Abstract
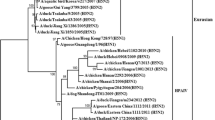
We performed whole genome sequencing of 22 H9N2 avian influenza viruses (AIV) isolated from domestic laying hens on farms between 2005 and 2008, and compared the sequences with viruses previously reported in Asia. A previous study revealed that two antigenically distinct sublineages were established within the MS96 lineage by antigenic drift since the first H9N2 AIV outbreak in South Korea. We designated them as the 01310-like lineage and the 116/04-like lineage. Since late 2004, most identified isolates in Korea have belonged to the 116/04-like lineage, however, in this study we found that six among twenty-two isolates were belonged to 01310-like lineage, indicating that the genetic divergence is still occurring after 2004. Furthermore, it is noteworthy that five isolates among the defined 01310-like lineage had a 24 amino acid deletion in the neuraminidase stalk region, which were not in any other H9N2 isolates previously reported. The internal genes analysis demonstrated extensive reassortment events among isolates from poultry farms, live bird markets, and wild birds, and multiple new genotypes were identified. We identified several features of gene evolution in H9N2 AIV suggesting that the long-term H9N2 AIV surveillance study should be continued in South Korea.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.A. Lamb, R.M. Krug, Orthomyxoviridae: the viruses and their replication, in Fields virology, ed. by D.M. Knipe, P.M. Howle (Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001), pp 1487–1532
R.J. Webby, R.G. Webster, Emergence of influenza A viruses. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356, 1817–1828 (2001)
D.A. Steinhauer, Role of hemagglutinin cleavage for the pathogenicity of influenza virus. Virology 256, 1–20 (1999)
A. Vines, K. Wells, M. Matrosovich, M.R. Castrucci, T. Ito, Y. Kawaoka, The role of influenza A virus hemagglutinin residues 226 and 228 in receptor specificity and host range restriction. J Virol 72, 7626–7631 (1998)
R.W. Compans, N.J. Dimmock, H. Meier-Ewert, Effect of antibody to neuraminidase on the maturation and hemagglutinating activity of an influenza A2 virus. J Virol 4, 528–534 (1969)
M.R. Castrucci, Y. Kawaoka, Biologic importance of neuraminidase stalk length in influenza virus. J Virol 67, 759–764 (1993)
M. Matrosovich, N. Zhou, Y. Kawaoka, R. Webster, The surface glycoproteins of H5 influenza viruses isolated from humans, chickens, and wild aquatic birds have distinguishable properties. J Virol 73, 1146–1155 (1999)
H. Zhou, Z. Yu, Y. Hu, J. Tu, W. Zou, Y. Peng, J. Zhu, Y. Li, A. Zhang et al., The special neuraminidase stalk-motif responsible for increased virulence and pathogenesis of H5N1 influenza A virus. PLoS ONE 4(7), e6277 (2009)
C. Li, K. Yu, G. Tian, D. Yu, L. Liu, B. Jing, J. Ping, H. Chen, Evolution of H9N2 influenza viruses from domestic poultry in Mainland China. Virology 340, 70–83 (2005)
H.J. Moon, M.S. Song, D.J. Cruz et al., Active reassortment of H9 influenza viruses between wild birds and live-poultry markets in Korea. Arch Virol 155, 229–241 (2010)
D.J. Alexander, A review of avian influenza in different bird species. Vet Microbiol 74, 3–13 (2000)
K. Naeem, A. Ullah, R.J. Manvell, D.J. Alexander, Avian influenza A subtype H9N2 in poultry in Pakistan. Vet Rec 145, 560 (1999)
C.W. Lee, C.S. Song, Y.J. Lee, I.P. Mo, M. Garcia, D.L. Suarez, S.J. Kim, Sequence analysis of the hemagglutinin gene of H9N2 Korean avian influenza viruses and assessment of the pathogenic potential of isolate MS96. Avian Dis 44, 527–535 (2000)
Halvorson DA, Frame DD, Friendshuh AJ, Shaw DP (1997) Outbreaks of low pathogenicity avian influenza in USA. In: Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on avian influenza, 29–31 May 1997. US Animal Health Association, Athens, pp 36–46
Y.J. Guo, S. Krauss, D.A. Senne, I.P. Mo, K.S. Lo, X.P. Xiong, M. Norwood, K.F. Shortridge, R.G. Webster, Characterization of the pathogenicity of members of the newly established H9N2 influenza virus lineages in Asia. Virology 267, 279–288 (2000)
Mo IP, Song CS, Kim KS, Rhee JC (1997) An occurence of non-highly pathogenic avian influenza in Korea. In: Swayne D, Slemons R (eds) Proceedings of the 4th international symposium on avian influenza. United States Animal Health Association, Rose Printing Company, Tallahassee, pp 379–383
Y.K. Choi, S.H. Seo, J.A. Kim, R.J. Webby, R.G. Webster, AI viruses in Korean live poultry markets and their pathogenic potential. Virology 332, 529–537 (2005)
Y.J. Lee, J.Y. Shin, M.S. Song, Y.M. Lee, J.G. Choi et al., Continuing evolution of H9 influenza viruses in Korean poultry. Virology 359, 313–323 (2007)
Senne DA, Pearson JE, Panigrahy B (1993) Live bird markets: a missing link in the epidemiology of avian influenza. In: Proceeding of the third international symposium on avian influenza. University Wisconsin, Medison, pp 7–19
M. Liu, S. He, D. Walker, N. Zhou, D.R. Perez, B. Mo, F. Li, X. Huang, R.G. Webster, R.J. Webby, The influenza virus gene pool in a poultry market in South central China. Virology 305, 267–275 (2003)
M.S. Song, T.K. Oh, H.J. Moon, D.W. Yoo, E.H. Lee, Y.K. Choi et al., Ecology of H3 avian influenza viruses in Korea and assessment of their pathogenic potentials. J Gen Virol 89, 949–957 (2008)
M. Munch, L.P. Nielsen, K.J. Handberg, P.H. Jorgensen, Detection and subtyping (H5 and H7) of avian type A influenza virus by reverse transcription-PCR and PCR-ELISA. Arch Virol 146, 87–97 (2001)
E. Hoffmann, J. Stech, Y. Guan, R.G. Webster, D.R. Perez, Universal primer set for the full-length amplification of all influenza A viruses. Arch Virol 146, 2275–2289 (2001)
O.T.W. Li, I. Barr, C.Y.H. Leung, H. Chena, Y.J.S. Guana, M. Peiris, L.L.M. Poona, Reliable universal RT-PCR assays for studying influenza polymerase subunit gene sequences from all 16 haemagglutinin subtypes. J Virol Methods 142, 218–222 (2007)
J.D. Thompson, T.J. Gibson, F. Plewniak, F. Jeanmougin, D.G. Higgins, The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25(24), 4876–4882 (1997)
K. Tamura, D. Peterson, N. Peterson, G. Stecher, M. Nei, S. Kumar, MEGA 5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28(10), 2731–2739 (2011)
L. Campitelli, A.D. Martino, D. Spagnolo, G.J.D. Smith, I. Donatelli et al., Molecular analysis of avian H7 influenza viruses circulating in Eurasia in 1999–2005: detection of multiple reassortant virus genotypes. J Gen Virol 89, 48–59 (2008)
M.N. Matrosovich, S. Krauss, R.G. Webster, H9N2 influenza A viruses from poultry in Asia have human virus-like receptor specificity. Virology 281, 156–162 (2001)
H.J. Kwon, S.H. Cho, M.C. Kim, Y.J. Ahn, S.J. Kim, Molecular epidemiology of recurrent low pathogenic avian influenza by H9N2 subtype virus in Korea. Avian Pathol 35, 309–315 (2006)
K.J. Park, H.I. Kwon, M.S. Song, P.N.Q. Pascua, Y.H. Baek, J.H. Lee, Y.K. Choi et al., Rapid evolution of low pathogenic H9N2 avian influenza viruses following poultry vaccination programs. J Gen Virol (2010). doi:10.1099/vir.0.024992-0
E. Sorrell, H. Wan, Y. Araya, H. Song, D.R. Perez, Minimal molecular constraints for respiratory droplet transmission of an avian–human H9N2 influenza A virus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 5, 7565–7570 (2009)
A. Fusaro, I. Monne, A. Salviato et al., Phylogeography and evolutionary history of reassortant H9N2 viruses with potential human health implications. J Virol 85, 8413–8421 (2011)
J. Banks, E.S. Speidel, E. Moore, L. Plowright, A. Piccirillo, I. Capua, P. Cordioli, A. Fioretti, D.J. Alexander, Changes in the haemagglutinin and the neuraminidase genes prior to the emergence of highly pathogenic H7N1 avian influenza viruses in Italy. Arch Virol 146, 963–973 (2001)
J. Li, H. Dohna, C.J. Cardona, J. Miller, T.E. Carpenter, Emergence and genetic variation of neuraminidase stalk deletions in avian influenza viruses. PLoS ONE 6, e14722 (2011)
J.G. Choi, Y.J. Lee, Y.J. Kim, E.K. Lee, O.M. Jeong, H.W. Sung, J.H. Kim, J.H. Kwon, An inactivated vaccine to control the current H9N2 low pathogenic avian influenza in Korea. J Vet Sci 9, 67–74 (2008)
K.L. Deshpande, C.W. Naeve, R.G. Webster, The neuraminidases of the virulent and avirulent A/Chicken/Pennsylvania/83 (H5N2) influenza A viruses: sequence and antigenic analyses. Virology 147, 49–60 (1985)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, CH., Byun, SH., Lee, YJ. et al. Genetic evolution of the H9N2 avian influenza virus in Korean poultry farms. Virus Genes 45, 38–47 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0737-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11262-012-0737-6