Abstract
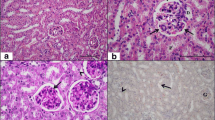
Nephrotoxicity is a major complication of acetaminophen (APAP), a widely used analgesic and antipyretic drug, and there is no specific treatment for APAP-induced renal damage. It has been reported that reactive oxygen metabolites or free radicals are important mediators of APAP toxicity. In this study, the protective role of melatonin (MLT) on APAP-induced nephrotoxicity was investigated in rats. For this purpose, nephrotoxicity was induced in male Wistar albino rats by intraperitoneal (i.p.) administration of a single dose of 1,000 mg/kg APAP. Some of these rats also received i.p. melatonin (10 mg/kg) 20 min after administration of APAP. The rats were sacrificed 24 h after administration of APAP. Urea and creatinine levels were measured in the blood, and levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and glutathione (GSH), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), catalase (CAT), and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were determined in renal tissue. Serum urea and creatinine levels increased significantly as a result of APAP nephrotoxicity. A significant increase in MDA and decreases in GSH level and GSH-Px, CAT, and SOD activity indicated that APAP-induced renal damage was mediated through oxidative stress. Significant beneficial changes were noted in serum and tissue oxidative stress indicators in rats treated with MLT. These biochemical observations were supplemented by histopathological examination of kidney sections, which revealed that MLT also reduced the severity of APAP-induced histological alterations in the kidney. These results indicate that administration of APAP causes oxidative stress to renal tissue and that MLT protects against the oxidative damage associated with APAP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kanno S, Tomizawa A, Hiur T et al (2006) Melatonin protects on toxicity by acetaminophen but not on pharmacological effects in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 29(3):472–476. doi:10.1248/bpb.29.472
Mazer M, Perrone J (2008) Acetaminophen–induced nephrotoxicity: pathophysiology, clinical manifestation, and management. J Med Toxicol 4(1):2–6
O’Grady JG (1997) Paracetamol-induced liver failure: prevention and management. J Hepatol 26:41–46. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(97)82332-X
Presscott LR, Wright N, Roscoe P et al (1971) Plasma paracetamol half-life and hepatic necrosis in patients with paracetamol overdosage Lancet 1:519–522. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(71)91125-1
Eguia L, Materson BJ (1997) Acetaminophen related acute renal failure without fulminant liver failure. Pharmacotherapy 17:363–370
Potter WZ, Davis DC, Mitchell JR et al (1973) Acetaminophen induced hepatic necrosis: III. Cytochrome P-450 mediated covalent binding in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 87:203–210
Moller-Hartmann W, Seigers CP (1992) Nephrotoxicity of paracetamol in the rat. Mechanistic and therapeutic aspects. J Appl Toxicol 11:141–146. doi:10.1002/jat.2550110213
Prescott LF (1993) Paracetamol overdose: Pharmacological considerations and clinical management. Drugs 25:290–314. doi:10.2165/00003495-198325030-00002
Gu J, Cui H, Behr M et al (2005) In vivo mechanisms of tissue-selective drug toxicity: effects of liver-specific knockout of the NADPH-cytochrome P–450 reductase gene on acetaminophen toxicity in kidney, lung, and nasal mucosa. Mol Pharmacol 67:623–630. doi:10.1124/mol.104.007898
Zaher H, Buters JT, Ward JM et al (1998) Protection against acetaminophen toxicity in CYP1A2 and CYP2E1 double-null mice. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 152:193–199. doi:10.1006/taap.1998.8501
Matthews AM, Roberts DW, Hinson JA et al (1996) Acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Analysis of total covalent binding vs. specific binding to cysteine. Drug Metab Dispos 24:1192–1196
Tükel SS (1995) Effects of acetaminophen on methemoglobin, superoxide dismutase and Na (+)-K+ ATPase activities of human erythrocytes. Biochem Mol Biol Int 35:719–724
Kapiotis S, Sengoelge G, Hermann M et al (1997) Paracetamol catalyzes myeloperoxidase-initiated lipid oxidation in LDL. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 17:2855–2860
Bessems JG, Vermeulen NP (2001) Paracetamol (acetaminophen)-induced toxicity: molecular and biochemical mechanisms, analogues and protective approaches. Crit Rev Toxicol 31:55–138. doi:10.1080/20014091111677
Khandkar MA, Parmar DV, Das M et al (1996) Is activation of lysosomal enzymes responsible for paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity? J Pharm Pharmacol 48:437–440
Lorz C, Justo P, Sanz AB et al (2005) Role of Bcl-xL in paracetamol-induced tubular epithelial cell death. Kidney Int 67:592–601. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.67115.x
Flanagan RJ, Meredith TJ (1991) Use of N-acetylcysteine in clinical toxicology. Am J Med 91:131S–139S. doi:10.1016/0002-9343(91)90296-A
Larsen LC, Fuller SH (1996) Management of acetaminophen toxicity. Am Fam Physician 53:185–190
Engelhardt G, Hopmma D (1996) Effect of acetyl salicylic acid, paracetamol and caffeine and a combination of these substances on kidney glutathione levels. Arzneimittelforschung 46:513–518
Davenport A, Finn R (1988) Paracetamol (acetaminophen) poisoning resulting in renal failure without hepatic coma. Nephron 50:55–56
Blakely P, McDonald BR (1995) Acute renal failure due to acetaminophen ingestion: a case report and review of the literature. J Am Soc Nephrol 6:48–53
Karbownik M, Lewinski A, Reiter RJ (2001) Anticarcinogenic actions of melatonin which involve antioxidative processes: comparison with other antioxidants. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 33:735–753. doi:10.1016/S1357-2725(01)00059-0
Bangha E, Elsner P, Kistler GS (1997) Suppression of UV-induced erythema by topical treatment with melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine). Influence of the application time point. Dermatology 195:248–252
Belles M, Linares V, Albina ML et al (2007) Melatonin reduces uranium-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. J Pineal Res 43:87–95. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2007.00447.x
Sener G, Sehirli O, Ayanoğlu-Dülger G (2005) Melatonin protects against mercury (II)-induced oxidative tissue damage in rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 93:290–296. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0773.2003.pto930607.x
El-Sokkary GH, Abdel-Rahman GH, Kames ES (2005) Melatonin protects against lead-induced hepatic and renal toxicity in male rats. Toxicology 213:25–33. doi:10.1016/j.tox.2005.05.003
Parlakpınar H, Özer MK, Sahna E et al (2003) Amikacin-induced acute renal injury in rats: protective role of melatonin. J Pineal Res 35:85–90. doi:10.1034/j.1600-079X.2003.00059.x
Longoni B, Migliori M, Ferretti A et al (2002) Melatonin prevents cyclosporine-induced nephrotoxicity in isolated and perfused rat kidney. Free Radic Res 36:357–363. doi:10.1080/10715760290019381
Abraham P (2005) Vitamin C may be beneficial the prevention of paracetamol-induced renal damage. Clin Exp Nephrol 9:24–30. doi:10.1007/s10157-004-0335-6
Sener G, Sehirli AÖ, Ayanoğlu-Dülger G (2003) Protective effects of melatonin, vitamin E and N-acetylcysteine against acetaminophen toxicity in mice: a comparative study. J Pineal Res 35:61–68. doi:10.1034/j.1600-079X.2003.00050.x
Sanchez DJ, Belles M, Albina ML et al (2001) Nephrotoxicity of simultaneous exposure to mercury and uranium in comparison to individual effects of these metals in rats. Biol Trace Elem Res 84:139–154. doi:10.1385/BTER:84:1-3:139
Wasowicz W, Neve J, Peretz A (1993) Optimized steps in fluorimetric determination thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances in serum: importance of extraction pH and influence sample preservation and storage. Clin Chem 39:2522–2528
Beutler E (1975) Glutathione in red blood cell metabolism. A manual of biochemical methods. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 112–114
Paglia D, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–163
Aebi H (1982) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed.) Methods in enzymatic analysis. Weinheim: Verlag Chemic, pp. 273–282
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Houghton DC, Plamp CE, DeFehr JM et al (1978) Gentamicin and tobramycin nephrotoxicity. A morphologic and functional comparison in the rat. Am J Pathol 93:137–152
Simic T, Mimic-Oka J, Sindjic M (1996) Glutathione and enzymes associated with glutathione metabolism in Adriamycin nephropathy. Srp Arh Celok Lek 124:45–47
Li C, Lui J, Saaedra JE et al (2003) The nitric oxide donor, V-PYRRO/NO, protects against acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in mice. Toxicology 189:173–180. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(03)00129-X
Isik B, Bayrak R, Akcay A et al (2006) Erdosteine against acetaminophen induced renal toxicity. Mol Cell Biochem 287:185–191. doi:10.1007/s11010-005-9110-6
Cuzzocrea S, Reiter RJ (2002) Pharmacological actions of melatonin in acute and chronic inflammation. Curr Top Med Chem 2:153–165. doi:10.2174/1568026023394425
Uyemura SA, Santos AC, Mingatto FE et al (1997) Diclofenac sodium and mefenamic acid: potent inducers of the membrane permeability transition in renal cortex mitochondria. Arch Biochem Biophys 342:231–235. doi:10.1006/abbi.1997.9985
Trumper L, Monasterolo LA, Elías MM (1998) Probenecid protects against In vivo acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in male Wistar rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:606–610
Manautou JE, Silva VM, Hennig GE (1998) Repeated dosing with the peroxisome proliferator clofibrate decreases the toxicity of model hepatotoxic agents in male mice. Toxicology 127:1–10. doi:10.1016/S0300-483X(98)00013-4
Björck S, Svalander CT, Aurell M (1988) Acute renal failure after analgesic drugs including paracetamol (acetaminophen). Nephron 49:45–53
Kleinman JG, Breitenfield RV, Roth DA (1980) Acute renal failure associated with acetaminophen ingestion: report of a case and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol 14:201–205
Venkatesan N, Punithavathi D, Arumugam V (2000) Curcumin prevents adriamycin nephrotoxicity in rats. Br J Pharmacol 129:231–234. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703067
Tan DX, Pöeggeler B, Reiter RJ et al (1993) The pineal hormone melatonin inhibits DNA-adduct formation induced by the chemical carcinogen safrole in vivo. Cancer Lett 70:65–71. doi:10.1016/0304-3835(93)90076-L
Barchas J, DaCosta F, Spector S (1967) Acute pharmacology of melatonin. Nature 214:919–920. doi:10.1038/214919a0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İlbey, Y.Ö., Ozbek, E., Cekmen, M. et al. Melatonin prevents acetaminophen-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int Urol Nephrol 41, 695–702 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9503-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-008-9503-z