Abstract
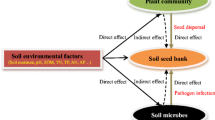
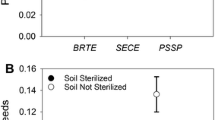
Soil pH is one of the main factors determining grassland plant community composition. However, its effects on seed persistence are not well understood, and it is not clear whether soil pH influences seed persistence, either directly or indirectly through microbial pathogens. This study examined the soil seed bank along a natural pH gradient from acidic to calcareous grassland in the Peak District National Park, UK. In addition, a seed burial experiment was performed using three species and including a fungicide treatment. Seeds of a calcicole species (Scabiosa columbaria), a calcifuge (Hypericum pulchrum) and a third species growing over a wide range of soil pH (Campanula rotundifolia) were buried, and seed germination, viability and damage (both physical and fungal) were recorded. Increasing soil pH was correlated with decreased total and grass seed abundance in the seed bank, and with a decline in the probability that H. pulchrum seeds persisted, mainly due to physical damage. In soils with pH higher than 5.6, fungicide increased seed persistence of all three species. Viability of intact, undamaged seeds and germination were not affected by soil pH. Decreasing soil pH was correlated with an increased proportion of persistent seeds. Results suggest that acid soils are associated with increased seed persistence, the size and longevity of grassland seed banks decrease as soil pH increases, and that pH influences seed persistence by an indirect effect mediated by microbial pathogens, while germination is not influenced by pH.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alday JG, Marrs RH, Martínez-Ruiz C (2011) Vegetation succession on reclaimed coal wastes in Spain: the influence of soil and environmental factors. Appl Veg Sci 14:84–94. doi:10.1111/j.1654-109X.2010.01104.x
Basto S, Dorca-Fornell C, Thompson K, Rees M (2013) Effect of pH buffer solutions on seed germination of Hypericum pulchrum, Campanula rotundifolia and Scabiosa columbaria. Seed Sci Technol 41:298–302. doi:10.15258/sst.2013.41.2.12
Basto S, Thompson K, Phoenix G, Sloan V, Leake J, Rees M (2015) Long-term nitrogen deposition depletes grassland seed banks. Nat Commun 6:6185. doi:10.1038/ncomms7185
Bates D, Maechler M, Bolker B, Walker S (2013) lme4: linear mixed-effects models using Eigen and S4 (R package version 1.0-4), http://cran.r-project.org/package=lme4/
Bekker RM, Verweij GL, Smith REN, Reine R, Bakker JP, Schneider S (1997) Soil seed banks in European grasslands: does land use affect regeneration perspectives? J Appl Ecol 34:1293–1310. doi:10.2307/2405239
Bekker RM, Knevel IC, Tallowin JBR, Troost EML, Bakker JP (1998) Soil nutrient input effects on seed longevity: a burial experiment with fen meadow species. Funct Ecol 12:673–682
Brady NC, Weil RR (2008) The nature and properties of soils. Prentice-Hall Press, New York
Carrow RN, Waddington DV, Rieke PE (2001) Turfgrass soil fertility and chemical problems: assessment and management. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New Jersey
Chauhan BS, Gill G, Preston C (2006) Influence of environmental factors on seed germination and seedling emergence of rigid ryegrass (Lolium rigidum). Weed Sci 54:1004–1012. doi:10.1614/WS-06-087R.1
Cheplick GP, Clay K, Marks S (1989) Interactions between infection by endophytic fungi and nutrient limitation in the grasses Lolium perenne and Festuca arundinacea. New Phytol 111:89–97. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.1989.tb04222.x
Chytrý M, Danihelka J, Ermakov N, Hájek M, Hájková P, Kočí M, Kubešová S, Lustyk P, Otýpková Z, Popov D, Roleěek J, Řezníčková M, Šmarda P, Valachovič M (2007) Plant species richness in continental southern Siberia: effects of pH and climate in the context of the species pool hypothesis. Global Ecol Biogeogr 16:668–678. doi:10.1111/j.1466-8238.2007.00320.x
Clarke DL, Wilson MV (2003) Post-dispersal seed fates of four prairie species. Am J Bot 90:730–735. doi:10.3732/ajb.90.5.730
Clay K (1987) Effects of fungal endophytes on the seed and seedling biology of Lolium perenne and Festuca arundinacea. Oecologia 73:358–362. doi:10.1007/BF00385251
Crawley MJ (2013) The R book, 2nd edn. John Wiley & Sons Inc, Chichester
Davis AS, Cardina J, Forcella F, Johnson GA, Kegode G, Lindquist JL, Luschei EC, Renner KA, Sprague CL, Williams MM (2005) Environmental factors affecting seed persistence of annual weeds across the US corn belt. Weed Sci 53:860–868. doi:10.1614/WS-05-064R1.1
Deska J, Jankowski K, Bombik A, Jankowska J (2011) Effect of growing medium pH on germination and initial development of some grassland plants. Acta Sci Pol 10:45–46
Duprè C, Stevens CJ, Ranke T, Bleeker A, Peppler-Lisbach C, Gowing DJG, Dise NB, Dorland E, Bobbink R, Diekmann M (2010) Changes in species richness and composition in European acidic grasslands over the past 70 years: the contribution of cumulative atmospheric nitrogen deposition. Global Change Biol 16:344–357. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.01982.x
Ellis MB, Ellis JP (1997) Microfungi on land plants. An identification handbook, 2nd edn. Richmond Publishing Co Ltd., London
Fang F, Zhang C, Wei S, Huang H, Liu W (2012) Factors affecting Tausch’s goatgrass (Aegilops tauschii Coss.) seed germination and seedling emergence. J Agric Sci 4:114–121. doi:10.5539/jas.v4n1p114
Fernández-Calviño D, Rousk J, Brookes PC, Bååth E (2011) Bacterial pH-optima for growth track soil pH, but are higher than expected at low pH. Soil Biol Biochem 43:1569–1575. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.04.007
Galinato MI, Van der Valk AG (1986) Seed germination traits of annuals and emergents recruited during drawdowns in the Delta Marsh, Manitoba, Canada. Aquat Bot 26:89–102. doi:10.1016/0304-3770(86)90007-0
Godfree R, Lepschi B, Reside A, Bolger T, Robertson B, Marshall D, Carnegie M (2011) Multiscale topoedaphic heterogeneity increases resilience and resistance of a dominant grassland species to extreme drought and climate change. Global Change Biol 17:943–958. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02292.x
Grime JP, Hodgson JG, Hunt R (1988) Comparative plant ecology. Unwin Hyman, London
Grootjans AP, Geelen HWT, Jansen AJM, Lammerts EJ (2002) Restoration of coastal dune slacks in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 478:181–203. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-1335-1_10
Helsen K, Hermy M, Honnay O (2014) Changes in the species and functional trait composition of the seed bank during semi-natural grassland assembly: seed bank disassembly or ecological palimpsest? J Veg Sci 26:58–67. doi:10.1111/jvs.12210
Horswill P, O’Sullivan O, Phoenix GK, Lee JA, Leake JR (2008) Base cation depletion, eutrophication and acidification of species-rich grasslands in response to long-term simulated nitrogen deposition. Environ Pollut 155:336–349. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2007.11.006
Hou JQ, Simpson GM (1994) Effects of immersing dry seeds in alkaline solutions on seed dormancy and water uptake in wild oat (Avena fatua). Can J Plant Sci 74:19–24. doi:10.4141/cjps94-005
Jansen P, Ison R (1995) Factors contributing to the loss of seed from the seed bank of Trifolium balansae and Trifolium resupinatum over summer. Aust J Ecol 20:248–256. doi:10.1111/j.1442-9993.1995.tb00536.x
Jeger MJ, Salama NKG, Shaw MW, van den Berg F, van den Bosch F (2014) Effects of plant pathogens on population dynamics and community composition in grassland ecosystems: two case studies. Eur J Plant Pathol 138:513–527. doi:10.1007/s10658-013-0325-1
Ji CJ, Yang YH, Han WX, He YF, Smith J, Smith P (2014) Climatic and edaphic controls on soil pH in alpine grasslands on the Tibetan Plateau, China: a quantitative analysis. Pedosphere 24:39–44. doi:10.1016/S1002-0160(13)60078-8
Johnson PA (1971) Soils in Derbyshire. 1. Sheet SK17 (Tideswell), Soil Survey Record No. 4. Soil Survey of England and Wales, Harpenden
Jones M, Rotherham ID (2011) Management issues in urban ancient woodlands: a case study of Bowden Housteads Wood, Sheffield. Asp Appl Biol 108:113–121
Kalusová V, Le Duc MG, Gilbert JC, Lawson CS, Gowing DJG, Marrs RH (2009) Determining the important environmental variables controlling plant species community composition in mesotrophic grasslands in Great Britain. Appl Veg Sci 12:459–471. doi:10.1111/j.1654-109X.2009.01041.x
Kopeć D, Michalska-Hejduk D (2012) How threatened is the Polish wetland flora? Oceanol Hydrobiol Stud 41:79–89. doi:10.2478/s13545-012-0030-2
Leishman MR, Masters GJ, Clarke IP, Brown VK (2000) Seed bank dynamics: the role of fungal pathogens and climate change. Funct Ecol 14:293–299. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2435.2000.00425.x
Liu Y, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Cui J, Chen G, Xie B, Wu Ch, Liu H (2014) Synergistic and antagonistic effects of salinity and pH on germination in Switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.). PLoS ONE 9:e85282. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0085282
Long RL, Steadman KJ, Panetta FD, Adkins SW (2009) Soil type does not affect seed ageing when soil water potential and temperature are controlled. Plant Soil 320:131–140. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9878-8
Long RL, Gorecki MJ, Renton M, Scott JK, Colville L, Goggin DE, Commander LE, Westcott DA, Cherry H, Finch-Savage WE (2015) The ecophysiology of seed persistence: a mechanistic view of the journey to germination or demise. Biol Rev 90:31–59. doi:10.1111/brv.12095
Luschei EC, Buhler DD, Dekker JH (1998) Effect of separating giant foxtail (Setaria faberi) seeds from soil using potassium carbonate and centrifugation on viability and germination. Weed Sci 46:545–548
Ma H, Yang H, Lü X, Pan Y, Wu H, Liang Z, Ooi MKJ (2015) Does high pH give a reliable assessment of the effect of alkaline soil on seed germination? A case study with Leymus chinensis (Poaceae). Plant Soil 1–9 doi:10.1007/s11104-015-2487-4
Macdonald CA (2004) The influence of anthropogenic nitrogen pollution upon the structure and functioning of microbial communities in two grasslands. PhD thesis, The University of Sheffield
Måren IE, Vandvik V (2009) Fire and regeneration: the role of seed banks in the dynamics of northern heathlands. J Veg Sci 20:871–888. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2009.01091.x
Marrs RH (2002) Manipulating the chemical environment of the soil. In: Perrow MR, Davy AJ (eds) Handbook of ecological restoration. Principles of restoration, 1. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 155–183
Maskell LC, Smart SM, Bullock JM, Thompson K, Stevens CJ (2010) Nitrogen deposition causes widespread loss of species richness in British habitats. Global Change Biol 16:671–679. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2009.02022.x
McGovern S, Evans CD, Dennis P, Walmsley C, McDonald MA (2011) Identifying drivers of species compositional change in a semi-natural upland grassland over a 40-year period. J Veg Sci 22:346–356. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2011.01256.x
Michalcová D, Gilbert JC, Lawson CS, Gowing DJG, Marrs RH (2011) The combined effect of waterlogging, extractable P and soil pH on α-diversity: a case study on mesotrophic grasslands in the UK. Plant Ecol 212:879–888. doi:10.1007/s11258-010-9871-1
Milberg P (1995) Soil seed bank after 18 years of succession from grassland to forest. Oikos 72:3–13. doi:10.2307/3546031
Mitschunas N, Filser J, Wagner M (2009) On the use of fungicides in ecological seed burial studies. Seed Sci Res 19:51–60. doi:10.1017/S096025850818727X
Nacke H, Thürmer A, Wollherr A, Will C, Hodac L, Herold N, Schöning I, Schrumpf M, Daniel R (2011) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of bacterial community structure along different management types in German forest and grassland soils. PLoS ONE 6:e17000. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0017000
Ottewell KM, Bickerton D, Lowe AJ (2011) Can a seed bank provide demographic and genetic rescue in a declining population of the endangered shrub Acacia pinguifolia? Conserv Genet 12:669–678. doi:10.1007/s10592-010-0173-x
Owen KM, Marrs RH, Snow CSR, Evans CE (1999) Soil acidification-the use of sulphur and acidic plant materials to acidify arable soils for the recreation of heathland and acidic grassland at Minsmere, UK. Biol Conserv 87:105–121. doi:10.1016/S0006-3207(98)00027-5
Pakeman RJ, Small JL, Torvell L (2012) Edaphic factors influence the longevity of seeds in the soil. Plant Ecol 213:57–65. doi:10.1007/s11258-011-0006-0
Pérez-Fernández MA, Calvo-Magro E, Montanero-Fernández J, Oyola-elasco JA (2006) Seed germination in response to chemicals: effect of nitrogen and pH in the media. J Environ Biol 27:13
Piessens K, Honnay O, Nackaerts K, Hermy M (2004) Plant species richness and composition of heathland relics in north-western Belgium: evidence for a rescue-effect? J Biogeogr 31:1683–1692. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2699.2004.01056.x
Pluess AR, Stöcklin J (2004) Genetic diversity and fitness in Scabiosa columbaria in the Swiss Jura in relation to population size. Conserv Genet 5:145–156. doi:10.1023/B:COGE.0000029999.10808.c2
Prach K, Marrs R, Pyšek P, van Diggelen R (2007) Manipulation of succession. In: Walker LR, Walker J, Hobbs RJ (eds) Linking restoration and ecological succession. Springer Verlag, New York, pp 121–149
R Core Team (2014) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, URL http://www.R-project.org/
Rasmussen HN, Whigham DF (1993) Seed ecology of dust seeds in situ: a new study technique and its application in terrestrial orchids. Am J Bot 80:1374–1378
Rodwell JS (1992) British plant communities 3. Grasslands and montane communities. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Sayer EJ, Wagner M, Oliver AE, Pywell RF, James P, Whiteley AS, Heard MS (2013) Grassland management influences spatial patterns of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 61:61–68. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2013.02.012
Shrestha RK, Lal R (2011) Changes in physical and chemical properties of soil after surface mining and reclamation. Geoderma 161:168–176. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2010.12.015
Simpson RL, Leck MA, Parker VT (1989) Seed banks: general concepts and methodological issues. In: Leck MA, Parker VT, Simpson RL (eds) Ecology of soil seed banks. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 3–8
Singh VP, Mall SL, Billore SK (1975) Effect of pH on germination of four common grass species of Ujjain (India). J Range Manag 28:497–498
Sposito G (2008) The chemistry of soils, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Stanisavljević RS, Vucković SM, Simić AS, Marković JP, Lakić ZP, Terzić DV, Dokić DJ (2012) Acid and temperature treatments result in increased germination of seeds of three fescue species. Not Bot Horti Agrobo 40:220–226
Stevens CJ, Dise NB, Mountford JO, Gowing DJ (2004) Impact of nitrogen deposition on the species richness of grasslands. Science 303:1876–1879. doi:10.1126/science.1094678
Stevens CJ, Duprè C, Dorland E, Gaudnik C, Gowing DJ, Bleeker A, Diekmann M, Alard D, Bobbink R, Fowler D, Corcket E, Mountford JO, Vandvik V, Aarrestad PA, Muller S, Dise NB (2010) Nitrogen deposition threatens species richness of grasslands across Europe. Environ Pollut 158:2940–2945. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2010.06.006
Stevens C, Duprè C, Gaudnik C, Dorland E, Dise N, Gowing D, Bleeker A, Alard D, Bobbink R, Fowler D, Vandvik V, Corcket E, Mountford JO, Aarrestad PA, Muller S, Diekmann M (2011) Changes in species composition of European acid grasslands observed along a gradient of nitrogen deposition. J Veg Sci 22:207–215. doi:10.1111/j.1654-1103.2010.01254.x
Stevens CJ, Wilson J, McAllister HA (2012) Biological Flora of the British Isles: Campanula rotundifolia. J Ecol 100:821–839. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2745.2012.01963.x
Strickland MS, Rousk J (2010) Considering fungal: bacterial dominance in soils—methods, controls, and ecosystem implications. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1385–1395. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.05.007
Stubbendieck J (1974) Effect of pH on germination of three grass species. J Range Manag 27:78–79
Thompson K, Bakker JP, Bekker RM (1997) The soil seed banks of north west Europe: methodology, density and longevity. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Tremblay A (2015) Package ‘LMERConvenienceFunctions’. Model Selection and Post-hoc Analysis for GLMER Models (R package version 2.10), http://cran.r-project.org/package=LMERConvenienceFunctions/
Ullrich SD, Buyer JS, Cavigelli MA, Seidel R, Teasdale JR (2011) Weed seed persistence and microbial abundance in long-term organic and conventional cropping systems. Weed Sci 59:202–209. doi:10.1614/WS-D-10-00142.1
Van Mourik TA, Stomph TJ, Murdoch AJ (2005) Why high seed densities within buried mesh bags may overestimate depletion rates of soil seed banks. J Appl Ecol 42:299–305. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2664.2005.01016.x
Varga Z, Krautzer B, Graiss W (2008) Mycological investigations of seeds of cultivated grasses. Die Bodenkultur 59:95–100
Wagner M, Mitschunas N (2008) Fungal effects on seed bank persistence and potential applications in weed biocontrol: a review. Basic Appl Ecol 9:191–203. doi:10.1016/j.baae.2007.02.003
Walker KJ, Stevens PA, Stevens DP, Mountford JO, Manchester SJ, Pywell RF (2004a) The restoration and re-creation of species-rich lowland grassland on land formerly managed for intensive agriculture in the UK. Biol Conserv 119:1–18. doi:10.1016/j.biocon.2003.10.020
Walker KJ, Hodder KH, Bullock JB, Pywell RF (2004b) A review of the potential effects of seed sowing for habitat re-creation on the conservation of intraspecific biodiversity. Defra Contract BD1447. Centre for Ecology and Hydrology, Monks Wood
Warr SJ, Thompson K, Kent M (1992) Antifungal activity in seed coat extracts of woodland plants. Oecologia 92:296–298. doi:10.1007/BF00317378
Waters SJP, Pigott CD (1971) Mineral nutrition and calcifuge behaviour in Hypericum. J Ecol 59:179–187. doi:10.2307/2258460
Zhang ZQ, Shu WS, Lan CY, Wong MH (2001) Soil seed bank as an input of seed source in revegetation of lead/zinc mine tailings. Restor Ecol 9:378–385. doi:10.1046/j.1526-100X.2001.94007.x
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Programme Alβan, the European Union Programme of High Level Scholarships for Latin America, scholarship No. (E07D400528CO) and Pontificia Universidad Javeriana (to S.B.). We acknowledge Geoffrey Odds and Irene Johnson for field assistance and lab assistance, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Glenda Wardle.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Basto, S., Thompson, K. & Rees, M. The effect of soil pH on persistence of seeds of grassland species in soil. Plant Ecol 216, 1163–1175 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-015-0499-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11258-015-0499-z