Abstract
Objective
To evaluate risk factors related to bladder cancer recurrence in patients with pathologically negative pelvic lymph nodes.
Methods
We reviewed 192 patients who underwent radical cystectomy for muscle invasive bladder cancer between 1999 and 2009. Patients with pathologically positive pelvic lymph nodes and <6-month follow-up were excluded. Clinicopathological parameters including grade, stage, lymphadenectomy type (standard vs. extended), number of nodes removed, margin status, lymphovascular invasion, perineural invasion, presence of carcinoma in situ, ureteral invasion, prostatic urethral invasion, and longest tumor dimension were evaluated. Kaplan–Meier and multivariate Cox analyses were used to evaluate these parameters for 5-year recurrence-free survival (5RFS) and 5-year overall survival (5OS).
Results
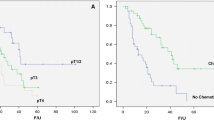
One hundred and fifty-five patients were included in this study. Mean follow-up duration was 36.6 months (12–141 months). Nuclear grade according to 2004 WHO classification (P = 0.006, P = 0.001), perineural invasion (P = 0.041, P = 0.048), lymphovascular invasion (P = 0.005, P = 0.027), and number of nodes removed (P < 0.001, P < 0.001) demonstrated differences in 5RFS and 5OS, respectively. In multivariate analysis, 5RFS was related to perineural invasion (P = 0.008; HR: 10.951; 95% CI: 1.891–63.407) and the number of nodes removed (P = 0.038; HR: 1.087; 95% CI: 1.004–1.176), and 5OS was correlated with lymphovascular invasion (P = 0.035; HR: 6.694; 95% CI: 1.143–39.217).
Conclusions
Perineural invasion and the number of nodes removed were independent risk factors for 5RFS, and lymphovascular invasion was for 5OS in patients with node-negative bladder cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58:71–96
Dalbagni G, Genega E, Hashibe M et al (2001) Cystectomy for bladder cancer: a contemporary series. J Urol 165:1111–1116
Takahashi A, Tsukamoto T, Tobisu K et al (2004) Radical cystectomy for invasive bladder cancer: results of multi-institutional pooled analysis. Jpn J Clin Oncol 34:14–19
Bassi P, Ferrante GD, Piazza N et al (1999) Prognostic factors of outcome after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a retrospective study of a homogeneous patient cohort. J Urol 161:1494–1497
Cheng L, Weaver AL, Leibovich BC et al (2000) Predicting the survival of bladder carcinoma patients treated with radical cystectomy. Cancer 88:2326–2332
Horikawa Y, Kumazawa T, Narita S et al (2007) Lymphatic invasion is a prognostic factor for bladder cancer treated with radical cystectomy. Int J Clin Oncol 12:131–136
Hugen CM, Polcari AJ, Fitzgerald MP et al (2010) Risk factors for recurrence following radical cystectomy for pathologic node negative bladder cancer. J Surg Oncol 15(102):334–337
Greene FL, Page DL, Fleming ID et al (2002) AJCC cancer staging manual. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia
Resorlu B, Beduk Y, Baltaci S et al (2009) The prognostic significance of advanced age in patients with bladder cancer treated with radical cystectomy. BJU Int 103:480–483
Takashi M, Murase T, Mizuno S et al (1987) Multivariate evaluation of prognostic determinants in bladder cancer patients. Urol Int 42:368–374
Thrasher JB, Frazier HA, Robertson JE et al (1994) Clinical variables which serve as predictors of cancer-specific survival among patients treated with radical cystectomy for transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder and prostate. Cancer 73:1708–1715
Lipponen PK, Eskelinen MJ, Kiviranta J et al (1991) Prognosis of transitional cell bladder cancer: a multivariate prognostic score for improved prediction. J Urol 146:1535–1540
Skinner EC, Lieskovsky G, Skinner DG (1984) Radical cystectomy in the elderly patient. J Urol 131:1065–1068
Raitanen MP, Nieminen P, Tammela TL (1995) Impact of tumour grade, stage, number and size, and smoking and sex, on survival in patients with transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Br J Urol 76:470–474
Pollack A, Zagars GK, Dinney CP et al (1994) Preoperative radiotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder carcinoma. Long term follow-up and prognostic factors for 338 patients. Cancer 74:2819–2827
Stein JP, Lieskovsky G, Cote R et al (2001) Radical cystectomy in the treatment of invasive bladder cancer: long-term results in 1,054 patients. J Clin Oncol 19:666–675
Honma I, Masumori N, Sato E et al (2006) Removal of more lymph nodes may provide better outcome, as well as more accurate pathologic findings, in patients with bladder cancer–analysis of role of pelvic lymph node dissection. Urology 68:543–548
Herr HW (2003) Extent of surgery and pathology evaluation has an impact on bladder cancer outcomes after radical cystectomy. Urology 61:105–108
Herr HW, Bochner BH, Dalbagni G et al (2002) Impact of the number of lymph nodes retrieved on outcome in patients with muscle invasive bladder cancer. J Urol 167:1295–1298
Leissner J, Ghoneim MA, Abol-Enein H et al (2004) Extended radical lymphadenectomy in patients with urothelial bladder cancer: results of a prospective multicenter study. J Urol 171:139–144
Dotan ZA, Kavanagh K, Yossepowitch O et al (2007) Positive surgical margins in soft tissue following radical cystectomy for bladder cancer and cancer specific survival. J Urol 178:2308–2312; discussion 2313
Hong SK, Kwak C, Jeon HG et al (2005) Do vascular, lymphatic, and perineural invasion have prognostic implications for bladder cancer after radical cystectomy? Urology 65:697–702
Nangia AK, Konety BR, Wachtel S et al (1997) Perineural invasion in transitional cell carcinoma and the effect on prognosis following radical cystectomy. Urology 49:968–972
Liebig C, Ayala G, Wilks JA et al (2009) Perineural invasion in cancer: a review of the literature. Cancer 115:3379–3391
Jaeger TM, Weidner N, Chew K et al (1995) Tumor angiogenesis correlates with lymph node metastases in invasive bladder cancer. J Urol 154:69–71
Heney NM, Proppe K, Prout GR Jr et al (1983) Invasive bladder cancer: tumor configuration, lymphatic invasion and survival. J Urol 130:895–897
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by clinical research grant from Pusan National University Hospital 2011.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, E., Ha, H.K. & Chung, M.K. Prediction of prognosis after radical cystectomy for pathologic node-negative bladder cancer. Int Urol Nephrol 43, 1059–1065 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-9920-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-011-9920-2