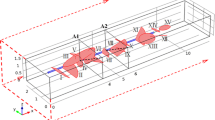
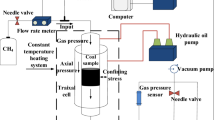
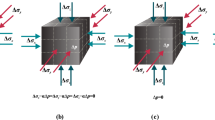
Abstract
Production data of coalbed methane have shown that coalbed may be wet for a long time after the completion of water flow and water–gas two-phase flow stages. In this period, water flows out in moisture vapor, but the water in matrix does not change so much. The moisture loss is mainly from the water film in fracture network. Experiments also observed that such a moisture loss has a profound impact on the storage and transport of coalbed methane. However, this impact has not been investigated so far. This study investigates this impact through following works: firstly, a new conceptual permeability model is proposed based on water film adhered to the surface of fractures in a dual-porosity porous medium. The effect of water film is further described in gas flow equation by a non-Darcy law with threshold pressure gradient. Thirdly, a coupled multi-physical model is established to consider the interactions among coal deformation, gas flow, gas sorption and moisture loss. This model is validated by the gas production data of a coal seam in the Fruitland formation of San Juan basin. Finally, four scenarios are computed to comprehensively study the impact of moisture loss. These simulations show that the proposed model can well fit the history of gas production data. Non-Darcy flow has different velocity profile from Darcy flow. For the non-Darcy flow, the gas flow velocity increases quickly, then slowly, and finally decreases once gas starts to flow at a point. Moisture evaporation with gas flow mainly occurs in the zone near wellbore. This loss has a delay to the gas flow velocity. It also reveals that this moisture loss in coal seams can significantly improve coal permeability and thus enhance gas production. Therefore, the change of water film has significant impacts on gas production.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brakel, J.V.: Mass transfer in convective drying. Adv. Dry. 1, 217–267 (1980)
Busch, A., Gensterblum, Y.: CBM and CO\(_{2}\)-ECBM related sorption processes in coal: a review. Int. J. Coal Geol. 87, 49–71 (2011)
Cai, J.C.: A fractal approach to low velocity non-Darcy flow in a low permeability porous medium. Chin. Phys. B 23(4), 044701 (2014)
Carrier, B., Wang, L., Vandamme, M., Pellenq, R.J.M., Bornert, M., Tanguy, A., Damme, H.V.: ESEM study of the humidity-induced swelling of clay film. Langmuir 29, 12823–12833 (2013)
Chen, D., Pan, Z.J., Liu, J., Connell, L.D.: Modeling and simulation of moisture effect on gas storage and transport in coal seams. Energy Fuels 26, 1695–1706 (2012)
Chen, D., Pan, Z., Liu, J., Connell, L.D.: An improved relative permeability model for coal reservoirs. Int. J. Coal Geol. 109, 45–57 (2013)
Clarkson, C.R., Rahmanian, M., Kantzas, A., Morad, K.: Relative permeability of CBM reservoirs: controls on curve shape. Int. J. Coal Geol. 88(4), 204–217 (2011)
Coppens, L.: L’adsorption du méthane par les houilles sous pression élevée. Annales des Mines de Belgique 37, 173 (1936)
Crosdale, P.J., Moore, T.A., Mares, T.E.: Influence of moisture content and temperature on methane adsorption isotherm analysis for coals from a low-rank, biogenically-sourced gas reservoir. Int. J. Coal Geol. 76, 166–174 (2008)
Day, S., Sakurovs, R., Weir, S.: Supercritical gas sorption on moist coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 74, 203–214 (2008)
Derjaguin, B.V., Churayev, N.: Investigation of the properties of water II. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 36(4), 415–426 (1971)
Derjaguin, B.V., Zorin, Z.M., Rabinovich, Y.I., Churaev, N.V.: Results of analytical investigation of the composition of “anomalous” water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 46(3), 437–441 (1974)
Detournay, E., Cheng, A.H.D.: Fundamentals of poroelasticity. In: Fairhurst, C. (ed.) Comprehensive Rock Engineering, pp. 113–171 (1993)
Ettinger, I.L., Lidin, G.D., Dmitriev, A.M., Shaupachina, E.S: Systematic Handbook for the Determination of the Methane Content of Coal Seams from the Seam Pressure of the Gas and the Methane Capacity of the Coal; U.S. Bureau of Mines Translation No. 1505/National Board Translation No. A.1606/SHE: Moscow (1958)
Gensterblum, Y., Busch, A., Krooss, B.M.: Molecular concept and experimental evidence of competitive adsorption of H\(_{2}\)O, CO\(_{2}\) and CH\(_{4}\) on organic material. Fuel 115, 581–588 (2014)
Gensterblum, Y., Merkel, A., Busch, A., Krooss, B.M.: High-pressure CH4 and CO2 sorption isotherms as a function of coal maturity and the influence of moisture. Int. J. Coal Geol. 118, 45–57 (2013)
Horn, R., Smith, D., Haller, W.: Surface forces and viscosity of water measured between silica sheets. Chem. Phys. Lett. 62(4–5), 404–408 (1989)
Ibrahim, A.F., Nasr-El-Din, H.A.: A comprehensive model to history match and predict gas/water production from coal seams. Int. J. Coal Geol. 146, 79–90 (2015)
Jahangir, M.H., Sadrnejad, S.A.: A new coupled heat, moisture and air transfer model in unsaturated soil. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 26(11), 3661–3672 (2012)
Joubert, J.I., Grein, C.T., Bienstock, D.: Effect of moisture on the methane capacity of American coals. Fuel 53, 186–191 (1974)
Laxminarayana, C., Crosdale, P.J.: Role of coal type and rank on methane sorption characteristics of Bowen Basin, Australia coals. Int. J. Coal Geol. 40, 309–325 (1999)
Lehmann, P., Assouline, S., Or, D.: Characteristic lengths affecting evaporative drying of porous media. Phys. Rev. E 77(5), 056309 (2008)
Levy, J.H., Day, S.J., Killingley, J.S.: Methane capacities of Bowen Basin coals related to coal properties. Fuel 76, 813–881 (1997)
Liu, J., Elsworth, D., Brady, B.H.: Linking stress-dependent effective porosity and hydraulic conductivity fields to RMR. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 36(5), 581–596 (1999)
Martin, C.H.: Australian Coal Mining Practice. Monographys, No. 12. Australasian Institute of Mining and Metallurgy: Parkville, Vic, 342 (1986)
Mastalerz, M., Solano-Acosta, W., Schimmelmann, A., Drobniak, A.: Effects of coal storage in air on physical and chemical properties of coal and on gas adsorption. Int. J. Coal Geol. 79, 167–174 (2009)
Nakagawa, T., Komaki, I., Sakawa, M., Nishikawa, K.: Small angle X-ray scattering study on change of fractal property of Witbank coal with heat treatment. Fuel 79(11), 1341–1346 (2000)
Nimmo, J.R.: Theory for source-responsive and free-surface film modeling of unsaturated flow. Vadose Zone J. 9, 295–306 (2010)
Nishiyama, N., Yokoyama, T.: Estimation of water film thickness in geological media associated with the occurrence of gas entrapment. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 7, 620–623 (2013a)
Nishiyama, N., Yokoyama, T.: Does the reactive surface area of sandstone depend on water saturation? The role of reactive-transport in water film. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 122, 153–169 (2013b)
Nishiyama, N., Yokoyama, T., Takeuchi, S.: Size distributions of pore water and entrapped air during drying-infiltration processes of sandstone characterized by water-expulsion porosimetry. Water Resour. Res. 48(9), W09556 (2012)
Ozdemir, E., Schroeder, K.: Effect of moisture on adsorption isotherms and adsorption capacities of CO\(_{2}\) on coals. Energy Fuels 23, 2821–2831 (2009)
Packham, R., Cinar, Y., Moreby, R.: Simulation of an enhanced gas recovery field trial for coal mine gas management. Int. J. Coal Geol. 85, 247–256 (2011)
Pan, Z., Connell, L.D., Camilleri, M., Connelly, L.: Effects of matrix moisture on gas diffusion and flow in coal. Fuel 89, 3207–3217 (2010)
Pan, Z.: Modeling of coal swelling induced by water vapor adsorption. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 6(1), 94–103 (2012)
Philip, J.R.: Evaporation, and moisture and heat fields in the soil. J. Meteorol. 14(4), 354–366 (1957)
Philip, J.R., Vries, D.A.D.: Moisture movement in porous materials under temperature gradients. EOS Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 38, 222–232 (1957)
Plug, W.J., Mazumder, S., Bruining, J., Siemons, N., Wolf, K,H.: Capillary pressure and wettability behavior of the coal-water–carbon dioxide system at high pressures. Paper presented at 2006 international CBM symposium, Tuscaloosa, Al; 22–26 (2006)
Schmatz, J., Urai, J.L., Berg, S., Ott, H.: Nanoscale imaging of pore-scale fluid-fluid-solid contacts in sandstone. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42(7), 2189–2195 (2015). doi:10.1002/2015GL063354
Shokri, N., Lehmann, P., Or, D.: Effects of hydrophobic layers on evaporation from porous media. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35(19), L19407, 1–4 (2008). doi:10.1029/2008GL035230
Su, S., Chen, H.W., Teakle, P., Xue, S.: Characteristics of coal mine ventilation air flows. J. Environ. Manag. 86(1), 44–62 (2008)
Swartzendruber, D.: Non-Darcy flow behavior in liquid-saturated porous media. J. Geophys. Res 67(13), 5205–5213 (1962)
Tokunaga, T.K.: DLVO-based estimates of adsorbed water film thicknesses in geologic CO\(_{2}\) reservoirs. Langmuir 28, 8001–8009 (2012)
Tokunaga, T.K.: Physicochemical controls on adsorbed water film thickness in unsaturated geological media. Water Resour. Res. 47, W08514 (2011)
Wang, J.G., Kabir, A., Liu, J.S., Chen, Z.W.: Effect of non-Darcy flow on the performance of coal seam gas wells. Int. J. Coal Geol. 93(1), 62–74 (2012)
Wang, J.G., Leung, C.F., Chow, Y.K.: Numerical solutions for flow in porous media. Int. J. Numer. Anal. Methods Geomech. 27(7), 565–583 (2003)
Wang, S., Huang, Y., Civan, F.: Experimental and theoretical investigation of the Zaoyuan field heavy oil flow through porous media. J. Petrol. Sci. Eng. 50(2), 83–101 (2006)
Warren, J.E., Root, P.J.: The behavior of naturally fractured reservoirs. Soc. Pet. Eng. 3(3), 245–255 (1963)
Wei, J.P., Wei, L., Wang, D.K.: Experimental study of moisture content influences on permeability of coal containing gas. J. China Coal Soc. 39(a), 97–103 (2014)
Wu, Y., Liu, J., Chen, Z., Elsworth, D., Pone, D.: A dual poroelastic model for CO\(_{2}\)-enhanced coalbed methane recovery. Int. J. Coal Geol. 86(2–3), 177–189 (2011)
Xu, M., Dehghanpour, H.: Advances in understanding wettability of gas shales. Energy Fuels 28, 4362–4375 (2014)
Ye, Z.H., Chen, D., Wang, J.G.: Evaluation of the non-Darcy effect in coalbed methane production. Fuel 121, 1–10 (2014)
Yokoyama, T., Nishiyama, N.: Role of water film in weathering of porous rhyolite under water unsaturated condition. Procedia Earth Planet. Sci. 7, 916–919 (2013)
Zhang, H., Liu, J., Elsworth, D.: How sorption-induced matrix deformation affects gas flow in coal seams: a new FE model. Int. J. Rock Mech. Min. Sci. 45(8), 1226–1236 (2008)
Zhu, W.C., Wei, C.H., Liu, J., Qu, H.Y., Elsworth, D.: A model of coal–gas interaction under variable temperatures. Int. J. Coal Geol. 86(2), 213–221 (2011)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the financial support from Creative Research and Development Group Program of Jiangsu Province (2014-27), Innovation Project for Graduates in Jiangsu Province (KYLX15-1409) and the Fundamental Research Funds for Central Universities (Grant Nos. 2015XKZD02, 2015XKZD03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teng, T., Wang, J.G., Gao, F. et al. Impact of Water Film Evaporation on Gas Transport Property in Fractured Wet Coal Seams. Transp Porous Med 113, 357–382 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0698-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-016-0698-7