Abstract
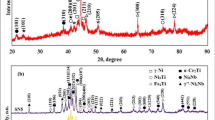
A Fe-based composite coating reinforced by multiple TiB2–TiC–Al2O3 ceramic particles was developed by gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) melting process. Mixture of aluminum (Al), boron carbide (B4C), and titanium dioxide (TiO2) powders was used as precursors, and as a consequence TiB2–TiC–Al2O3 multiple ceramic particles were in situ synthesized during GTAW melting process. Microstructural investigations showed that TiB2 particles exhibit a blocky morphology, TiC particles are of flower-like shape, and the Al2O3 particles exist as small black dots and located in the core of reinforced particles. The hardness and wear resistance of the coatings increased drastically in comparison with that of the substrate.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vallauri, D., Atías Adrián, I.C., Chrysanthou, A.: TiC–TiB2 composites: a review of phase relationships, processing and properties. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 28, 1697–1713 (2008)
Li, B., Liu, Y., Li, J., Cao, H., He, L.: Effect of sintering process on the microstructures and properties of in situ TiB2–TiC reinforced steel matrix composites produced by spark plasma sintering. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 210, 91–95 (2010)
Farid, A.: Microstructure evolution and wear properties of in situ synthesized TiB2 and TiC reinforced steel matrix composites. J. Alloys Compd. 459, 491–497 (2008)
Jiang, Q.C., Ma, B.X., Wang, H.Y., Wang, Y., Dong, Y.P.: Fabrication of steel matrix composites locally reinforced with in situ TiB2–TiC particulates using self-propagating high-temperature synthesis reaction of Al–Ti–B4C system during casting. Compos. Part A 37, 133–138 (2006)
Du, B., Paital, S.R., Dahotre, N.B.: Phase constituents and microstructure of laser synthesized TiB2–TiC reinforced composite coating on steel. Scr. Mater. 59, 1147–1150 (2008)
Chen, X., Yang, C., Guan, L., Yan, B.: TiB2/Al2O3 ceramic particle reinforced aluminum fabricated by spray deposition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 496, 52–58 (2008)
Tjong, S.C., Wang, G.S.: High-cycle fatigue properties of Al-based composites reinforced with in situ TiB2 and Al2O3 particulates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 386, 48–53 (2004)
Masanta, M., Ganesh, P., Kaul, R., Nath, A.K., Choudhury, A.R.: Development of a hard nano-structured multi-component ceramic coating by laser cladding. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 508, 134–140 (2009)
Hu, C., Barnard, L., Mridha, S., Baker, T.N.: Role of SiC particulate and Al2O3 (Saffil) fibers in several alloys during the formation of in situ MMCs developed by laser processing. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 58, 87–95 (1996)
Liu, Y., Chen, L.F., Tang, H.P., Liu, C.T., Liu, B., Huang, B.Y.: Design of powder metallurgy titanium alloys and composites. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 418, 25–35 (2006)
Yilmaz, O., Buytoz, S.: Abrasive wear of Al2O3-reinforced aluminium-based MMCs. Compos. Sci. Technol. 61, 2381–2392 (2001)
Du, B., Zou, Z., Wang, X., Qu, S.: In situ synthesis of TiB2/Fe composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Lett. 62, 689–691 (2008)
Dubourg, L., Ursescu, D., Hlawka, F., Cornet, A.: Laser cladding of MMC coatings on aluminium substrate: influence of composition and microstructure on mechanical properties. Wear 25, 1745–1754 (2005)
Cui, C., Guo, Z., Wang, H., Hu, J.: In situ TiC particles reinforced grey cast iron composite fabricated by laser cladding of Ni–Ti–C system. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 183, 380–385 (2007)
Kang, H., Kang, S.B.: Thermal decomposition of silicon carbide in a plasma-sprayed Cu/SiC composite deposit. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 428, 336–345 (2006)
Laha, T., Chen, Y., Lahiri, D., Agarwal, A.: Tensile properties of carbon nanotube reinforced aluminum nanocomposite fabricated by plasma spray forming. Compos. Part A 40, 589–594 (2009)
Wang, H.Y., Huang, L., Jiang, Q.C.: In situ synthesis of TiB2–TiC particulates locally reinforced medium carbon steel–matrix composites via the SHS reaction of Ni–Ti–B4C system during casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 407, 98–104 (2005)
Yang, Y., Wang, H., Liang, Y., Zhao, R., Jiang, Q.: Fabrication of steel matrix composites locally reinforced with different ratios of TiC/TiB2 particulates using SHS reactions of Ni–Ti–B4C and Ni–Ti–B4C–C systems during casting. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 445, 398–404 (2007)
Zhang, G.J., Ando, M., Yang, J.F., Ohji, T.: Boron carbide and nitride as reactants for in situ synthesis of boride-containing ceramic composites. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 24, 171–178 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X.H., Zhang, M. & Du, B.S. Fabrication In Situ TiB2–TiC–Al2O3 Multiple Ceramic Particles Reinforced Fe-Based Composite Coatings by Gas Tungsten Arc Welding. Tribol Lett 41, 171–176 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9701-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-010-9701-6