Abstract
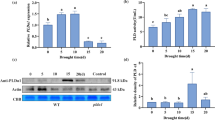
Maintaining high cytosolic K+/Na+ ratio and detoxicity of Na+ is important for plant cell metabolism and resistance to salt stress. Cation calcium exchangers, CCXs, are a novel family of genes that have recently been separated from the family of cation exchangers, CAXs, and these are likely to be correlated with Na+ transport. In this study, an Arabidopsis CCX putative gene, AtCCX1, has been cloned, and second structure model is constructed. Moreover, expression patterns in various tissues of Arabidopsis have been investigated along with heterologous expression of AtCCX1 in yeast. The gene AtCCX1 contains 1713 nucleotides, with a short N-terminal hydrophilic domain that does not support an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. Expression of AtCCX1 in Arabidopsis is higher under salt stress and drought stress when compared to wild-type, but when plants are exposed to either cold stress or abscisic acid treatment, no differences in expression levels are observed. Yeast lines expressing AtCCX1 are more tolerant to low pH medium and have displayed higher level of tolerance to sodium salt stress compared to wild-type lines. Inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy analysis has revealed that following overexpression of AtCCX1 in yeast, accumulation of Na+ is increased, while accumulation of K+ and Cu2+ is decreased. These findings support the fact that AtCCX1 is critical for Na+ tolerance and may serve as a Na+/K+ exchanger, similar to AtCCX3.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CCXs:
-
Cation calcium exchangers
- CaCA:
-
Ca2+/cation antiporter superfamily proteins
- NCX:
-
Na+/Ca2+ antiporters
- NCKX:
-
K+-dependent Na+/Ca2+ antiporters
- CAXs:
-
Cation exchangers
- YPD:
-
Yeast peptone dextrose medium
References
Amoroso S, Gobbi P, Castaldo P, Minelli A, Salucci S, Magi S, Corcione E (2007a) Mitochondrial localization of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers NCX1–3 in neurons and astrocytes of adult rat brain in situ. Pharmacol Res 56(6):556–565
Amoroso S, Minelli A, Castaldo P, Gobbi P, Salucci S, Magi S (2007b) Cellular and subcellular localization of Na+–Ca2+ exchanger protein isoforms, NCX1, NCX2, and NCX3 in cerebral cortex and hippocampus of adult rat. Cell Calcium 41(3):221–234
Amtmann A, Sanders D (1999) Mechanisms of Na+ uptake by plant cells. Adv Bot Res 29:75–112
Baek D, Jiang JF, Chung JS, Wang BS, Chen JP, Xin ZG, Shi HZ (2011) Regulated AtHKT1 gene expression by a distal enhancer element and DNA methylation in the promoter plays an important role in salt tolerance. Plant Cell Physiol 52(1):149–161
Blumwald E (2000) Sodium transport and salt tolerance in plants. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12(4):431–434
Cai XJ, Lytton J (2004) The cation/Ca2+ exchanger superfamily: phylogenetic analysis and structural implications. Mol Biol Evol 21(9):1692–1703
Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Shigaki T, Lachmansingh J, LeClere S, Lahner B, Salt DE, Hirschi KD (2005) Functional association of Arabidopsis CAX1 and CAX3 is required for normal growth and ion homeostasis. Plant Physiol 138(4):2048–2060
Darley CP, van Wuytswinkel OCM, van der Woude K, Mager WH, de Boer AH (2000) Arabidopsis thaliana and Saccharomyces cerevisiae NHX1 genes encode amiloride sensitive electroneutral Na+-/H+ exchangers. Biochem J 351:241–249
Dubcovsky J, Maria GS, Epstein E, Luo MC, Dvorak J (1996) Mapping of the K+/Na+ discrimination locus Kna1 in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 92(3–4):448–454
Eide DJ, Clark S, Nair TM, Gehl M, Gribskov M, Guerinot ML, Harper JF (2005) Characterization of the yeast ionome: a genome-wide analysis of nutrient mineral and trace element homeostasis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genome Biol 6(9):1–13
Fliegel L (2008) Molecular biology of the myocardial Na+/H+ exchanger. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44(2):228–237
Fukuda A, Nakamura A, Hara N, Toki S, Tanaka Y (2011) Molecular and functional analyses of rice NHX-type Na+/H+ antiporter genes. Planta 233(1):175–188
Gaxiola RA, Rao R, Sherman A, Grisafi P, Alper SL, Fink GR (1999) The Arabidopsis thaliana proton transporters, AtNhx1 and Avp1, can function in cation detoxification in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(4):1480–1485
Hanana M, Cagnac O, Zarrouk M, Blumwald E (2009) Biological roles of NHX vacuolar antiport: achievements and prospects of plant breeding. Botany-Botanique 87(11):1023–1035
Hauser F, Horie T (2010) A conserved primary salt tolerance mechanism mediated by HKT transporters: a mechanism for sodium exclusion and maintenance of high K+/Na+ ratio in leaves during salinity stress. Plant Cell Environ 33(4):552–565
Hirschi KD, Morris J, Tian H, Park S, Sreevidya CS, Ward JM (2008) AtCCX3 is an Arabidopsis Endomembrane H+-dependent K+ transporter. Plant Physiol 148(3):1474–1486
Ikegami K, Okamoto M, Seo M, Koshiba T (2009) Activation of abscisic acid biosynthesis in the leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana in response to water deficit. J Plant Res 122(2):235–243
Jimenez-Bremont JF, Silva-Ortega CO, Ochoa-Alfaro AE, Reyes-Aguero JA, Aguado-Santacruz GA (2008) Salt stress increases the expression of p5cs gene and induces proline accumulation in cactus pear. Plant Physiol Biochem 46(1):82–92
Kajiya H, Li JP, Okamoto F, Nakao A, Iwamoto T, Okabe K (2007) Three Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX) variants are expressed in mouse osteoclasts and mediate calcium transport during bone resorption. Endocrinology 148(5):2116–2125
Kinclova O, Flegelova H, Sychrova H (2003) Functional expression of the oryza sativa NHX1 antiporter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 20:S231–S231
Kuai BK, Wei Q, Guo YJ, Cao HM (2011) Cloning and characterization of an AtNHX2-like Na(+)/H(+) antiporter gene from Ammopiptanthus mongolicus (Leguminosae) and its ectopic expression enhanced drought and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Tiss Org 105(3):309–316
Lakshmidevi K, Subramanyam K, Sailaja KV, Subramanyam K, Rao DM (2011) Ectopic expression of an osmotin gene leads to enhanced salt tolerance in transgenic chilli pepper (Capsicum annum L.). Plant Cell Tiss Org 105(2):181–192
Laurie S, Feeney KA, Maathuis FJM, Heard PJ, Brown SJ, Leigh RA (2002) A role for HKT1 in sodium uptake by wheat roots. Plant J 32(2):139–149
Leidi EO, Barragan V, Rubio L, El-Hamdaoui A, Ruiz MT, Cubero B, Fernandez JA, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Quintero FJ, Pardo JM (2010) The AtNHX1 exchanger mediates potassium compartmentation in vacuoles of transgenic tomato. Plant J 61(3):495–506
Li TX, Zhang Y, Liu H, Wu YT, Li WB, Zhang HX (2010) Stable expression of Arabidopsis vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1, and salt tolerance in transgenic soybean for over six generations. Chin Sci Bull 55(12):1127–1134
Liu LX, Jin TC, Chang Q, Li WF, Yin DX, Li ZJ, Wang DL, Liu B (2010) Stress-inducible expression of GmDREB1 conferred salt tolerance in transgenic alfalfa. Plant Cell Tiss Org 100(2):219–227
Lu YT, Zhang XH, Rao XL, Shi HT, Li RJ (2011) Overexpression of a cytosolic glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene OsGAPC3 confers salt tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Tiss Org 107(1):1–11
Maser P, Thomine S, Schroeder JI, Ward JM, Hirschi K, Sze H, Talke IN, Amtmann A, Maathuis FJM, Sanders D, Harper JF, Tchieu J, Gribskov M, Persans MW, Salt DE, Kim SA, Guerinot ML (2001) Phylogenetic relationships within cation transporter families of Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 126(4):1646–1667
Mason MG, Jha D, Salt DE, Tester M, Hill K, Kieber JJ, Schaller GE (2010) Type-B response regulators ARR1 and ARR12 regulate expression of AtHKT1;1 and accumulation of sodium in Arabidopsis shoots. Plant J 64(5):753–763
McManus MT, Somboonwatthanaku I, Dorling S, Leung S (2010) Proline biosynthetic gene expression in tissue cultures of rice (Oryza sativa L.) in response to saline treatment. Plant Cell Tiss Org 103(3):369–376
Morris J, Tian H, Park S, Sreevidya CS, Ward JM, Hirschi KD (2008) AtCCX3 Is an Arabidopsis endomembrane H+-dependent K+ transporter. Plant Physiol 148(3):1474–1486
Munns R (2005) Genes and salt tolerance: bringing them together. New Phytol 167(3):645–663
Nakamura I, Hasthanasombut S, Supaibulwatana K, Mii M (2011) Genetic manipulation of Japonica rice using the OsBADH1 gene from Indica rice to improve salinity tolerance. Plant Cell Tiss Org 104(1):79–89
Pal A, Paul S, Kundu A (2011) Identification and validation of conserved microRNAs along with their differential expression in roots of Vigna unguiculata grown under salt stress. Plant Cell Tiss Org 105(2):233–242
Piqueras A, Hernandez JA, Olmos E, Hellin E, Sevilla F (1996) Changes in antioxidant enzymes and organic solutes associated with adaptation of citrus cells to salt stress. Plant Cell Tiss Org 45(1):53–60
Pittman JK, Hirschi KD (2001) Regulation of CAX1, an Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ antiporter. Identification of an N-terminal autoinhibitory domain. Plant Physiol 127(3):1020–1029
Pittman JK, Shigaki T, Cheng NH, Hirschi KD (2002a) Mechanism of N-terminal autoinhibition in the Arabidopsis Ca2+/H+ antiporter CAX1. J Biol Chem 277(29):26452–26459
Pittman JK, Sreevidya CS, Shigaki T, Ueoka-Nakanishi H, Hirschi KD (2002b) Distinct N-terminal regulatory domains of Ca2+/H+ antiporters. Plant Physiol 130(2):1054–1062
Pittman JK, Shigaki T, Marshall JL, Morris JL, Cheng NH, Hirschi KD (2004) Functional and regulatory analysis of the Arabidopsis thaliana CAX2 cation transporter. Plant Mol Biol 56(6):959–971
Plett D, Safwat G, Gilliham M, Moller IS, Roy S, Shirley N, Jacobs A, Johnson A, Tester M (2010) Improved salinity tolerance of rice through cell type-specific expression of AtHKT1;1. PLos One 5(9):e12571
Ren ZH, Gao JP, Li LG, Cai XL, Huang W, Chao DY, Zhu MZ, Wang ZY, Luan S, Lin HX (2005) A rice quantitative trait locus for salt tolerance encodes a sodium transporter. Nat Genet 37(10):1141–1146
Roslyakova TV, Vasekina AV, De Boer AH, Babakov AV (2009) NHX-isoforms in barley under salt stress: expression and immunolocalization. Comp Biochem Phys A 153A(2):S190–S190
Sher AA, Noble PJ, Hinch R, Gavaghan DJ, Noble D (2008) The role of the Na+/Ca2+ exchangers in Ca2+ dynamics in ventricular myocytes. Prog Biophys Mol Bio 96(1–3):377–398
Shi HZ, Lee BH, Wu SJ, Zhu JK (2003) Overexpression of a plasma membrane Na+/H+ antiporter gene improves salt tolerance in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Biotechnol 21(1):81–85
Shigaki T, Cheng NH, Pittman JK, Hirschi K (2001) Structural determinants of Ca2+ transport in the Arabidopsis H+/Ca2+ antiporter CAX1. J Biol Chem 276(46):43152–43159
Shigaki T, Pittman JK, Hirschi KD (2003) Manganese specificity determinants in the Arabidopsis metal/H+ antiporter CAX2. J Biol Chem 278(8):6610–6617
Shigaki T, Rees I, Nakhleh L, Hirschi KD (2006) Identification of three distinct phylogenetic groups of CAX cation/proton antiporters. J Mol Evol 63(6):815–825
Shigekawa M, Iwamoto T, Uehara A, Nakamura TY, Imanaga I (1999) Chimeric analysis of Na+/Ca2+ exchangers NCX1 and NCX3 reveals structural domains important for differential sensitivity to external Ni2+ or Li+. J Biol Chem 274(33):23094–23102
Shinozaki K, Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K (2000) Molecular responses to dehydration and low temperature: differences and cross-talk between two stress signaling pathways. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3(3):217–223
Sunarpi HorieT, Motoda J, Kubo M, Yang H, Yoda K, Horie R, Chan WY, Leung HY, Hattori K, Konomi M, Osumi M, Yamagami M, Schroeder JI, Uozumi N (2005) Enhanced salt tolerance mediated by AtHKT1 transporter-induced Na+ unloading from xylem vessels to xylem parenchyma cells. Plant J 44(6):928–938
Tian N, Wang J, Xu ZQ (2011) Overexpression of Na+/H+ antiporter gene AtNHX1 from Arabidopsis thaliana improves the salt tolerance of kiwifruit (Actinidia deliciosa). S Afr J Bot 77(1):160–169
Uozumi N, Kim EJ, Rubio F, Yamaguchi T, Muto S, Tsuboi A, Bakker EP, Nakamura T, Schroeder JI (2000) The Arabidopsis HKT1 gene homolog mediates inward Na+ currents in Xenopus laevis oocytes and Na+ uptake in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Physiol 122(4):1249–1259
Wang Y, Guan B, Jiang GQ, Wang YX, Wang ZC, Haxim Y, Bao QA, Hu YZ, Zhang FC (2010) Identification of differentially expressed transcripts involved in the salt-stress response of Salsola ferganica by suppression subtractive hybridization. Plant Cell Tiss Org 103(3):343–352
Wang GY, Xuan N, Jin Y, Zhang HW, Xie YH, Liu YJ (2011) A putative maize zinc-finger protein gene, ZmAN13, participates in abiotic stress response. Plant Cell Tiss Org 107(1):101–112
Wu SJ, Ding L, Zhu JK (1996) SOS1, a genetic locus essential for salt tolerance and potassium acquisition. Plant Cell 8(4):617–627
Xia GM, Zhao JS, Zhi DY, Xue ZY, Liu H (2007) Enhanced salt tolerance of transgenic progeny of tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea) expressing a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter gene from Arabidopsis. J Plant Physiol 164(10):1377–1383
Xu K, Hong P, Luo LJ, Xia T (2009) Overexpression of AtNHX1, a vacuolar Na+/H+ antiporter from Arabidopsis thalina, in Petunia hybrida enhances salt and drought tolerance. J Plant Biol 52(5):453–461
Yokoi S, Quintero FJ, Cubero B, Ruiz MT, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM, Pardo JM (2002) Differential expression and function of Arabidopsis thaliana NHX Na+/H+ antiporters in the salt stress response. Plant J 30(5):529–539
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6(2):66–71
Zhu JK (2003) Regulation of ion homeostasis under salt stress. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6(5):441–445
Zhu JK, Liu JP, Xiong LM (1998) Genetic analysis of salt tolerance in Arabidopsis: evidence for a critical role of potassium nutrition. Plant Cell 10(7):1181–1191
Acknowledgments
We thank two anonymous reviewer’s comments and two editor’s advices, especially Schuyler S. Korban’s cirtical reading and very useful revision advices. We thank Toshiro Shigaki for providing Yeast strains K667. We thank National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (Grant 30600384 and 50809068) and Young Outstanding Scholar Foundation of Northwest A&F University for providing the study funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors wish to retract this publication due to duplication of partial data from a formerly published article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Z., Wu, Y., Di, L. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: The AtCCX1 transporter mediates salinity tolerance in both Arabidopsis and yeast. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 109, 91–99 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0077-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-0077-6