Abstract
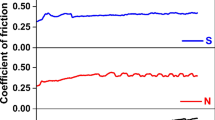
In this study, the effects of resin type and fiber length on mechanical properties and friction characteristics of automotive brake materials were studied. Three types of resin, viz. straight phenolic resin (SR), cashew nut shell liquid modified resin (CR), and melamine resin (MR) were used as matrix material. Lapinus with different lengths was used as inorganic fiber. Three series of friction composites composed of nine composites in the form of brake materials were manufactured. Physical, mechanical, and tribological properties of all composites were investigated. The friction tests were performed using a Chase type friction tester. The results showed that both resin type and fiber length played an important role on the mechanical and tribological properties of the friction materials. The highest and the lowest friction coefficient for resin types were recorded for SR and MR composites, respectively, while MR and CR composites showed the highest and the lowest wear resistance, respectively. For the fiber length considered, increasing the fiber length increased the wear resistance of the composites. The coefficient of friction, in general, showed a good correlation with the wear resistance of the composites. But, there was no clear correlation with the mechanical and tribological properties of the composites. The morphological features of worn surfaces and wear debris of the composites were analyzed in order to understand the friction and wear mechanisms of this tribosystem.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Satapathy, B.K., Bijwe, J.: Fade and recovery of non-asbestos organic (NAO) composite friction materials based on combinations of rock fibers and organic fibers. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 24, 563–576 (2005)
Kim, S.J., Cho, M.H., Lim, D.S., Jang, H.: Synergistic effects of aramid pulp and potassium titanate whiskers in the automotive friction material. Wear 251, 1484–1491 (2001)
Kim, S.J., Lee, J.Y., Jang, H.: Effect of humidity on friction characteristics of automotive friction materials. KSTL Int. J. 2, 150–153 (2001)
Ertan, R., Yavuz, N.: An experimental study on the effects of manufacturing parameters on the tribological properties of brake lining materials. Wear 268, 1524–1532 (2010)
Satapathy, B.K., Bijwe, J.: Composite friction materials based on organic fibers: Sensitivity of friction and wear operating variables. Composites A 37, 1557–1567 (2006)
Kim, S.J., Jang, H.: Friction and wear of friction materials containing two different phenolic resins reinforced with aramid pulp. Tribol. Int. 33, 477–484 (2000)
Gurunath, P.V., Bijwe, J.: Friction and wear studies on brake-pad materials based on newly developed resin. Wear 263, 1212–1219 (2007)
Kumar, M., Bijwe, J.: Role of different metallic fillers in non-asbestos organic (NAO) friction composites for controlling sensitivity of coefficient of friction to load and speed. Tribol. Int. 43, 965–974 (2010)
Gopal, P., Dharani, L.R., Blum, F.D.: Fade and wear characteristics of a glass-fiber-reinforced phenolic friction material. Wear 174, 119–127 (1994)
Bijwe, J., Nidhi, Satapathy, B.K.: Influence of amount of resin on fade and recovery behaviour of non-asbestos organic (NAO) friction materials. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 57, 335–344 (2004)
Zhang, H., Zhang, Z., Friedrich, K.: Effect of fiber length on the wear resistance of short carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 67, 222–230 (2007)
Subramaniam, N., Sinha, B.R., Blum, F.D., Chen, Y.R., Dharani, L.R.: Glass fiber based friction materials. Int. J. Polym. Mater. 15, 93–102 (1991)
Eriksson, M., Jacobson, S.: Tribological surfaces of organic brake pads. Tribol. Int. 33, 817–827 (2000)
Nidhi, Bijwe, J., Mazumdar, N.: Influence of amount and modification of resin on fade and recovery behavior of non-asbestos organic (NAO) friction materials. Tribol. Lett. 23, 215–222 (2006)
Öztürk, B., Arslan, F., Öztürk, S.: Hot wear properties of ceramic and basalt fiber reinforced hybrid friction materials. Tribol. Int. 40, 37–48 (2007)
Callaghan, D.J., Vaziri, A., Hashemi, H.N.: Effect of fiber volume fraction and length on the wear characteristics of glass fiber-reinforced dental composites. Dent. Mater. 22, 84–93 (2006)
Vishwanath, B., Verma, A.P., Rao, C.V.S.K.: Friction and wear of a glass woven roving/modified phenolic composite. Composites 21, 531–536 (1990)
Mosleh, M., Blau, P.J., Dumitrescu, D.: Characteristics and morphology of wear particles from laboratory testing of disk brake materials. Wear 256, 1128–1134 (2004)
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support of this study by the Karadeniz Technical University Research Fund under Grant no. 2007.112.010.1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Öztürk, B., Öztürk, S. Effects of Resin Type and Fiber Length on the Mechanical and Tribological Properties of Brake Friction Materials. Tribol Lett 42, 339–350 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9779-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-011-9779-5