Abstract
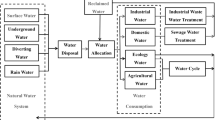
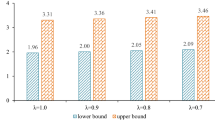
In this research, a large-scale inexact optimization method was developed for the conjunctive use management of a watershed-lake water distribution system. The modeling framework has the advantages in taking into account the water balance of multi-reservoirs, satisfying the municipal industrial and agricultural water demands in the multi-period context, reflecting the relationship among multi-reservoirs, multiple water related projects, and maintaining the operational rules of certain lake levels. Moreover, such a method can also handle the uncertainty expressed as fuzzy membership functions through integrating the fuzzy credibility chance-constrained programming. The developed method was applied to the conjunctive use management of water resources in the lake Dianchi watershed, China. Cost-effective water allocation schemes for the groundwater project and the water transfer project, and optimal operational rules for the lake and multiple reservoirs were successfully obtained. Also, the annual water balance of the watershed-lake system and the system cost of the conjunctive water use were investigated and analyzed under multiple credibility levels of meeting the water demands for municipal, industrial and agricultural users.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cai YP, Huang GH, Yang ZF, Tan Q (2009) Identification of optimal strategies for energy management systems planning under multiple uncertainties. Appl Energy 86:480–495
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q, Yang Z (2011a) An integrated approach for climate-change impact analysis and adaptation planning under multi-level uncertainties. Part I: Methodology. Renew Sust Energ Rev 15:2779–2790
Cai YP, Huang GH, Tan Q, Chen B (2011b) Identification of optimal strategies for improving eco-resilience to floods in ecologically vulnerable regions of a wetland. Ecol Model 222:360–369
Chen YW, Chang LC, Huang CW, Chu HJ (2013) Applying genetic algorithm and neural network to the conjunctive use of surface and subsurface water. Water Resour Manag 27:4731–4757
Chen CW, Wei CC, Liu HJ, Hsu NS (2014) Application of neural networks and optimization model in conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater. Water Resour Manag 28:2813–2832
Chiu Y-C, Nishikawa T, Yeh WWG (2010) Optimal pump and recharge management model for nitrate removal in the warren groundwater basin, California. J Water Resour Plann Manage-Asce 136:299–308
Dai C, Cai YP, Li YP, Sun W, Wang XW, Guo HC (2014) Optimal strategies for carbon capture, utilization and storage based on an inexact mλ-measure fuzzy chance-constrained programming. Energy 78:465–478
Dai C, Cai YP, Liu Y, Wang WJ, Guo HC (2015) A generalized interval fuzzy chance-constrained programming method for domestic wastewater management under uncertainty – a case study of Kunming, China. Water Resour Manag 29:3015–3036
Dai C, Tan Q, Lu WT, Liu Y, Guo HC (2016) Identification of spatial water transfer schemes for restoration of a eutrophic lake in China: an integrated simulation-optimization method. Ecol Eng. doi:10.1016/j.ecoleng.2016.06.080
Daneshmand F, Karimi A, Nikoo MR, Bazargan-Lari MR, Adamowski J (2014) Mitigating socio-economic-environmental impacts during drought periods by optimizing the conjunctive management of water resources. Water Resour Manag 28:1517–1529
Fowe T, Nouiri I, Ibrahim B, Karambiri H, Paturel JE (2015) OPTIWAM: an intelligent tool for optimizing irrigation water management in coupled reservoir-groundwater systems. Water Resour Manag 29:3841–3861
Hu Q, Huang G, Cai Y, Sun W (2014) Planning of electric power generation systems under multiple uncertainties and constraint-violation levels. Journal of Environmental Informatics 23:55–64
Huang X (2006) Credibility-based chance-constrained integer programming models for capital budgeting with fuzzy parameters. Inf Sci 176:2698–2712
Iwamura K, Liu B (1998) Chance constrained integer programming models for capital budgeting in fuzzy environments. J Oper Res Soc 49:854–860
Jafarzadegan K, Abed-Elmdoust A, Kerachian R (2014) A stochastic model for optimal operation of inter-basin water allocation systems: a case study. Stoch Env Res Risk A 28:1343–1358
Karsak EE, Kuzgunkaya O (2002) A fuzzy multiple objective programming approach for the selection of a flexible manufacturing system. Int J Prod Econ 79:101–111
Liu B (2006) A survey of credibility theory. Fuzzy Optim Decis Making 5:387–408
Liu B, Liu YK (2002) Expected value of fuzzy variable and fuzzy expected value models. IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst 10:445–450
Liu H, Gaboury B, Liu T, Liu Y, Guo H (2015) An integrated system dynamics model developed for managing lake water quality at the watershed scale. J Environ Manag 155:11–23
Montazar A, Riazi H, Behbahani SM (2010) Conjunctive water use planning in an irrigation command area. Water Resour Manag 24:577–596
Parsapour-Moghaddam P, Abed-Elmdoust A, Kerachian R (2015) A heuristic evolutionary game theoretic methodology for conjunctive use of surface and groundwater resources. Water Resour Manag 29:3905–3918
Safavi HR, Chakraei I, Kabiri-Samani A, Golmohammadi MH (2013) Optimal reservoir operation based on conjunctive use of surface water and groundwater using neuro-fuzzy systems. Water Resour Manag 27:4259–4275
Tabari MMR, Yazdi A (2014) Conjunctive use of surface and groundwater with inter-basin transfer approach: case study Piranshahr. Water Resour Manag 28:1887–1906
Tan Q, Huang GH, Cai YP (2011) Radial interval chance-constrained programming for agricultural non-point source water pollution control under uncertainty. Agric Water Manag 98:1595-1606
Troin M, Vallet-Coulomb C, Sylvestre F, Piovano E (2010) Hydrological modelling of a closed lake (Laguna Mar Chiquita, Argentina) in the context of twentieth century climatic changes. J Hydrol 393:233–244
Zhang YM, Huang GH (2011) Optimal water resource planning under fixed budget by interval-parameter credibility constrained programming. Eng Optim 43:879–889
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by the Major Science and Technology Program for Water Pollution Control and Treatment of China (2013ZX07102-006), and the National Science Foundation for Innovative Research Group (No. 51121003 and 51522901). Also, the authors are grateful to the editors and the anonymous reviewers for their insightful comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, C., Cai, Y.P., Lu, W.T. et al. Conjunctive Water Use Optimization for Watershed-Lake Water Distribution System under Uncertainty: a Case Study. Water Resour Manage 30, 4429–4449 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1430-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1430-7