Abstract
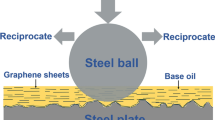
Fabricating high-quality graphene with simple methods has aroused considerable interests in recent years. In this paper, graphite was dispersed in esterified bio-oil as a lubricant for steel/gray cast iron friction pairs, and the shear-induced transformation from graphite to graphene was observed. The tribological behavior during this process, including the influence of the normal load and sliding velocity, was investigated. The products formed after sliding were confirmed by Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results showed that friction induces exfoliation, accounting for the transformation from graphite into graphene, and the frictional conditions influence the products. It was also found that high loads and low sliding velocities facilitate the formation of high-quality single-layer graphene during sliding, and high loads and low sliding velocities also contributed to obtaining excellent tribological performance for friction pairs. Friction-induced transformation demonstrates a potentially new strategy for in situ graphene preparation.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, Y., Tan, Y.-W., Stormer, H.L., Kim, P.: Experimental observation of the quantum Hall effect and Berry’s phase in graphene. Nature 438, 201–204 (2005)
Li, X., Cai, W., An, J., Kim, S., Nah, J., Yang, D., Piner, R., Velamakanni, A., Jung, I., Tutuc, E.: Large-area synthesis of high-quality and uniform graphene films on copper foils. Science 324, 1312–1314 (2009)
Kostarelos, K., Novoselov, K.S.: Exploring the interface of graphene and biology. Science 344, 261–263 (2014)
Bonaccorso, F., Colombo, L., Yu, G., Stoller, M., Tozzini, V., Ferrari, A.C., Ruoff, R.S., Pellegrini, V.: Graphene, related two-dimensional crystals, and hybrid systems for energy conversion and storage. Science 347, 1246501 (2015)
Le, T.X.H., Bechelany, M., Lacour, S., Oturan, N., Oturan, M.A., Cretin, M.: High removal efficiency of dye pollutants by electron-Fenton process using a graphene based cathode. Carbon 94, 1003–1011 (2015)
Novoselov, K.S., Geim, A.K., Morozov, S., Jiang, D., Zhang, Y., Dubonos, S.A., Grigorieva, I., Firsov, A.: Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 306, 666–669 (2004)
Raccichini, R., Varzi, A., Passerini, S., Scrosati, B.: The role of graphene for electrochemical energy storage. Nat. Mater. 14, 271–279 (2015)
Wu, K.-H., Cheng, H.-H., Mohammad, A.A., Blakey, I., Jack, K., Gentle, I.R., Wang, D.-W.: Electron-beam writing of deoxygenated micro-patterns on graphene oxide film. Carbon 95, 738–745 (2015)
Yao, J., Shi, X., Zhai, W., Ibrahim, A.M.M., Xu, Z., Chen, L., Zhu, Q., Xiao, Y., Zhang, Q., Wang, Z.: The enhanced tribological properties of NiAl intermetallics: combined lubrication of multilayer graphene and WS2. Tribol. Lett. 56, 573–582 (2014)
Kay, L., Porter, A.L., Youtie, J., Rafols, I., Newman, N.: Mapping graphene science and development: focused research with multiple application areas. J. Am. Soc. Inf. Sci. Tech. 41, 22–25 (2015)
Yi, M., Shen, Z.: A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 11700–11715 (2015)
Tetlow, H., De Boer, J.P., Ford, I., Vvedensky, D., Coraux, J., Kantorovich, L.: Growth of epitaxial graphene: theory and experiment. Phys. Rep. 542, 195–295 (2014)
Strudwick, A.J., Weber, N.E., Schwab, M.G., Kettner, M., Weitz, R.T., Wünsch, J.R., Müllen, K., Sachdev, H.: Chemical vapor deposition of high quality graphene films from carbon dioxide atmospheres. ACS Nano 9, 31–42 (2014)
Chua, C.K., Pumera, M.: Chemical reduction of graphene oxide: a synthetic chemistry viewpoint. Chem. Soc. Rev. 43, 291–312 (2014)
Novoselov, K.S., Fal, V., Colombo, L., Gellert, P., Schwab, M., Kim, K.: A roadmap for graphene. Nature 490, 192–200 (2012)
Kuila, T., Bose, S., Hong, C.E., Uddin, M.E., Khanra, P., Kim, N.H., Lee, J.H.: Preparation of functionalized graphene/linear low density polyethylene composites by a solution mixing method. Carbon 49, 1033–1037 (2011)
Barham, G.: Good and bad lubricants. J. Am. Soc. Nav. Eng. 27, 694–697 (1915)
Gillett, H.W.: Analyses and friction tests of lubricating greases. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1, 351–360 (1909)
Mabery, C.F.: Lubrication with oils, and with colloidal graphite. Ind. Eng. Chem. 5, 717–723 (1913)
Shaji, S., Radhakrishnan, V.: Analysis of process parameters in surface grinding with graphite as lubricant based on the Taguchi method. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 141, 51–59 (2003)
Alberts, M., Kalaitzidou, K., Melkote, S.: An investigation of graphite nanoplatelets as lubricant in grinding. Int. J. Mach. Tool Manuf. 49, 966–970 (2009)
Suresh Kumar Reddy, N., Venkateswara Rao, P.: Performance improvement of end milling using graphite as a solid lubricant. Mater. Manuf. Process. 20, 673–686 (2005)
Kumar, N., Dash, S., Tyagi, A.K., Raj, B.: Super low to high friction of turbostratic graphite under various atmospheric test conditions. Tribol. Int. 44, 1969–1978 (2011)
Mungse, H.P., Kumar, N., Khatri, O.P.: Synthesis, dispersion and lubrication potential of basal plane functionalized alkylated graphene nanosheets. RSC Adv. 5, 25565–25571 (2015)
Toyoda, M., Inagaki, M.: Heavy oil sorption using exfoliated graphite: new application of exfoliated graphite to protect heavy oil pollution. Carbon 38, 199–210 (2000)
Marks, N.: Generalizing the environment-dependent interaction potential for carbon. Phys. Rev. B 63, 035401 (2000)
León, V., Rodriguez, A.M., Prieto, P., Prato, M., Vázquez, E.: Exfoliation of graphite with triazine derivatives under ball-milling conditions: preparation of few-layer graphene via selective noncovalent interactions. ACS Nano 8, 563–571 (2014)
Xu, Y., Zheng, X., Hu, X., Dearn, K.D., Xu, H.: Effect of catalytic esterification on the friction and wear performance of bio-oil. Wear 311, 93–100 (2014)
Xu, Y., Hu, X., Yuan, K., Zhu, G., Wang, W.: Friction and wear behaviors of catalytic methylesterified bio-oil. Tribol. Int. 71, 168–174 (2014)
Xu, Y., Peng, Y., Dearn, K.D., Zheng, X., Yao, L., Hu, X.: Synergistic lubricating behaviors of graphene and MoS2 dispersed in esterified bio-oil for steel/steel contact. Wear 342, 297–309 (2015)
Wang, G., Shen, X., Wang, B., Yao, J., Park, J.: Synthesis and characterisation of hydrophilic and organophilic graphene nanosheets. Carbon 47, 1359–1364 (2009)
Li, D., Muller, M.B., Gilje, S., Kaner, R.B., Wallace, G.G.: Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 101–105 (2008)
Liang, S., Shen, Z., Yi, M., Liu, L., Zhang, X., Ma, S.: In-situ exfoliated graphene for high-performance water-based lubricants. Carbon 96, 1181–1190 (2016)
Han, H., Gao, Y., Zhang, Y., Du, S., Liu, H.: Effect of magnetic field distribution of friction surface on friction and wear properties of 45 steel in DC magnetic field. Wear 328, 422–435 (2015)
Ferrari, A.C., Meyer, J.C., Scardaci, V., Casiraghi, C., Lazzeri, M., Mauri, F., Piscanec, S., Jiang, D., Novoselov, K.S., Roth, S., Geim, A.K.: Raman spectrum of graphene and graphene layers. Phys. Rev. Lett. 97, 187401 (2006)
Schmucker, S.W., Cress, C.D., Culbertson, J.C., Beeman, J.W., Dubon, O.D., Robinson, J.T.: Raman signature of defected twisted bilayer graphene. Carbon 93, 250–257 (2015)
Umair, A., Raza, H.: Controlled synthesis of bilayer graphene on nickel. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 7, 1–5 (2012)
Gupta, B., Panda, K., Kumar, N., Melvin, A.A., Dash, S., Tyagi, A.K.: Chemically grafted graphite nanosheets dispersed in poly (ethylene-glycol) by γ-radiolysis for enhanced lubrication. RSC Adv. 5, 53766–53775 (2015)
Ferrari, A.C.: Raman spectroscopy of graphene and graphite: disorder, electron–phonon coupling, doping and nonadiabatic effects. Solid State Commun. 143, 47–57 (2007)
Lin, J., Wang, L., Chen, G.: Modification of graphene platelets and their tribological properties as a lubricant additive. Tribol. Lett. 41, 209–215 (2011)
Chen, B., Bi, Q., Yang, J., Xia, Y., Hao, J.: Tribological properties of solid lubricants (graphite, h-BN) for Cu-based P/M friction composites. Tribol. Int. 41, 1145–1152 (2008)
Xu, Y.F., Zheng, X.J., Yin, Y.G., Huang, J., Hu, X.G.: Comparison and analysis of the influence of test conditions on the tribological properties of emulsified bio-oil. Tribol. Lett. 55, 543–552 (2014)
Gong, T., Yao, P., Xiao, Y., Fan, K., Tan, H., Zhang, Z., Zhao, L., Zhou, H., Deng, M.: Wear map for a copper-based friction clutch material under oil lubrication. Wear 328, 270–276 (2015)
Muthuraja, A., Senthilvelan, S.: Adhesive wear performance of tungsten carbide based solid lubricant material. Int. J. Refract. Hard Met. 52, 235–244 (2015)
Major, L., Janusz, M., Kot, M., Lackner, J., Major, B.: Development and complex characterization of bio-tribological Cr/CrN+ aC: H (doped Cr) nano-multilayer protective coatings for carbon-fiber-composite materials. RSC Adv. 5, 9405–9415 (2015)
Li, X., Zhou, Y., Ji, X., Li, Y., Wang, S.: Effects of sliding velocity on tribo-oxides and wear behavior of Ti–6Al–4 V alloy. Tribol. Int. 91, 228–234 (2015)
Allen, M.J., Tung, V.C., Kaner, R.B.: Honeycomb carbon: a review of graphene. Chem. Rev. 110, 132–145 (2009)
Wang, L., Zhang, Q., Li, X., Cui, X., Wang, S.: Severe-to-mild wear transition of titanium alloys as a function of temperature. Tribol. Lett. 53, 511–520 (2014)
Karlsson, P., Gåård, A., Krakhmalev, P.: Influence of tool steel microstructure on friction and initial material transfer. Wear 319, 12–18 (2014)
Berman, D., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Few layer graphene to reduce wear and friction on sliding steel surfaces. Carbon 54, 454–459 (2013)
Kim, K.-S., Lee, H.-J., Lee, C., Lee, S.-K., Jang, H., Ahn, J.-H., Kim, J.-H., Lee, H.-J.: Chemical vapor deposition-grown graphene: the thinnest solid lubricant. ACS Nano 5, 5107–5114 (2011)
Sarno, M., Senatore, A., Cirillo, C., Petrone, V., Ciambelli, P.: Oil lubricant tribological behaviour improvement through dispersion of few layer graphene oxide. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 14, 4960–4968 (2014)
Berman, D., Erdemir, A., Sumant, A.V.: Reduced wear and friction enabled by graphene layers on sliding steel surfaces in dry nitrogen. Carbon 59, 167–175 (2013)
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate Prof. Wilfred T. Tysoe of University of Wisconsin–Milwaukee for giving helpful revisions and constructive suggestions. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51405124), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (Grant No. 2015T80648 & 2014M560505), the Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 1408085ME82) and the Tribology Science Fund of State Key Laboratory of Tribology (Grant No. STKLKF15A05).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Y., Geng, J., Zheng, X. et al. Friction-Induced Transformation from Graphite Dispersed in Esterified Bio-Oil to Graphene. Tribol Lett 63, 18 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0708-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-016-0708-5