Abstract
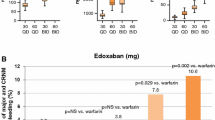
Edoxaban, an oral direct inhibitor of factor Xa, was recently approved in the United States and Japan for prevention of stroke and systemic embolism in patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation and for treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE). It is also licensed in Japan for prevention of VTE after major orthopedic surgery. Although routine laboratory monitoring of edoxaban is not required, laboratory measurement may be desirable in special circumstances. Our objective was to provide a systematic review of current evidence on laboratory measurement of the anticoagulant activity of edoxaban. PubMed and the Cochrane Library were searched for studies that reported a relationship between coagulation tests and plasma edoxaban levels. Study quality was assessed using Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 (QUADAS-2). We identified 9 eligible studies. Anti-Xa activity is linear across a broad range of drug levels (R 2 > 0.95) and may be used for edoxaban quantification. The assay shows greater variability at above on-therapy drug concentrations. The PT is less sensitive to edoxaban. A normal prothrombin time may not exclude clinically relevant on-therapy drug levels. The activated partial thromboplastin time has insufficient sensitivity to edoxaban for measurement of its anticoagulant activity. Edoxaban exhibits variable effects on coagulation assays. Understanding these effects facilitates interpretation of test results in edoxaban-treated patients. More data on the relationship between drug levels, coagulation test results, and clinical outcomes in patients are needed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giugliano RP, Ruff CT, Braunwald E, Murphy SA, Wiviott SD, Halperin JL, Waldo AL, Ezekowitz MD, Weitz JI, Spinar J, Ruzyllo W, Ruda M, Koretsune Y, Betcher J, Shi M, Grip LT, Patel SP, Patel I, Hanyok JJ, Mercuri M, Antman EM, ENGAGE AF-TIMI 48 Investigators (2013) Edoxaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med 369:2093–2104
Investigators Hokusai-VTE, Büller HR, Décousos H, Grosso MA, Mercuri M, Middledorp S, Prins MH, Raskob GE, Schellong SM, Schwocho L, Segers A, Shi M, Verhamme P, Wells P (2013) Edoxaban versus warfarin for the treatment of symptomatic venous thromboembolism. N Engl J Med 369:1406–1415
Matsushima N, Lee F, Sato T, Weiss D, Mendell J (2013) Bioavailability and safety of the factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban and the effects of quinidine in healthy subjects. Clinical Pharm in Drug Dev 2:358–366
Ogata K, Mendell-Harary J, Tachibana M, Masumoto H, Oguma T, Kojima M, Kunitada S (2010) Clinical safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the novel factor Xa inhibitor edoxaban in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 50:743–753
Weitz JI, Connolly SJ, Patel I, Salazar D, Rohatagi S, Mendell J, Kastrissios H, Jin J, Kunitada S (2010) Randomised, parallel-group, multicentre, multinational phase 2 study comparing edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, with warfarin for stroke prevention in patients with atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost 104:633–641
Chung N, Jeon HK, Lien LM, Lai WT, Tse HF, Chung WS, Lee TH, Chen SA (2010) Safety of edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, in Asian patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation. Thromb Haemost 105:535–544
Cuker A, Siegal DM, Crowther MA, Garcia DA (2014) Laboratory measurement of the anticoagulant activity of the non-vitamin K oral anticoagulants. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:1128–1139
Whiting PF, Rutjes AW, Westwood ME, Mallett S, Deeks JJ, Reitsma JB, Leeflang MM, Sterne JA, Bossuyt PM, QUADAS-2 Group (2011) QUADAS-2: a revised tool for the quality assessment of diagnostic accuracy studies. Ann Intern Med 155:529–536
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, PRISMA Group (2009) Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann Intern Med 151:264–269
Zafar MU, Vorchheimer DA, Gaztanaga J, Velez M, Yadegar D, Moreno PR, Kunitada S, Pagan J, Fuster V, Badimon JJ (2007) Antithrombotic effects of factor Xa inhibition with DU-176b: phase-I study of an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor using an ex vivo flow chamber. Thromb Haemost 98:883–888
Furugohri T, Isobe K, Honda Y, Kamisato-Matsumoto C, Sugiyama N, Nagahara T, Morishima Y, Shibano T (2008) DU-176b, a potent and orally active factor Xa inhibitor: in vitro and in vivo pharmacological profiles. J Thromb Haemost 6:1542–1549
Mendell J, Tachibana M, Shi M, Kunitada S (2011) Effects of food on the pharmacokinetics of edoxaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor, in healthy volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol 51:687–694
Wolzt M, Samama MM, Kapiotis S, Ogata K, Mendell J, Kunitada S (2011) Effect of edoxaban on markers of coagulation in venous and she blood compared with fondaparinux. Thromb Haemost 105:1080–1090
Fukada T, Honda Y, Kamisato C, Morishima Y, Shibano T (2012) Reversal of anticoagulant effects of edoxaban, an oral, direct factor Xa inhibitor, with haemostatic agents. Thromb Haemost 107:253–259
Samama MM, Mendell J, Guinet C, Le Flem L, Kunitada S (2012) In vitro study of the anticoagulant effects of edoxaban and its effect on thrombin generation in comparison to fondaparinux. Thromb Res 129:e77–e82
Mendell J, Noveck RJ, Shi M (2013) A randomized trial of the safety, pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of edoxaban, an oral factor Xa inhibitor, following a switch from warfarin. Br J Clin Pharmacol 75:966–978
Noguchi K, Morishima Y, Takahashi S, Ishihara H, Shibano T, Murata M (2015) Impact of nonsynonymous mutations of factor X on the functions of factor X and anticoagulant activity of edoxaban. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 26:117–122
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by HL112903 (National Heart Lung and Blood Institute, Bethesda, MD) to AC.
Conflict of interest
AC has provided consulting services for Bracco and Genzyme, has participated in an advisory board for CSL Behring, and has received research support from Stago and T2 Biosystems. HH has no conflicts to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cuker, A., Husseinzadeh, H. Laboratory measurement of the anticoagulant activity of edoxaban: a systematic review. J Thromb Thrombolysis 39, 288–294 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-015-1185-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-015-1185-7