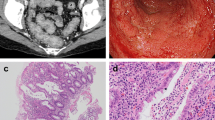
Abstract
Systemic chemotherapy can be complicated by colonic toxicity, which usually determines the onset of pseudomembranous colitis and, rarely, of ischemic colitis in patients with cancer. This report describes the case of a 45-year-old man with advanced gastric cancer who developed severe ischemic colitis after chemotherapy with cisplatin and capecitabine. The patient developed symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity with abdominal pain and bloody diarrhea. He had a normal white blood cell count throughout his illness; the assay of stool specimens for Clostridium difficile toxins and the stool cultures were both negative. An endoscopy showed a mild, transient ischemic colitis. Although cisplatin is related to severe colonic cytotoxicity, it has not been previously reported that capecitabine induces arterial thrombosis and necrosis of the gastrointestinal mucosa and inhibits angiogenesis. Pseudomembranous colitis is the most frequent complication in patients with cancer who undergo capecitabine-based chemotherapy and develop gastrointestinal toxicity. Once Clostridium difficile infection has been excluded, a diagnosis of ischemic colitis should be considered, especially in patients with cancer who have normal white blood cell counts.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dosik GM, Luna M, Valdivieso M et al (1979) Necrotizing colitis in patients with cancer. Am J Med 67:646–656
Cappell MS, Simon T (1993) Colonic toxicity of administered medications and chemicals. Am J Gastroenterol 88:1684–1699
Mitchell EP, Schein PS (1982) Gastrointestinal toxicity of chemotherapeutic agents. Semin Oncol 9:52–64
Anand A, Glatt AE (1993) Clostridium difficile infection associated with antineoplastic chemotherapy: a review. Clin Infect Dis 17:109–113
Trevisani F, Simoncini M, Alampi G et al (1997) Colitis associated to chemotherapy with 5-fluorouracil. Hepatogastroenterology 44:710–712
Emoto M, Kawarabayashi T, Hachisuga MD et al (1996) Clostridium difficile colitis associated with cisplatin-based chemotherapy in ovarian cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol 61:369–372
Heit JA, Silverstein MD, Mohr DN et al (2000) Risk factors for deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism: a population-based case-control study. Arch Intern Med 160:809–815
Haddad TC, Greeno EW (2006) Chemotherapy-induced thrombosis. Thromb Res 118:555–568
Levine MN, Gent M, Hirsh J et al (1988) The thrombogenic effect of anticancer drug therapy in women with stage II breast cancer. N Engl J Med 318:404–407
Rella C, Coviello M, Giotta F et al (1996) A prothrombotic state in breast cancer patients treated with adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 40:151–159
von Tempelhoff GF, Dietrich M, Hommel G et al (1996) Blood coagulation during adjuvant epirubicin/cyclophosphamide chemotherapy in patients with primary operable breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 14:2560–2568
Doll DC, Ringenberg QS, Yarbro JW (1986) Vascular toxicity associated with antineoplastic agents. J Clin Oncol 4:1405–1417
Lee AY, Levine MN (1999) The thrombophilic state induced by therapeutic agents in the cancer patient. Semin Thromb Hemost 25:137–145
Díaz-Rubio E, Tabernero J, Gómez-España A et al (2007) Phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with continuous-infusion fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: final report of the Spanish Cooperative Group for the Treatment of Digestive Tumors Trial. J Clin Oncol 25:4224–4230
Cassidy J, Clarke S, Díaz-Rubio E et al (2008) Randomized phase III study of capecitabine plus oxaliplatin compared with fluorouracil/folinic acid plus oxaliplatin as first-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:2006–2012
Starling N, Raos S, Cunningham D et al (2009) Thromboembolism in patients with advanced cancer treated with anthracyline, platinum, and fluoropyrimidine combination chemotherapy: a report from the UK National Cancer Research Institute Upper Gastrointestinal Clinical Studies Group. J Clin Oncol 27:3786–3793
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cetin, B., Buyukberber, S., Sentürk, S. et al. Ischemic colitis after capecitabine plus cisplatin treatment in advanced gastric cancer. J Thromb Thrombolysis 31, 503–506 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-010-0525-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-010-0525-x