Abstract
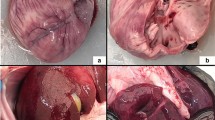
Trypanosoma evansi infection typically produces wasting disease, but it can also develop into a neurological or meningoencephalitis form in equids. Trypanosomiasis in horses was treated with quinapyramine sulfate, and all the 14 infected animals were recovered clinically. After clinical recovery, four animals developed a neurological form of the disease at various intervals. Two of these animals treated with diminazene aceturate recovered temporarily. Repeated attempts failed to find the parasite in the blood or the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), but all of the animals were positive in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The calculation of the antibody index (AI) in the serum and the CSF and polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of the CSF and brain tissue were carried out to confirm the neuro-infection. We found PCR and AI analyses of the CSF to be useful tools in the diagnosis of the neurological form of trypanosomiasis when the organism cannot be found in the blood or CSF. The increased albumin quotient is indicative of barrier leakage due to neuroinflammation. The biochemical changes in the CSF due to nervous system trypanosomiasis include increases in the albumin quotient, total protein, and urea nitrogen. It seems to be the first report on relapse of the nervous form of trypanosomiasis in equids even after quinapyramine treatment in endemic areas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananyutthawongese, C.T., Saengsombut, K., Sukhumsirichat, W., Uthaisang, W., Sarataphanm, N., Chansiri, K., 1999. Detection of bovine hemoparasite infection using multiplex polymerase chain reaction. Science Asia, 25, 85–90.
Berlin, D., Loeb, E., Baneth, G., 2009. Disseminated central nervous system disease caused by Trypanasoma evansi in a horse. Veterinary Parasitology, 161, 316 – 319.
Furr, M., 2002. Antigen-specific antibodies in cerebrospinal fluid after intramuscular injection of ovalbumin in horses. Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine, 16, 588–592.
Furr, M., 2008, In: Furr, M., and Reed, S., (eds.), Equine Neurology. Blackwell publishing, Iowa, USA, pp. 47 – 218.
Furr, M., Andrews, F., 2008. Cerebrospinal fluid and the blood – brain barrier. In: Furr, M., and Reed, S., (eds.), Equine Neurology. Blackwell Publishing, Iowa, USA, pp. 33 – 46.
Hunter, C.A., Jennings, F.W., Adams, J.H., Murray, M., Kennedy, P.G.E., 1992. Subcurative chemotherapy and fatal post-treatment reactive encephalitis in African trypanosomiasis. The Lancet. 339(8799), 95–958.
Joshi, S.S., Singh, B., 2000. Evaluation of therapeutic and chemoprophylactic efficacy of certain drugs against clinical surra in buffalo. Indian Veterinary Journal, 77, 895–897.
Kennedy, P.G.E., 2006. Human African trypanosomiasis—neurological aspects. Journal of Neurology, 253, 411 – 416.
Laha, R., Sasmal, N.K., 2008. Endemic status of Trypanasoma evansi infection in a horse stable of eastern region of India: a field investigation. Tropical Animal Health and Production, 40, 357 – 361.
Lanham, S.M., Godfrey, D.G., 1970. Isolation of salivarian trypanosomes from man and other animals using DEAE cellulose. Experimental Parasitology, 28, 521–534.
Lejon, V., Reiber, H., Legros, D., Dje, N., Magnus, E., Wouters, I., Sindic, C.J.M., Bu”scher, P., 2003. Intrathecal Immune response pattern for improved diagnosis of central nervous system involvement in Trypanosomiasis. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 187, 1475–1483.
Lillie, R.D., Fulmer, H.M., 1976. Histopathologic techniques in practical histochemistry. McGraw Hill, New York.
Masocha, W., Rottenberg, M.E., Kristensson, K., 2007. Migration of African trypanosomes across the blood–brain barrier. Physiology & Behaviour, 92, 110–114.
Monzon, C.M., Mancebo, O.A., Russo, A.M., 2003. Antibody levels by indirect ELISA test in Trypanosoma evansi infected horses following treatment with quinapyramine sulfate. Veterinary Parasitology, 111, 59–63.
Mulenga, C., Mhlanga, J.D., Kriistensson, K., Robertson, B., 2001. Trypanosoma brucei brucei crosses the blood–brain barrier while tight junction proteins are preserved in a rat chronic disease model. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 27, 77–85.
OIE - Office International Des Epizootics, 2004. Surra (Trypanasoma evansi) In: Manual of diagnostic tests and vaccines for terrestrial animals, Chapter 2.5, 15.
Pathak, K.M.L., Arora, J.K., Kapoor, M., 1993. Camel trypanosomiasis in Rajesthan, India. Veterinary Parasitology, 49, 319–323.
Philip, K.A., Dascombe, M.J., Fraser, P.A., Pentreath, V.W., 1994. Blood–brain barrier damage in experimental African trypanosomiasis. Annals of Tropical Medicine and Parasitology, 88, 607–616.
Ranjithkumar, M., Kamili, N.M., Saxena, A., Dan, Ananya, Dey, S., Raut, S.S., 2011. Disturbance of oxidant or antioxidant equilibrium in horses naturally infected with Trypanasoma evansi. Veterinary Parasitology, 180 (3–4), 349–353.
Reid, S.A., 2002. Trypanosoma evansi control and containment in Australia. Trends in Parasitology. 18 (5), 219–224.
Rodgers, J., 2010. Trypanosomiasis and the brain. Parasitology, 137, 1995–2006.
Rodrigues, A., Fighera, R.A., Souza, T.M., Sehild, A.L., Barros, C.S.L., 2009. Neuropathology of naturally occurring Trypanasoma evansi infection of horses. Veterinary Pathology, 46 (2), 251 – 258.
Seiler, R.J., Omar, S., Jackson, A.R.B., 1981. Meningoencephalitis in naturally occurring Trypanasoma evansi infection (Surra) of horses. Veterinary Pathology, 18, 120 – 122.
Sellon, D.C., 2007. Surra – miscellaneous parasitic infections. In: Sellon, D.C., Long, M.T., (Eds). Equine infectious diseases. Saunders Elsevier, St.Louis MO, pp. 475 – 476.
Terlizzi, R.D., Platt, S.R. 2009. The function, composition and analysis of cerebrospinal fluid in companion animals, Part –II – Analysis. Veterinary Journal, 80 (1), 15 – 32.
Tuntasuvan, D., Sarataphan, N., Nishikawa, H., 1997. Cerebral trypanasomiasis in native cattle. Veterinary Parasitology, 73, 357 – 363.
Tuntasuvan, D., Mimapan, S., Sarataphanm, N., Trongwongsa, L., Intraraksa, R., Lukins, A.G., 2000. Detection of Trypansoma evansi in brains of the naturally infected hog deer by streptavidine – biotin immunohistochmistry. Veterinary Parasitology, 87, 223 – 230.
Whitelaw, D.D., Gardiner, P.R., Murray, M., 1988. Extravasular foci of Trypansoma vivax in goats: the central nervous system and aqueous humour of the eye as potential sources of relapse infections after chemotherapy. Parasitology, 97, 51–61.
WHO (1998) Control and surveillance of African trypanasomiasis. Report of a WHO expert committee. World health organization. Geneva, Switzerland, Technical report series No. 881, pp. 114.
Yadav, S.C., Kumar, R., Kumar, S., Tatu, U., Singh, R.K., Gupta, A.K., 2011. Identification and characterization of cysteine proteinases of Trypanosoma evansi. Parasitology Research, 109, 559–565.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ranjithkumar, M., Saravanan, B.C., Yadav, S.C. et al. Neurological trypanosomiasis in quinapyramine sulfate-treated horses—a breach of the blood–brain barrier?. Trop Anim Health Prod 46, 371–377 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-013-0498-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11250-013-0498-9