix genes (pel) of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology, 189, 5383–5386.
Sheng, G.-P., Yu, H.-Q., & Li, X.-Y. (2010). Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnology Advances, 28, 882–894.
Smolders, G., Van der Meij, J., Van Loosdrecht, M., & Heijnen, J. (1994). Model of the anaerobic metabolism of the biological phosphorus removal process: Stoichiometry and pH influence. Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 43, 461–470.
Sun, Y., Guan, Y., Pan, M., Zhan, X., Hu, Z., & Wu, G. (2017). Enhanced biological nitrogen removal and N2O emission characteristics of the intermittent aeration activated sludge process. Reviews in Environmental Science and Bio/technology, 16, 761–780.
Sun, Y., Guan, Y., Wang, D., Liang, K., & Wu, G. (2018a). Potential roles of acyl homoserine lactone based quorum sensing in sequencing batch nitrifying biofilm reactors with or without the addition of organic carbon. Bioresource Technology, 259, 136–145.
Sun, Y., Guan, Y., Zeng, D., He, K., & Wu, G. (2018b). Metagenomics-based interpretation of AHLs-mediated quorum sensing in Anammox biofilm reactors for low-strength wastewater treatment. Chemical Engineering Journal, 344, 42–52.
Sun, Y., He, K., Yin, Q., Echigo, S., Wu, G., & Guan, Y. (2018c). Determination of quorum-sensing signal substances in water and solid phases of activated sludge systems using liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Journal of Environmental Sciences., 69, 85–94.
Tan, C. H., Koh, K. S., Xie, C., Tay, M., Zhou, Y., Williams, R., Ng, W. J., Rice, S. A., & Kjelleberg, S. (2014). The role of quorum sensing signalling in EPS production and the assembly of a sludge community into aerobic granules. The ISME Journal, 8, 1186–1197.
Wang, N., Gao, J., Liu, Y., Wang, Q., Zhuang, X. & Zhuang, G. (2021). Realizing the role of N-acyl-homoserine lactone-mediated quorum sensing in nitrification and denitrification: A review. Chemosphere, 129970.
Wang, J., Ding, L., Li, K., Huang, H., Hu, H., Geng, J., & Ren, H. (2018). Estimation of spatial distribution of quorum sensing signaling in sequencing batch biofilm reactor (SBBR) biofilms. Science of the Total Environment, 612, 405–414.
Wang, J., Liu, Q., Hu, H., Wu, B., Zhang, X. X., & Ren, H. (2019b). Insight into mature biofilm quorum sensing in full-scale wastewater treatment plants. Chemosphere, 234, 310–317.
Wang, J., Liu, Q., Li, X., Ma, S., Hu, H., Wu, B., & Ren, H. (2020a). In-situ monitoring AHL-mediated quorum-sensing regulation of the initial phase of wastewater biofilm formation. Environment International, 135, 105326.
Wang, J., Liu, Q., Wu, B., Zhao, F., Ma, S., Hu, H., Zhang, X., & Ren, H. (2019a). Quorum sensing signaling distribution during the development of full-scale municipal wastewater treatment biofilms. Science of the Total Environment, 685, 28–36.
Wang, J., Zhou, J., Wang, Y., Wen, Y., He, L., & He, Q. (2020b). Efficient nitrogen removal in a modified sequencing batch biofilm reactor treating hypersaline mustard tuber wastewater: The potential multiple pathways and key microorganisms. Water Research, 177, 115734.
Waters, C. M., & Bassler, B. L. (2005). Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 21, 319–346.
Xiong, F., Zhao, X., Wen, D., & Li, Q. (2020). Effects of N-acyl-homoserine lactones-based quorum sensing on biofilm formation, sludge characteristics, and bacterial community during the start-up of bioaugmented reactors. Science of the Total Environment, 735, 139449.
Yu, H., Xu, G., Qu, F., Li, G., & Liang, H. (2016). Effect of solid retention time on membrane fouling in membrane bioreactor: From the perspective of quorum sensing and quorum quenching. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 100, 7887–7897.
Zhang, Z., Yu, Z., Wang, Z., Ma, K., Xu, X., Alvarezc, P. J., & Zhu, L. (2019). Understanding of aerobic sludge granulation enhanced by sludge retention time in the aspect of quorum sensing. Bioresource Technology, 272, 226–234.
Zheng, M., Li, S., Ni, G., Xia, J., Hu, S., Yuan, Z., Liu, Y., & Huang, X. (2020). Critical factors facilitating candidatus nitrotoga to be prevalent nitrite-oxidizing bacteria in activated sludge. Environmental Science & Technology, 54, 15414–15423.
Funding
No funds, grants, or other support was received.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Tianle Li carried out the experiments and wrote the manuscript. Bo Li and Guangxue Wu revised the manuscript. Yuepeng Sun conceived the study and were in charge of overall direction and planning. All authors discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, T., Li, B., Sun, Y. et al. Insights into the Effect of Sludge Retention Times on System Performance, Microbial Structure and Quorum Sensing in an Activated Sludge Bioreactor. Water Air Soil Pollut 233, 230 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05716-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-022-05716-4