Abstract
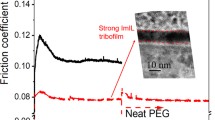
The tribological properties of trifluorotris(pentafluoroethyl) phosphate [(C2F5)3PF −3 , FAP]-derived ionic liquids were evaluated under boundary conditions. The anion is hydrophobic in comparison with bis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide [(CF3SO2)2N−, TFSI]. 1,3-Dialkylimidazolium salts of FAP provided much lower friction than 1,3-dialkylimidazolium salts of TFSI. In addition, the FAP salts exhibit better anti-wear properties than the TFSI salts. Another advantage of the FAP anion is availability of several cations to prepare ionic liquids. For example, tetraalkylphosphonium, N,N-dialkylpyrrolidium, and tetramethylisouronium salts of FAP provided friction coefficient of approximately 0.1. Straight-chain carboxylic acids as model friction-reducing additives improved the tribological properties of the FAP salts. Surface analyses were conducted to study the boundary film formed by rubbing. It was found that the boundary film is composed of adsorbed anion on uppermost surfaces and reacted anion on sub-surfaces. The model friction-reducing additives were found on the rubbed surfaces.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BF4:
-
Tetrafluoroborate
- FAP:
-
Trifluorotris(pentafluoroethyl) phosphate
- PF6:
-
Hexafluorophosphate
- TFSI:
-
bis(Trifluoromethylsulfonyl)imide
- d-C12A:
-
Perdeuteriododecanoic acid, C11D23COOH
- mM:
-
Unit of concentration (mmol kg−1)
- JIS:
-
Japanese Industrial Standards
- m/z:
-
Mass-to-charge ratio
- SUJ2:
-
Bearing steel assigned by JIS
- TOF-SIMS:
-
Time-of-flight secondary ion mass spectroscopy
- XPS:
-
X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy
References
Ye, C., Liu, W., Chen, Y., Yu, L.: Room-temperature ionic liquids: a novel versatile lubricant. Chem. Commun. 2244–2245 (2001)
Liu, W., Ye, C., Gong, Q., Wang, H., Wang, P.: Tribological performance of room-temperature ionic liquids as lubricant. Tribol. Lett. 13, 81–85 (2002)
Reich, R.A., Stewart, P.A., Bohaychick, J., Urbanski, J.A.: Base oil properties of ionic liquids. Lubric. Eng. 59, 16–22 (2003)
Chen, Y.X., Ye, C.F., Wang, H.Z., Liu, W.M.: Tribological performance of an ionic liquid as a lubricant for steel/aluminium contacts. J. Synth. Lubric. 20, 217–225 (2003)
Wang, H., Lu, Q., Ye, C., Liu, W., Cui, Z.: Friction and wear behaviors of ionic liquid of alkylimidazolium hexafluorophosphates as lubricants for steel/steel contact. Wear. 256, 44–48 (2004)
Lu, Q., Wang, H., Ye, C., Liu, W., Xue, Q.: Room temperature ionic liquid 1-ethyl-3-hexylimidazoliumbis(trifluoromethylsulfonyl)-imide as lubricant for steel/steel contact. Tribol. Int. 37, 547–552 (2004)
Xia, Y., Wang, S., Zhou, F., Wang, H., Lin, Y., Xu, T.: Tribological properties of plasma nitride stainless steel against SAE52100 steel under ionic liquid lubrication condition. Tribol. Int. 39, 635–640 (2006)
Sanes, J., Carrion, F.J., Bermudez, M.D., Martnez-Nicolas, G.: Ionic liquids as lubricants of polystyrene and polyamide 6-steel contacts. Preparation and properties of new polymer-ionic liquid dispersions. Tribol. Lett. 21, 121–133 (2006)
Kamimura, H., Chiba, T., Watanabe, N., Kubo, T., Minami, I., Mori, S.: Effects of carboxylic acids on wear and friction reducing properties for alkylimidazorium-derived ionic liquids. Tribol. Online 1, 40–43 (2006)
Kamimura, H., Kubo, T., Minami, I., Mori, S.: Effect and mechanism of additives for ionic liquids as new lubricants. Tribol. Int. 40, 620–625 (2007)
Mua, Z., Zhou, F., Zhang, S., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Effect of the functional groups in ionic liquid molecules on the friction and wear behavior of aluminum alloy in lubricated aluminum-on-steel contact. Tribol. Int. 38, 725–731 (2005)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Iglesias, P., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G.: 1-N-alkyl-3-methylimidazolium ionic liquids as neat lubricants and lubricant additives in steel aluminium contacts. Wear 260, 766–782 (2006)
Yua, B., Zhou, F., Mu, Z., Liang, Y., Liu, W.: Tribological properties of ultra-thin ionic liquid films on single-crystal silicon wafers with functionalized surfaces. Tribol. Int. 39, 879–887 (2006)
Jin, C-M., Ye, C., Phillips, B.S., Zabinski, J.S., Liu, X., Liu, W., Shreeve, J.M.: Polyethylene glycol functionalized dicationic ionic liquids with alkyl or polyfluoroalkyl substituents as high temperature lubricants. J Mater. Chem. 16, 1529–1535 (2006)
Yu, G., Zhou, F., Liu, W., Liang, Y., Yan, S.: Preparation of functional ionic liquids and tribological investigation of their ultra-thin films. Wear 260, 1076–1080 (2006)
Jimenez, A.E., Bermudez, M.D., Carrion, F.J., Martinez-Nicolas, G.: Room temperature ionic liquids as lubricant additives in steel–aluminium contacts: influence of sliding velocity, normal load and temperature. Wear 261, 347–359 (2006)
Qu, J., Truhan, J.J., Dai, S., Luo, H., Blau, P.J.: Ionic liquids with ammonium cations as lubricants or additives. Tribol. Lett. 22, 207–214 (2006)
Liu, X.Q., Zhou, F., Liang, Y.M., Liu, W.M.: Tribological performance of phosphonium based ionic liquids for an aluminum-on-steel system and opinions on lubrication mechanism. Wear 261, 1174–1179 (2006)
Omotowa, B.A., Phillips, B.S., Zabinski, J.S., Shreeve, J.M.: Phosphazene-based ionic liquids: synthesis, temperature-dependent viscosity, and effect as additives in water lubrication of silicon nitride ceramics. Inorg. Chem. 43, 5466–5471 (2004)
Minami, I., Kamimura, H., Mori, S.: Thermo-oxidative stability of ionic liquids as lubricating fluids. J. Synth. Lubric. 24, 135–147 (2007)
Abedin, S.Z.E., Borissenko, N., Endres, F.: Electropolymerization of benzene in a room temperature ionic liquid. Electrochem. Commun. 6, 422–426 (2004)
Schneider, O., Bund, A., Ispas, A., Borissenko, N., Abedin, S.Z.E., Endres, F.: An EQCM study of the electropolymerization of benzene in an ionic liquid and ion exchange characteristics of the resulting polymer film. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 7159–7168 (2005)
Kyropoulos, S., Shobert, E.I.: A simple method for measuring the coefficient of nonviscous friction of thin lubricating layers. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 8 151–158 (1937)
Bowden, F.P., Gregory, J.N., Tabor D.: Lubrication of metal surfaces by fatty acids. Nature 156, 97–101 (1945)
Jahanmir, S.: Chain length effects in boundary lubrication. Wear 102, 331–349 (1985)
Minami, I., Kubo, T., Fujiwara, S., Ogasawara, Y., Nanao, H., Mori, S.: Investigation of tribo-chemistry by means of stable isotopic tracers; TOF-SIMS analysis of Langmuir–Blodgett films and examination of their tribological properties. Tribol. Lett. 20, 287–297 (2005)
Minami, I., Kubo, T., Nanao, H., Mori, S., Okuda, S., Sagawa, T.: Investigation of tribo-chemistry by means of stable isotopic tracers (part 2); Lubrication mechanism of friction modifiers on diamond like carbon. Tribol. Trans. 50, 477–487 (2007)
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the grants-in-aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas, “Science of Ionic Liquids” no. 18045003 from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of the Japanese Government. The authors are grateful to Merck KGaA (Germany) for supporting the ionic liquids.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minami, I., Kita, M., Kubo, T. et al. The Tribological Properties of Ionic Liquids Composed of Trifluorotris(pentafluoroethyl) Phosphate as a Hydrophobic Anion. Tribol Lett 30, 215–223 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9329-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11249-008-9329-y