Abstract
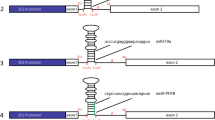
RT-PCR was used to detect gene expression in situ in single selected cells of tomato callus aggregates. The cytoplasm from one cell was removed with a micropipette viewed under a light microscope and used directly for RT-PCR, followed by nested PCR. This method to remove cytosolic contents prevented the introduction of genomic DNA into the RT-PCR, and only intron-spliced products were amplified when intron-containing genes were used as PCR targets. In addition, transcription of the intron-free gene was possibly detected by simultaneously tracing the intron-containing and intron-free genes using mixed primers for the targeted genes. The present study indicated that some stimuli-activated genes, such as CHI3 and TLC1-LTR, were constitutively transcribed in tomato callus cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Danhash N, Wagemakers CAM, van Kan JAL & de Wit PJGM (1993) Molecular characterization of four chitinase cDNAs obtained from Cladosporium fulvum-infected tomato. Plant Mol. Biol. 22: 1017–1029
Graham JS, Pearce G, Merryweather J, Titani K, Ericsson LH & Ryan CA (1985) Wound-induced proteinase inhibitors from tomato leaves. J. Biol. Chem. 260: 6561–6564
Matsuda Y, Toyoda H, Nogi Y, Tamai T & Ouchi S (1992) Foreign gene expression in barley coleoptile epidermis: an improved system for gene transfer and in situ detection of gene expression by dual microinjection. Plant Tissue Cult. Lett. 9: 154–163
Matsuda Y, Toyoda H, Kurita A & Ouchi S (1997) In situ PCR technique based on pricking microinjection for cDNA cloning in single cells of barley coleoptile and powdery mildew pathogen. Plant Cell Rep. 16: 612–618
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 15: 473–497
Murray MG & Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8: 4321–4325
Toyoda H, Matsuda Y, Utsumi R & Ouchi S (1988) Intranuclear microinjection for transformation of tomato callus cells. Plant Cell Rep. 7: 293–296
Toyoda H, Chatani K, Matsuda Y & Ouchi S (1989) Multiplication of tobacco mosaic virus in tobacco callus tissues and in vitro selection for viral disease resistance. Plant Cell Rep. 8: 433–436
Toyoda H, Yamaga T, Matsuda Y & Ouchi S (1990) Transient expression of the β-glucuronidase gene introduced into barley coleoptile cells by microinjection. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 299–302
Toyoda H, Matsuda Y, Yamaga T, Ikeda S, Morita M, Tamai T & Ouchi S (1991) Suppression of the powdery mildew pathogen by chitinase microinjected into barley coleoptile epidermal cells. Plant Cell Rep. 10: 217–230
Yañez M, Verdugo I, Rodriguez M, Prat S & Ruiz-Lara S (1998) Highly heterogeneous families of Ty1/copia retrotransposons in the Lycopersicon chilense genome. Gene 222: 223–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wada, M., Matsuda, Y., Fujita, K. et al. RT-PCR amplification of mRNAs in nuclei or cytosol of single cells of tomato. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture 79, 109–114 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-4289-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-004-4289-x