Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the safety and efficacy of mirabegron for patients with overactive bladder (OAB) that is unresponsive to antimuscarinic agents or is related to benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH).
Methods
Fifty-two newly diagnosed OAB patients (M group) and 45 patients with OAB that was unresponsive to antimuscarinics (S group) received mirabegron 50 mg once daily and were evaluated by OAB symptom score (OABSS), IPSS-QOL index, and IPSS at the time of baseline, 4 and 8 weeks. Newly diagnosed OAB patients treated with antimuscarinic agents were compared as controls.
Results
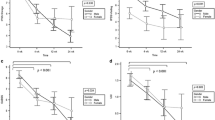
Mirabegron was effective for 85.2 % in M group. Significant improvements were seen in each domain of OABSS, and there was no significant difference with antimuscarinic therapy. Mirabegron was efficacious for 61.6 % of S group, and significant decreases of OABSS and IPSS-QOL index were observed. Significant improvements were also seen in voiding symptoms in men. Post-void residual urine volumes before and after treatment were 32.1 and 34.8 ml, and 26.2 and 31.3 ml in M and S group, respectively, and there was no significant difference. The incidence of adverse events was 8.4 %, although none were serious, and the patients recovered spontaneously after mirabegron was discontinued.
Conclusion
The present study suggests mirabegron is as effective as antimuscarinics for OAB. It improves OAB symptoms in patients with OAB for which antimuscarinic agents are insufficient. This study revealed that mirabegron improves not only OAB symptoms related to BPH, but also voiding symptoms in men. Low and mild incidences of side effects support the safe utility of mirabegron.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams P, Kelleher CJ, Kerr LA, Rogers RG (2000) Overactive bladder significantly affects quality of life. Am J Manag Care 6:S580–S590
D’Souza AO, Smith MJ, Miller LA, Doyle J, Ariely R (2008) Persistence, adherence, and switch rates among extended-release and immediate-release overactive bladder medications in a regional managed care plan. J Manag Care Pharm 14:291–301
Benner JS, Nichol MB, Rovner ES et al (2010) Patient-reported reasons for discontinuing overactive bladder medication. BJU Int 105:1276–1282
Wein AJ, Andersson KE (2007) Pharmacologic management of storage and emptying failure. In: Wein AJ, Kavoussi LR, Novick AC, Partin AW, Peters CA (eds) Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9th edn. Saunders Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 2093–2094
Igawa Y, Yamazaki Y, Takeda H et al (1999) Functional and molecular biological evidence. Br J Pharmacol 126:819–825
Takeda M, Obara K (1999) Evidence for beta3-adrenoreceptor subtypes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:1367–1373
Yamaguchi O (2002) Beta3-adrenreceptor in human. Urology 59(5 Suppl 1):25–29
Fujimura T, Tamura K (1999) Expression and possible functional role of beta3- adrenoceptor in human and rat detrusor muscle. J Urol 161:680–685
Woods M, Carson N (2001) Efficacy of the beta3-adrenergic receptor agonist CL-316243 on experimental bladder hyperreflexia and detrusor instability in the rat. J Urol 166:1142–1147
Takasu T, Ukai M, Sato S et al (2007) Effect of (R)-2-(2-aminothiazol-4-yl)-4′-{2-[(2-hydroxy-2-phenylethyl)amino]ethyl} acetanilide (YM178), a novel selective beta3-adrenoceptor agonist, on bladder function. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 321:642–647
Gillespie JI, Palea S, Guilloteau V, Guerard M, Lluel P, Korstanje C (2012) Modulation of non-voiding activity by the muscarinergic antagonist tolterodine and the β(3)-adrenoceptor agonist mirabegron in conscious rats with partial outflow obstruction. BJU Int 110(2 Pt 2):E132–E142. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11240.x
Homma Y, Yoshida M, Seki N, Yokoyama O, Kakizaki H, Gotoh M, Yamanishi T, Yamaguchi O, Takeda M, Nishizawa O (2006) Symptom assessment tool for overactive bladder syndrome–overactive bladder symptom score. Urology 68:318–323
Lee JY, Kim HW, Lee SJ, Koh JS, Suh HJ, Chancellor MB (2004) Comparison of doxazosin with or without tolterodine in men with symptomatic bladder outlet obstruction and an overactive bladder. BJU Int 94:817–820
Astellas, Betanis (mirabegron) package insert version 3, March 2012. PMDA. http://www.info.pmda.go.jp/downfiles/ph/PDF/80126_2590014F1021_1_02.pdf. Accessed 10 Aug 2012
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Otsuki, H., Kosaka, T., Nakamura, K. et al. β3-Adrenoceptor agonist mirabegron is effective for overactive bladder that is unresponsive to antimuscarinic treatment or is related to benign prostatic hyperplasia in men. Int Urol Nephrol 45, 53–60 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0343-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-012-0343-5