Abstract
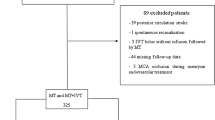
Recent clinical trials demonstrated that mechanical thrombectomy (MT) using second-generation endovascular devices has beneficial effects in acute ischemic stroke (AIS) due to large vessel occlusion (LVO). However, it remains controversial if intravenous thrombolysis (IVT) prior to MT is superior compared to direct mechanical thrombectomy (DMT). The aims of this study were to compare short and long-term outcomes between IVT + MT and DMT patients. We prospectively recruited AIS patients with LVO in the anterior or posterior circulation eligible for MT with and without prior IVT. Modified Rankin Scale (mRS) and mortality were assessed at baseline, at discharge, 90-days and 1-year after stroke. Favorable outcome was defined as a mRS score ≤2. Of the 66 patients included, 33 (50%) were in IVT + MT group and 33 (50%) were in DMT group. Except for a higher prevalence of patients using anticoagulants at admission in DMT group, baseline characteristics did not differ in the two groups. Procedural characteristics were similar in IVT + MT and DMT group. Rate of favorable outcome was significantly higher in IVT + MT patients than DMT ones both 90-days (51.5 vs. 18.2%; p = 0.004) and 1-year (51.5 vs. 15.2%; p = 0.002) after stroke. DMT patients were six times more likely to die during the 1-year follow-up compared to IVT + MT patients. This study suggests that bridging therapy may improve short and long-term outcomes in patients eligible for endovascular treatment. Further studies with larger patient numbers and randomized design are needed to confirm our findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wardlaw JM, Murray V, Berge E, Del Zoppo GJ (2014) Thrombolysis for acute ischaemic stroke. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 7:CDOOO213. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD000213
Bhatia R, Hill MD, Shobha N, Menon B, Bal S, Kochar P et al (2010) Low rates of acute recanalization with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in ischemic stroke: real-world experience and a call for action. Stroke 41:2254–2258. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.592535
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, EXTEND-IA Investigators et al. (2015) Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372:1009–1018. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1414792
Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, MR CLEAN Investigators et al (2015) A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:11–20. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1411587
Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, ESCAPE Trial Investigators et al. (2015) Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:1019–1030. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1414905
Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, SWIFT PRIME Investigators et al (2015) Stent-retriever thrombectomy after intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA alone in stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2285–2295. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415061
Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, REVASCAT Trial Investigators et al (2015) Thrombectomy within 8 h after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 372:2296–2306. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1503780
Guedin P, Larcher A, Decroix JP, Labreuche J, Dreyfus JF, Evrard S et al (2015) Prior IV thrombolysis facilitates mechanical thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24:952–957. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.12.015
Behme D, Kabbasch C, Kowoll A, Dorn F, Liebig T, Weber W, Mpotsaris A (2016) Intravenous thrombolysis facilitates successful recanalization with stent-retriever mechanicalthrombectomy in middle cerebral artery occlusions. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:954–959. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2016.01.007
Kablau M, Alonso A, Hennerici MG, Fatar M (2013) Treatment with tPA predicts better outcome even if MCA occlusion persists. Int J Stroke 8:496–502. doi:10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00750.x
Desilles JP, Loyau S, Syvannarath V, Gonzalez-Valcarcel J, Cantier M, Louedec L et al (2015) Alteplase reduces downstream microvascular thrombosis and improves the benefit of large artery recanalization in stroke. Stroke 46:3241–3248. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.010721
Cheng B, Golsari A, Fiehler J, Rosenkranz M, Gerloff C, Thomalla G (2011) Dynamics of regional distribution of ischemic lesions in middle cerebral artery trunk occlusion relates to collateral circulation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:36–40. doi:10.1038/jcbfm.2010.185
Kass-Hout T, Kass-Hout O, Mokin M, Thesier DM, Yashar P, Orion D et al (2014) Is bridging with intravenous thrombolysis of any benefit in endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke? World Neurosurg 82:e453–458. doi:10.1016/j.wneu.2013.01.097
Leker RR, Pikis S, Gomori JM, Cohen JE (2015) Is bridging necessary? A pilot study of bridging versus primary stentriever-based endovascular reperfusion in large anterior circulation strokes. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24:1163–1167. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.01.008
Broeg-Morvay A, Mordasini P, Bernasconi C, Bühlmann M, Pult F, Arnold M et al (2016) Direct mechanical intervention versus combined intravenous and mechanical intervention in large artery anterior circulation stroke: a matched-pairs analysis. Stroke 47:1037–1044. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.011134
Rebello LC, Haussen DC, Grossberg JA, Belagaje S, Lima A, Anderson A et al (2016) Early endovascular treatment in intravenous tissue plasminogen activator-ineligible patients. Stroke 47:1131–1134. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.115.012586
Abilleira S, Ribera A, Cardona P, Rubiera M, López-Cancio E, Amaro S, Catalan Stroke Code and Reperfusion Consortium et al (2017) Outcomes after direct thrombectomy or combined intravenous and endovascular treatment are not different. Stroke 48:375–378. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015857
Rai AT, Boo S, Buseman C, Adcock AK, Tarabishy AR, Miller MM, Roberts TD et al (2017) Intravenous thrombolysis before endovascular therapy for large vessel strokes can lead to significantly higher hospital costs without improving outcomes. Neurointerv Surg. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2016-012830
Coutinho JM, Liebeskind DS, Slater LA, Nogueira RG, Clark W, Dávalos A et al (2017) Combined intravenous thrombolysis and thrombectomy vs thrombectomy alone for acute ischemicstroke: a pooled analysis of the SWIFT and STAR studies. JAMA Neurol 74:268–274. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2016.5374
Sallustio F, Koch G, Di Legge S, Rossi C, Rizzato B, Napolitano S et al (2013) Intra-arterial thrombectomy versus standard intravenous thrombolysis in patients with anterior circulation stroke caused by intracranial arterial occlusions: a single-center experience. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 22:e323–e331. doi:10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2013.01.001
Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill MD, Sevick RJ, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME et al (2001) Use of the alberta stroke program early CT score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1534–1542
Steiner T, Al-Shahi Salman R, Ntaios G (2014) The European Stroke Organization (ESO) guidelines. Int J Stroke 9:838–839. doi:10.1111/ijs.12369
Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease, Council on Clinical Cardiology et al (2013) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 44:870–947. doi:10.1161/STR.0b013e318284056a
Turk AS, Spiotta A, Frei D, Mocco J, Baxter B, Fiorella D et al (2014) Initial clinical experience with the ADAPT technique: a direct aspiration first pass technique for stroke thrombectomy. J Neurointerv Surg 6:231–237. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2013-010713
Vargas J, Spiotta A, Fargen K, Turner R, Chaudry I, Turk A (2017) Long term experience using the ADAPT technique for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke. J Neurointerv Surg 9:437–441. doi:10.1136/neurintsurg-2015-012211
Chartrain AG, Awad AJ, Mascitelli JR, Shoirah H, Oxley TJ, Feng R et al (2017) Novel and emerging technologies for endovascular thrombectomy. Neurosurg Focus 42:E12. doi:10.3171/2017.1.FOCUS16518
Adams HP Jr, Bendixen BH, Kappelle LJ, Biller J, Love BB, Gordon DL, Marsh EE 3rd (1993) Classification of subtype of acute ischemic stroke. Definitions for use in a multicenter clinical trial. TOAST. Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment. Stroke 24:35–41
Higashida RT, Furlan AJ, Roberts H, Tomsick T, Connors B, Barr J, Technology Assessment Committee of the American Society of Interventional and Therapeutic Neuroradiology, Technology Assessment Committee of the Society of Interventional Radiology et al (2003) Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:e109–137
Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Lesaffre E, von Kummer R et al (1995) Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA 274:1017–1025
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, Brozman M, Dávalos A, Guidetti D, ECASS Investigators et al (2008) Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4.5 h after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med 359:1317–1329. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa0804656
Park HK, Chung JW, Hong JH, Jang MU, Noh HD, Park JM et al (2017) Preceding intravenous thrombolysis in patients receiving endovascular therapy. Cerebrovasc Dis 44:51–58. doi:10.1159/000471492
Maier IL, Behme D, Schnieder M, Tsogkas I, Schregel K, Kleinknecht A et al (2017) Bridging-therapy with intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator improves functional outcome in patients with endovascular treatment in acute stroke. J Neurol Sci 372:300–304. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2016.12.001
Pfefferkorn T, Holtmannspötter M, Patzig M, Brückmann H, Ottomeyer C, Opherk C, Dichgans M, Fesl G (2012) Preceding intravenous thrombolysis facilitates endovascular mechanical recanalization in large intracranial artery occlusion. Int J Stroke 7:14–18. doi:10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00639.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Merlino, G., Sponza, M., Petralia, B. et al. Short and long-term outcomes after combined intravenous thrombolysis and mechanical thrombectomy versus direct mechanical thrombectomy: a prospective single-center study. J Thromb Thrombolysis 44, 203–209 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1527-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-017-1527-8