Abstract
Purpose
Following patients after prostatectomy can be expensive and stressful, therefore, a novel and reliable approach to improve stratification is needed both at diagnosis of PCa and following its treatment. We evaluate the association of both ERG and claudin-4, claudin-5, and beta-catenin expression in tumor tissues of patients with organ-confined and advanced prostatic adenocarcinomas.
Methods
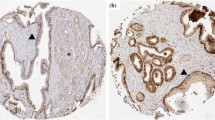
A total of 30 patients were included in the study. Nine men who underwent radical prostatectomy for organ-confined (pT2N0M0) cancer (OCC), 10 patients with clinically advanced cancer (CAC), and 11 controls with benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). Using immunohistochemistry applied to tissue microarrays, each group was evaluated for beta-catenin, claudin-4, claudin-5, and ERG expression.
Results
The expression of ERG was higher in the CAC group when compared to OCC and BPH (p = 0.7684, p = 0.0224, respectively). Among these patients, 5 from the CAC (45 %) and 5 from the OCC group (56 %) stained positively for ERG (p = 1.0). The mean staining score for those with ERG+ advanced cancer was greater than that for the ERG+ organ-confined cancer (p = 0.0209). ERG staining correlated with Gleason score (Pearson’s correlation: 0.498, p = 0.0051), but not with serum PSA level (Pearson’s correlation: 0.404, p = 0.1202). When analyzing outcome data, high ERG expressing tumors have shown a significantly worse overall survival (p = 0.0084).
Conclusions
Our results of presence or absence of claudin-4 and claudin-5 and ERG staining intensities suggest their potential as prognostic factors for prostate cancer.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coldman AJ, Phillips N, Pickles TA (2003) Trends in prostate cancer incidence and mortality: an analysis of mortality change by screening intensity. Can Med Assoc J 168(1):31–35
Roberts RO, Bergstralh EJ, Peterson NR, Bostwick DG, Lieber MM, Jacobsen SJ (2000) Positive and negative biopsies in the pre-prostate specific antigen and prostate specific antigen eras, 1980 to 1997. J urol 163(5):1471–1475
Andriole GL, Crawford ED, Grubb RL, Buys SS, Chia D, Church TR, Fouad MN, Gelmann EP, Kvale PA, Reding DJ, Weissfeld JL, Yokochi LA, O’Brien B, Clapp JD, Rathmell JM, Riley TL, Hayes RB, Kramer BS, Izmirlian G, Miller AB, Pinsky PF, Prorok PC, Gohagan JK, Berg CD (2009) Mortality results from a randomized prostate-cancer screening trial. N Engl J Med 360(13):1310–1319. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810696
Schröder FH, Hugosson J, Roobol MJ, Tammela TLJ, Ciatto S, Nelen V, Kwiatkowski M, Lujan M, Lilja H, Zappa M, Denis LJ, Recker F, Berenguer A, Maattanen L, Bangma CH, Aus G, Villers A, Rebillard X, van der Kwast T, Blijenberg BG, Moss SM, de Koning HJ, Auvinen A (2009) Screening and prostate-cancer mortality in a randomized European study. N Engl J Med 360(13):1320–1328. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0810084
Daskivich T, Chamie K, Kwan L, Labo J, Palvolgyi R, Dash A, Greenfield S, Litwin M (2011) Overtreatment of men with low-risk prostate cancer and significant comorbidity. Cancer 117(20):4805
Bangma C, Roemeling S, Schrà der F (2007) Overdiagnosis and overtreatment of early detected prostate cancer. World J Urol 25(1):3–9
Shao YH, Albertsen PC, Shih W, Roberts CB, Lu-Yao GL (2011) The impact of PSA testing frequency on prostate cancer incidence and treatment in older men. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 14(4):332–339
Roehl KA, Han M, Ramos CG, Antenor JAV, Catalona WJ (2004) Cancer progression and survival rates following anatomical radical Retropubic prostatectomy in 3,478 consecutive patients: long-term results. J urol 172(3):910–914
Han M, Partin AW, Piantadosi S, Epstein JI, Walsh PC (2001) Era specific biochemical recurrence-free survival following radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer. J urol 166(2):416–419
Stephenson AJ, Kattan MW, Eastham JA, Bianco FJ, Yossepowitch O, Vickers AJ, Klein EA, Wood DP, Scardino PT (2009) Prostate cancer-specific mortality after radical prostatectomy for patients treated in the prostate-specific antigen era. J Clin Oncol 27(26):4300–4305. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.18.2501
Tollefson MK, Blute ML, Rangel LJ, Karnes RJ, Frank I (2010) Lifelong yearly prostate specific antigen surveillance is not necessary for low risk prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. J urol 184(3):925–929
Dale W, Hemmerich J, Bylow K, Mohile S, Mullaney M, Stadler WM (2009) Patient anxiety about prostate cancer independently predicts early initiation of androgen deprivation therapy for biochemical cancer recurrence in older men: a prospective cohort study. J Clin Oncol 27(10):1557–1563. doi:10.1200/jco.2008.18.5850
Chism K, Kunkel E (2009) Prostate cancer: issues in psychosomatic medicine. Curr Psychiatry Rep 11(3):205–210
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141(7):1539–1550
Yamamoto T, Kojima T, Murata M, Takano K-I, Go M, Chiba H, Sawada N (2004) IL-1 beta regulates expression of Cx32, occludin, and claudin-2 of rat hepatocytes via distinct signal transduction pathways. Exp Cell Res 299(2):427–441
Heiskala M, Peterson PA, Yang Y (2001) The Roles of claudin superfamily proteins in paracellular transport. Traffic 2(2):92–98
Szasz AM, Nyirady P, Majoros A, Szendroi A, Szucs M, Szekely E, Tokes AM, Romics I, Kulka J (2010) Beta-catenin expression and claudin expression pattern as prognostic factors of prostatic cancer progression. BJU Int 105(5):716–722
Landers KA, Samaratunga H, Teng L, Buck M, Burger MJ, Scells B, Lavin MF, Gardiner RA (2008) Identification of claudin-4 as a marker highly overexpressed in both primary and metastatic prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 99(3):491–501
Tomlins SA, Rhodes DR, Perner S, Dhanasekaran SM, Mehra R, Sun X-W, Varambally S, Cao X, Tchinda J, Kuefer R, Lee C, Montie JE, Shah RB, Pienta KJ, Rubin MA, Chinnaiyan AM (2005) Recurrent fusion of TMPRSS2 and ETS Transcription factor genes in prostate cancer. Science (New York, NY 310 (5748): 644–648. doi: 10.1126/science.1117679
Magi-Galluzzi C, Tsusuki T, Elson P, Simmerman K, LaFargue C, Esgueva R, Klein E, Rubin MA, Zhou M (2011) TMPRSS2–ERG gene fusion prevalence and class are significantly different in prostate cancer of Caucasian, african-american and japanese patients. Prostate 71(5):489–497
Petrovics G, Liu A, Shaheduzzaman S, Furusato B, Sun C, Chen Y, Nau M, Ravindranath L, Chen Y, Dobi A, Srikantan V, Sesterhenn IA, McLeod DG, Vahey M, Moul JW, Srivastava S (2005) Frequent overexpression of ETS-related gene-1 (ERG1) in prostate cancer transcriptome. Oncogene 24(23):3847–3852
Soller MJ, Isaksson M, Elfving P, Soller W, Lundgren R, Panagopoulos I (2006) Confirmation of the high frequency of the TMPRSS2/ERG fusion gene in prostate cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45(7):717–719
Yoshimoto M, Joshua A, Chilton-MacNeill S, Bayani J, Selvarajah S, Evans AJ, Zielenska M, Squire JA (2006) Three-color fish analysis of TMPRSS2/ERG fusions in prostate cancer indicates genomic microdeletion of chromosome 21 is associated with rearrangement. Neoplasia (New York, NY) 8 (6)
Furusato B, Tan SH, Young D, Dobi A, Sun C, Mohamed AA, Thangapazham R, Chen Y, McMaster G, Sreenath T, Petrovics G, McLeod DG, Srivastava S, Sesterhenn IA (2010) ERG oncoprotein expression in prostate cancer: clonal progression of ERG-positive tumor cells and potential for ERG-based stratification. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 13(3):228–237
Arun P, Brown MS, Ehsanian R, Chen Z, Van Waes C (2009) Nuclear NF-κB p65 phosphorylation at Serine 276 by protein kinase a contributes to the malignant phenotype of head and neck cancer. Clin Cancer Res 15(19):5974–5984. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-09-1352
Clark JP, Cooper CS (2009) ETS gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 6(8):429–439
Attard G, Clark J, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G, Flohr P, Berney D, Foster CS, Fletcher A, Gerald WL, Moller H, Reuter V, De Bono JS, Scardino P, Cuzick J, Cooper CS (2007) Duplication of the fusion of TMPRSS2 to ERG sequences identifies fatal human prostate cancer. Oncogene 27(3):253–263
Mehra R, Tomlins SA, Yu J, Cao X, Wang L, Menon A, Rubin MA, Pienta KJ, Shah RB, Chinnaiyan AM (2008) Characterization of TMPRSS2-ETS Gene aberrations in androgen-independent metastatic prostate cancer. Cancer Res 68(10):3584–3590. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-07-6154
Gopalan A, Leversha MA, Satagopan JM, Zhou Q, Al-Ahmadie HA, Fine SW, Eastham JA, Scardino PT, Scher HI, Tickoo SK, Reuter VE, Gerald WL (2009) TMPRSS2-ERG gene fusion is not associated with outcome in patients treated by prostatectomy. Cancer Res 69(4):1400–1406
Hu Y, Dobi A, Sreenath T, Cook C, Tadase AY, Ravindranath L, Cullen J, Furusato B, Chen Y, Thangapazham RL, Mohamed A, Sun C, Sesterhenn IA, McLeod DG, Petrovics G, Srivastava S (2008) Delineation of TMPRSS2-ERG splices variants in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 14(15):4719–4725. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-08-0531
Spencer ES, Johnston RB, Gordon RR, Lucas JM, Ussakli CH, Hurtado-Coll A, Srivastava S, Nelson PS, Porter CR (2013) Prognostic value of ERG oncoprotein in prostate cancer recurrence and cause-specific mortality. The Prostate. doi:10.1002/pros.22636
van Leenders GJLH, Boormans JL, Vissers CJ, Hoogland AM, Bressers AA, Furusato B, Trapman J (2011) Antibody EPR3864 is specific for ERG genomic fusions in prostate cancer: implications for pathological practice. Mod Pathol 24(8):1128–1138
Yaskiv O, Zhang X, Simmerman K, Daly T, He H, Falzarano S, Chen L, Magi-Galluzzi C, Zhou M (2011) The utility of ERG/P63 double immunohistochemical staining in the diagnosis of limited cancer in prostate needle biopsies. Am J Surg Pathol 35(7):1062–1068. doi:1010.1097/PAS.1060b1013e318215cc318203
Rosen P, Sesterhenn IA, Brassell SA, McLeod DG, Srivastava S, Dobi A (2012) Clinical potential of the ERG oncoprotein in prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 9(3):131–137
Seruga B, Tannock IF (2011) Chemotherapy-based treatment for castration-resistant prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 29(27):3686–3694. doi:10.1200/jco.2010.34.3996
Reid AHM, Attard G, Ambroisine L, Fisher G, Kovacs G, Brewer D, Clark J, Flohr P, Edwards S, Berney DM, Foster CS, Fletcher A, Gerald WL, Moller H, Reuter VE, Scardino PT, Cuzick J, de Bono JS, Cooper CS (2010) Molecular characterisation of ERG, ETV1 and PTEN gene loci identifies patients at low and high risk of death from prostate cancer. Br J Cancer 102(4):678–684
Small EJ, de Bono JS (2011) Prostate cancer: evolution or revolution? J Clin Oncol 29(27):3595–3598. doi:10.1200/jco.2011.37.8653
Acknowledgments
Grant support: MTA-2012TKI643 grant to AMSz and JK. TÁMOP-4.2.2/B-10/1-2010-0013 grant to JK.
Conflict of interest
We the authors herewith declare that there is no any competing financial interest in relation to the work described.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szász, A.M., Majoros, A., Rosen, P. et al. Prognostic potential of ERG (ETS-related gene) expression in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 727–733 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0406-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-013-0406-2