Abstract
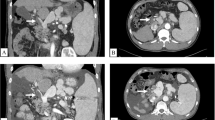
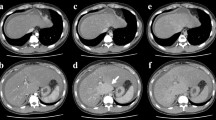
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is a rare complication of heparin treatment resulting in a severe acquired thrombophilic condition with an associated mortality of about 10 %. We report the first case of successful urgent liver transplantation (LT) in a patient with end-stage liver disease due to a Budd–Chiari syndrome, portal vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism due to acquired thrombophilia associated to polycythemia vera carrying JAK2V617F gene mutation and HIT in the acute phase. Lepirudin was used to provide anticoagulation in the LT perioperative period that was performed without haemorrhagic and thrombotic complications despite the donor received heparin during liver explantation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Stefano V, Martinelli I (2010) Splanchnic vein thrombosis: clinical presentation, risk factors and treatment. Intern Emerg Med 5:487–494
Tefferi A (2012) Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2012 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 87:285–293
Dentali F, Squizzato A, Brivio L et al (2009) JAK2V617F mutation for the early diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasms in patients with venous thromboembolism: a meta-analysis. Blood 113:5617–5623
Linkins LA, Dans AL, Moores LK et al (2012) Treatment and prevention of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis, 9th ed: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. Chest 141:495–530
Warkentin TE, How I (2011) Diagnose and manage HIT. Hematology 1:144–149
Fretschner R, Dietrich K, Unertl K et al (2005) Management of liver transplantation in a patient with a history of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Transpl Int 18:664–667
Bachmann R, Nadalin S, Li J, Lange J et al (2011) Donor heparinization is not a contraindication to liver transplantation even in recipients with acute heparin-induced thrombocytopenia type II: a case report and review of the literature. Transpl Int 24:89–92
Aloia TA, Goss JA (2009) A report of outcomes after orthotopic liver transplant with allografts from heparin antibody-positive donors. Exp Clin Transplant 7:13–17
Disclosures
All the Authors disclose any financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence (bias) the contents of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Biagioni, E., Pedrazzi, P., Marietta, M. et al. Successful liver transplantation in a patient with splanchnic vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism due to polycythemia vera with Jak2v617f mutation and heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. J Thromb Thrombolysis 36, 352–354 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0832-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0832-5