Abstract
Purpose
Hippocampus plays an important role in spatial learning and memory. Ghrelin, a brain-gut peptide, participates in the mnestic functions of hippocampus through its receptor growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHS-R) distributed in hippocampus. This study was to investigate whether there was a correlation between the changes of ghrelin system in hippocampus and the spatial cognitive impairment caused by chronic renal failure (CRF).
Methods
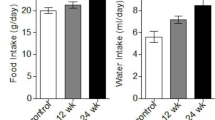
Sprague–Dawley rats (male, 180 ± 10 g, 7–8 weeks old) were randomly classified into CRF group and control group (n = 18 per group). The CRF model was constructed by 5/6 nephrectomy and the controls treated with sham operation. By the 8th week after the surgery, the spatial cognitive function of rats was assessed by Morris water-maze test (MWM), the protein expression of ghrelin and GHS-R in the hippocampus by immunohistochemistry, and the mRNA expression by real-time PCR. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA, Student–Newman–Keuls-q test and Pearson correlation analysis, and P < 0.05 was considered significant.
Results
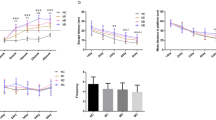
Compared with the controls, the time spent in “platform” quadrant (TSPQ) of rats with CRF was decreased, but the escape latency (EL) was increased significantly in MWM, and meanwhile the protein and mRNA expression of ghrelin and GHS-R in hippocampus was also increased significantly (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Correlation analysis suggested that the TSPQ was negatively but the EL was positively correlated with the mRNA expression of ghrelin and GHS-R (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
The CRF-caused changes of ghrelin system in hippocampus might be correlated with the CRF-caused cognitive function impairment.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murray AM, Tupper DE, Knopman DS, Gilbertson DT, Pederson SL, Li S, Smith GE, Hochhalter AK, Collins AJ, Kane RL (2006) Cognitive impairment in hemodialysis patients is common. Neurology 67(2):216–223. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000225182.15532.40
Madan P, Kalra OP, Agarwal S, Tandon OP (2007) Cognitive impairment in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transpl 22(2):440–444. doi:10.1093/Ndt/Gfl572
Burgess N, Maguire EA, O’Keefe J (2002) The human hippocampus and spatial and episodic memory. Neuron 35(4):625–641. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00830-9
Fujisaki K, Tsuruya K, Yamato M, Toyonaga J, Noguchi H, Nakano T, Taniguchi M, Tokumoto M, Hirakata H, Kitazono T (2014) Cerebral oxidative stress induces spatial working memory dysfunction in uremic mice: neuroprotective effect of tempol. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29(3):529–538. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft327
Horvath TL, Diano S, Sotonyi P, Heiman M, Tschop M (2001) Minireview: ghrelin and the regulation of energy balance—a hypothalamic perspective. Endocrinology 142(10):4163–4169. doi:10.1210/endo.142.10.8490
Chen CY, Asakawa A, Fujimiya M, Lee SD, Inui A (2009) Ghrelin gene products and the regulation of food intake and gut motility. Pharmacol Rev 61(4):430–481. doi:10.1124/pr.109.001958
Xu JJ, Wang SZ, Lin YT, Cao LL, Wang R, Chi ZF (2009) Ghrelin protects against cell death of hippocampal neurons in pilocarpine-induced seizures in rats. Neurosci Lett 453(1):58–61. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.01.067
Zigman JM, Jones JE, Lee CE, Saper CB, Elmquist JK (2006) Expression of ghrelin receptor mRNA in the rat and the mouse brain. J Comp Neurol 494(3):528–548. doi:10.1002/Cne.20823
Carlini VP, Varas MM, Cragnolini AB, Schioth HB, Scimonelli TN, de Barioglio SR (2004) Differential role of the hippocampus, amygdala, and dorsal raphe nucleus in regulating feeding, memory, and anxiety-like behavioral responses to ghrelin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 313(3):635–641. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.11.150
Fu RG, Wang L, Yao GL, Xue RL, Ge H, Ren ST, Ma LQ, Jiang HL, Liu X (2012) Chronic renal failure impacts the expression of ghrelin and its receptor in hypothalamus and hippocampus. Ren Fail 34(8):1027–1032. doi:10.3109/0886022x.2012.708379
Nunez J (2008) Morris water maze experiment. J Vis Exp. doi:10.3791/897
Swanson LW (2004) Brain maps III: structure of the rat brain: an atlas with printed and electronic templates for data, models, and schematics, 3rd rev. edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
McElroy MW, Korol DL (2005) Intrahippocampal muscimol shifts learning strategy in gonadally intact young adult female rats. Learn Mem 12(2):150–158. doi:10.1101/Lm.86205
Al Banchaabouchi M, D’Hooge R, Marescau B, De Deyn PP (1999) Behavioural deficits during the acute phase of mild renal failure in mice. Metab Brain Dis 14(3):173–187
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402(6762):656–660. doi:10.1038/45230
Cowley MA, Smith RG, Diano S, Tschop M, Pronchuk N, Grove KL, Strasburger CJ, Bidlingmaier M, Esterman M, Heiman ML, Garcia-Segura LM, Nillni EA, Mendez P, Low MJ, Sotonyi P, Friedman JM, Liu HY, Pinto S, Colmers WF, Cone RD, Horvath TL (2003) The distribution and mechanism of action of ghrelin in the CNS demonstrates a novel hypothalamic circuit regulating energy homeostasis. Neuron 37(4):649–661. doi:10.1016/S0896-6273(03)00063-1
Braak H, Braak E, Yilmazer D, Bohl J (1996) Functional anatomy of human hippocampal formation and related structures. J Child Neurol 11(4):265–275
Mcclelland JL, Mcnaughton BL, Oreilly RC (1995) Why there are complementary learning-systems in the hippocampus and neocortex—insights from the successes and failures of connectionist models of learning and memory. Psychol Rev 102(3):419–457. doi:10.1037/0033-295x.102.3.419
Lee I, Hunsaker MR, Kesner RP (2005) The role of hippocampal subregions in detecting spatial novelty. Behav Neurosci 119(1):145–153. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.119.1.145
Lee I, Kesner RP (2004) Encoding versus retrieval of spatial memory: double dissociation between the dentate gyrus and the perforant path inputs into CA3 in the dorsal hippocampus. Hippocampus 14(1):66–76. doi:10.1002/hipo.10167
Carlini VP, Monzon ME, Varas MM, Cragnolini AB, Schioth HB, Scimonelli TN, de Barioglio SR (2002) Ghrelin increases anxiety-like behavior and memory retention in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 299(5):739–743. doi:10.1016/S0006-291x(02)02740-7
Ferrini F, Salio C, Lossi L, Merighi A (2009) Ghrelin in central neurons. Curr Neuropharmacol 7(1):37–49
Diano S, Farr SA, Benoit SC, McNay EC, da Silva I, Horvath B, Gaskin FS, Nonaka N, Jaeger LB, Banks WA, Morley JE, Pinto S, Sherwin RS, Xu L, Yamada KA, Sleeman MW, Tschop MH, Horvath TL (2006) Ghrelin controls hippocampal spine synapse density and memory performance. Nat Neurosci 9(3):381–388. doi:10.1038/Nn1656
Carlini VP, Gaydou RC, Schioth HB, de Barioglio SR (2007) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (fluoxetine) decreases the effects of ghrelin on memory retention and food intake. Regul Pept 140(1–2):65–73. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2006.11.012
Jiang H, Betancourt L, Smith RG (2006) Ghrelin amplifies dopamine signaling by cross talk involving formation of growth hormone secretagogue receptor/dopamine receptor subtype 1 heterodimers. Mol Endocrinol 20(8):1772–1785. doi:10.1210/Me.2005-0084
Brouns R, De Deyn PP (2004) Neurological complications in renal failure: a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 107(1):1–16. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2004.07.012
Fujisaki K, Tsuruya K, Yamato M, Toyonaga J, Noguchi H, Nakano T, Taniguchi M, Tokumoto M, Hirakata H, Kitazono T (2014) Cerebral oxidative stress induces spatial working memory dysfunction in uremic mice: neuroprotective effect of tempol. Nephrol Dial Transpl 29(3):529–538. doi:10.1093/ndt/gft327
Yoshimoto A, Mori K, Sugawara A, Mukoyama M, Yahata K, Suganami T, Takaya K, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K (2002) Plasma ghrelin and desacyl ghrelin concentrations in renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 13(11):2748–2752. doi:10.1097/01.Asn.0000032420.12455.74
Fu RG, Xue RL, Wang J, Ma LQ, Lv JR, Wang L, Yao GL, Ge H, Chen Z, Duan ZY, Wang YR (2012) Uremic anorexia and ghrelin expression in the amygdala. Neurosci Lett 527(1):50–54. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2012.08.040
Buhot HC, Martin S, Segu L (2000) Role of serotonin in memory impairment. Ann Med 32(3):210–221
Bannon MJ, Poosch MS, Yue X, Goebel DJ, Cassin B, Kapatos G (1992) Dopamine transporter messenger-RNA content in human substantia-nigra decreases precipitously with age. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(15):7095–7099. doi:10.1073/pnas.89.15.7095
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81470968, 81400740, 81300581).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest was declared.
Additional information
Zhian Lv and Jie Gao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, Z., Gao, J., Wang, L. et al. Uremia-caused changes of ghrelin system in hippocampus may be associated with impaired cognitive function of hippocampus. Int Urol Nephrol 48, 807–815 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1228-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1228-9