Abstract
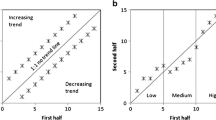
There are trend identification methodologies in the literature but they have three crucial points that should be cared with great attention in practical applications. These points are that the available time series should have independent serial correlation structure, Gaussian (normal) distribution and monotonic trend fitting to whole time series through the least square technique. The existing methods consider the whole duration of the time series and try to identify a monotonic trend in increasing or decreasing forms. This paper presents partial trend methodology as an innovative and simple trend identification method, which yields low, medium and high cluster trends separately. It provides the opportunity to segregate between the low, high and medium flow trends and their relative intensities, durations as well as magnitudes. The application of the partial trend methodology is presented for 7 precipitation stations from 7 different sub-climatic regions of Turkey leading to spatial and temporal trend interpretations.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abarghouei HB, Zarch MAA, Dastorani MT, Zarch MF (2011) The survey of climatic drought trend in Iran. Stoch Env Res Risk A 25(6):851–863
Bayazıt M, Bihrat Ö (2007) To pre-whiten or not to pre-whiten in trend analysis. Hydrol Sci J 52(4):611624
Becker S, Gemmer M, Jiang T (2006) Spatiotemporal analysis of precipitation trends in the Yangtze River catchment. Stoch Env Res Risk A 20(6):435–444
Calanca P, Roesch A, Jasper K, Wild M (2006) Global warming and the summertime evapotranspiration regime in the Alpine region. Climate Change 79(1–2):65–78
Cou L, Lettenmaier DP, Alberti M, Richey JE (2009) Effects of a century of land cover and climate change on the hydrology of the Puget Sound basin. Hydrol Process 23(6):907–933
Fu G, Charles SP, Viney NR, Chen SL, Wu JQ (2007) Impacts of climate variability on stream-flow in Yellow River. Hydrol Process 21(25):3431–3439
Jyrkama MI, Sykes (2007) The impact of climate change on spatially varying groundwater recharge in the Grand River watershed (Ontario). J Hydrol 338(3–4):237–250
Kendall MG (1975) Rank correlation methods. Oxford Univ Press, New York
Mann HB (1945) Nonparametric tests against trend’. Econometrica 13:245–259
Onyutha C (2015) Identification of sub-trends from hydro-meteorological series. Stoch Env Res Risk A
Sen PK (1968) Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J Am Stat Assoc 63:1379–1389
Şen Z (2009) Spatial modeling principles in earth sciences. Springer, London, 351 pp
Şen Z (2012) An innovative trend analysis methodology. ASCE J Hydrol Eng 17(9):1042–1046
Şen Z (2014) Trend identification simulation and application. J Hydrol Eng 19(3):635–642
Tao H, Fredric K, Men C, Zhao J (2014) Trends in extreme temperature indices in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Stoch Env Res Risk A 28(6):1543–1553
Xiong KG, Yang J, Wan SQ, Feng GL, Hu JG (2009) Monte Carlo simulation of the record breaking high temperature events. Environ Sci Technol 37(14):3048–3054
Yue S, Wang CY (2004) The Mann-Kendal test modified by effective sample size to detect trend in serially correlated hydrological series. Water Retour Manag 18:201–218
Yue S, Pylon P, Calvarias G (2002) Power of Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J Hydrol 259:254–271
Zhao G, Li E, Mu X, Wen Z, Ray burg S (2015) Changing trends and regime shift of streamflow in the Yellow River basin. Stoch Env Res Risk A 29(5):1331–1343
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Öztopal, A., Şen, Z. Innovative Trend Methodology Applications to Precipitation Records in Turkey. Water Resour Manage 31, 727–737 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1343-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-016-1343-5