Abstract
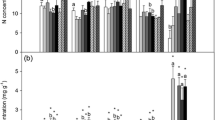
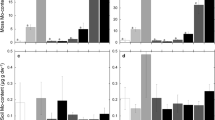
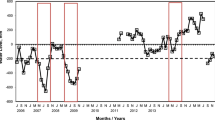
We studied the effects of N deposition (0, 10, 20 and 50 kg N ha−1 year−1) on cover and physiology of Pleurochaete squarrosa, a terricolous moss from semiarid Mediterranean ecosystems. We also investigated the effects of N fertilization under competition with vascular plants or under water stress. Under greenhouse conditions, vascular plant competition reduced moss cover, and there was a significant interaction between N and competition. Water stress reduced moss cover under high and low competition conditions. Nitrogen fertilization increased moss cover irrespectively of the N dose supplied at low competition conditions. Under field conditions, N deposition affected moss physiology but not cover. Most of the physiological variables analyzed responded to N deposition, although the response of some of them was saturated with only 10 kg N ha−1 year−1 over the background (nitrate reductase; phosphomonoesterase; tissue N and K+). The response of indicators such as chlorophyll a and lutein contents did not show any evidence of saturation, which probably makes them the best candidates in monitoring programs. Based on the data provided, the applicability of the phosphomonoesterase can also be considered. In addition, the importance of taking into account the existence of superimposed environmental gradients (such as those in soil mineral N content) interacting with the response of P. squarrosa to predict impacts of N deposition has been demonstrated. Therefore, detailed soil surveys and integrative physiological evaluations will be required to produce a significantly better picture of the effects of N deposition on Mediterranean ecosystems along extant N deposition gradients.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts, R., Wallen, B., & Malmer, N. (1992). Growth-limiting nutrients in Sphagnum-dominated bogs subject to low and high nitrogen supply. The Journal of Ecology, 80, 131–140.
Arróniz-Crespo, M., Leake, J. R., Horton, P., & Phoenix, G. K. (2008). Bryophyte physiological responses to, and recovery from, long-term nitrogen deposition and phosphorous fertilisation in acidic grassland. New Phytologist, 180, 864–874.
Aude, E., & Ejrnæs, R. (2005). Bryophyte colonization in experimental microcosms: the role of nutrients, defoliation and vascular vegetation. Oikos, 109, 323–330.
Bignal, K. L., Ashmore, M. R., & Headley, A. D. (2008). Effects of air pollution from road transport on growth and physiology of six transplanted bryophyte species. Environmental Pollution, 156, 332–340.
Bobbink, R., Hicks, K., Galloway, J., Spranger, T., Alkemade, R., Ashmore, M., et al. (2010). Global assessment of nitrogen deposition effects on terrestrial plant diversity: A synthesis. Ecological Applications, 20, 30–59.
Bowker, M. A., Koch, G. W., Belnap, J., & Johnson, N. C. (2008). Nutrient availability affects pigment production but not growth in lichens of biological soil crusts. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 40, 2819–2826.
Britton, A. J., & Fisher, J. M. (2007). Terricolous alpine lichens are sensitive to both load and concentration of applied nitrogen and have potential as bioindicators of nitrogen deposition. Environmental Pollution, 158, 1296–1302.
Carfrae, J. A., Sheppard, L. J., Raven, J. A., Leith, I. D., & Crossley, A. (2007). Potassium and phosphorus additions modify the response of Sphagnum capillifolium growing on a Scottish ombrotrophic bog to enhanced nitrogen deposition. Applied Geochemistry, 22, 1111–1121.
Christmas, M., & Whitton, B. A. (1998). Phosphorus and aquatic bryophytes in the Swale-Ouse river system, north-east England. 1. Relationship between ambient phosphatase, internal N:P ratio and surface phosphatase activity. The Science of the Total Environment, 210(211), 389–399.
DeLuca, T. H., Zackrisson, O., Gentili, F., Sellstedt, A., & Nilsson, M.-C. (2007). Ecosystem control son nitrogen fixation in boreal feather moss communities. Oecologia, 152, 121–130.
Duprè, C., Stevens, C. J., Ranke, T., Bleekers, A., Peppler-Lisbach, C., Gowing, D. J. G., et al. (2010). Changes in species richness and composition in European acidic grasslands over the past 70 years: The contribution of cumulative atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Global Change Biology, 16, 344–357.
Esposito, A., Mazzoleni, S., & Strumia, S. (1999). Post-fire bryophyte dynamics in Mediterranean vegetation. Journal of Vegetation Science, 10, 261–268.
Fenn, M. E., Baron, J. S., Allen, E. B., Rueth, H. M., Nydick, K. R., Geiser, L., et al. (2003). Ecological effects of nitrogen deposition in the Western United States. BioScience, 53, 404–420.
Hogan, E. J., Minnullina, G., Sheppard, L. J., Leith, I. D., & Crittenden, P. D. (2010). Response of phosphomonoesterase activity in the lichen Cladonia portentosa to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment in a field manipulation experiment. New Phytologist, 186, 926–933.
Hogan, E. J., Minullina, G., Smith, R. I., & Crittenden, P. D. (2010). Effects of nitrogen enrichment on phosphatase and nitrogen: Phosphorus relationships in Cladonia portentosa. New Phytologist, 186, 911–925.
Manninen, S., Woods, C., Leith, I. D., & Sheppard, L. J. (2011). Physiological and morphological effects of long-term ammonium or nitrate deposition on the green and red (shade and open grown) Sphagnum capillifolium. Environmental and Experimental Botany, 72, 140–148.
Ochoa-Hueso, R. (2012). Efectos de la deposición atmosférica de nitrógeno en ecosistemas mediterráneos. Doctoral thesis.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., & Manrique, E. (2010). Nitrogen fertilization and water supply affect germination and plant establishment of the soil seed bank present in a semi-arid Mediterranean scrubland. Plant Ecology, 210, 263–273.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., & Manrique, E. (2011). Effects of nitrogen deposition and soil fertility on cover and physiology of Cladonia foliacea (Huds) Willd a lichen of biological soil crusts from Mediterranean Spain. Environmental Pollution, 159, 449–457.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., Allen, E. B., Branquinho, C., Cruz, C., Dias, T., Fenn, M. E., et al. (2011a). Nitrogen deposition effects on Mediterranean-type ecosystems: An ecological assessment. Environmental Pollution, 159, 2265–2279.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., Hernandez, R. R., Pueyo, J. J., & Manrique, E. (2011b). Spatial distribution and physiology of biological soil crusts from semi-arid central Spain are related to soil chemistry and shrub cover. Soil Biology and Biochemistry, 43, 1894–1901.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., Paradela, C., Pérez-Corona, M.E., & Manrique, E. Pigment ratios of the Mediterranean bryophyte Pleurochaete squarrosa respond to simulated nitrogen deposition. In: Sutton, M et al. Nitrogen deposition, critical loads and biodiversity. Springer. In press.
Ochoa-Hueso, R., Mejías-Sanz, V., Pérez-Corona, M. E., & Manrique, E. (2013). Nitrogen deposition effects on tissue chemistry and phosphatase activity in Cladonia foliacea (Huds.) Willd. A common terricolous lichen of semi-arid Mediterranean shrublands. Journal of Arid Environments. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2012.07.007.
Opelt, K., & Berg, G. (2004). Diversity and antagonistic potential of bacteria associated with bryophytes from nutrient-poor habitats of the Baltic Sea coast. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 70, 6569–6579.
Pearce, I. S. K., Woodin, S. J., & van der Wal, R. (2003). Physiological and growth responses of the montane bryophyte Racomitrium lanuginosum to atmospheric nitrogen deposition. New Phytologist, 160, 145–155.
Pearce, I. S. K., & van der Wal, R. (2002). Effects of nitrogen deposition on growth and survival of montane Racromitrium lanuginosum heath. Biological Conservation, 104, 83–89.
Pinho, P., Dias, T., Cruz, C., Tang, Y. S., Sutton, M. A., Martins-Louçao, M. A., et al. (2011). Using lichen functional diversity to assess the effects of atmospheric ammonia in Mediterranean woodlands. Journal of Applied Ecology, 48, 1107–1116.
Rivas-Martínez, S. (1987). Memoria del mapa de series de vegetación de España. Madrid: ICONA.
Ruiz-Díez, B., Fajardo, S., Puertas-Mejía, M. A., de Felipe, M. R., & Fernández-Pascual, M. (2009). Stress tolerance, genetic analysis and symbiotic properties of root-nodulating bacteria isolated from Mediterranean shrubs in Central Spain. Archives of Microbiology, 191, 35–46.
Spagnuolo, V., Muscariello, L., Cozzolino, S., Cobianchi, R., & Giordano, S. (2007). Ubiquitous genetic diversity in ISSR markers between and within populations of the asexually producing moss Pleurochaete squarrosa. Plant Ecology, 188, 91–101.
Startsev, N. A., & Lieffers, V. J. (2007). Emission of nitrogen gas, nitrous oxide, and carbon dioxide on rehydration of dry feathermosses. SSSAJ, 71, 214–218.
Stevens, C., Dise, N. B., Mountford, J. O., & Gowing, D. J. (2004). Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science, 303, 1876–1879.
Vourlitis, G. L., Pasquini, S. C., & Mustard, R. (2009). Effects of dry-season N input on the productivity and N storage of Mediterranean-type shrublands. Ecosystems, 12, 473–488.
Acknowledgments
ROH was financially supported by an FPU grant of the Spanish Ministerio de Educación y Ciencia (AP2006-04638). We were also supported by national projects (CGL-2009-11015 and Remedinal-2 S2009/AMB-1783). We specially thank Prof. Alfredo Polo and Dr. Juan Carlos García-Gil for technical advice and their kind permission to use the spectrophotometer. Finally, we are very grateful to our editor (Dr. Trevors) and two anonymous referees, who greatly contributed to improve the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochoa-Hueso, R., Manrique, E. Effects of Nitrogen Deposition on Growth and Physiology of Pleurochaete squarrosa (Brid.) Lindb., a Terricolous Moss from Mediterranean Ecosystems. Water Air Soil Pollut 224, 1492 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1492-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-013-1492-6