Abstract
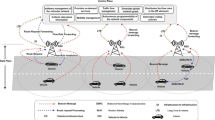
Currently, various efforts are being performed on specifying distributed mobility management (DMM) for IPv6 mobile networks. DMM is expected to eliminate the limitations of the current IPv6 mobility protocols and to cope with the rapid increase in mobile data traffic. In current DMM approaches, the mobility anchoring is distributed at the access router level and the mobile node changes dynamically the mobility anchor for new sessions. Although such approaches avoid any network bottleneck and allow optimal routing in most cases, they lack reachability support since the mobile node has no permanent IPv6 address. In this paper, we consider one of the DMM approaches, dynamic mobility anchoring, and study the usage of session initiation protocol (SIP) for providing reachability support. After defining different SIP-based location update modes, we carry out a comparative cost analysis considering new performance metrics related to the processing loads at each network entity. We consider the location update loads on the location server as well as the context, signaling, and tunneling loads on a mobility anchor. We investigate the different modes in several scenarios, allowing the mobile network operator to adopt the preferred mode depending on their architecture.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
GSM Association (GSMA). (2013). The Mobile Economy 2013.
Ericsson. (2013). Ericsson Mobility Report.
Cisco. (2013). Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2012–2017.
IETF RFC 3775. (2011). Mobility support in IPv6, Jun. 2004. Updated by: IETF RFC 6275.
IETF RFC 5213. (2008). Proxy Mobile IPv6
IETF, DMM Charter, Available online: http://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/dmm/charter/
Chan, Chan, Yokota, H., Xie, J., Seite, P., & Liu, D. (2011). Distributed and dynamic mobility management in mobile internet: Current approaches and issues. Journal of Communications, 6(1), 4–15.
IETF, DMM Documents, Available online: http://datatracker.ietf.org/wg/dmm/
Lee, J. H., et al. (2010). Cost analysis of IP mobility management protocols for consumer mobile devices. IEEE Transactions on Consumer Electronics, 56(2), 1010–1017.
Pack, S., et al. (2007). Adaptive Route Optimization in Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 Networks. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 6(8), 903–914.
Skorepa, M., & Klugl, R. (2013). Enhanced analytical method for IP mobility handover schemes cost evaluation. Telecommunication Systems, 52(3), 1573–1582.
Ali-Ahmad, H., Lagrange, X., Ouzzif, M., & Bertin, P. (2013). Comparative cost analysis on global mobility management schemes in IPv6 mobile networks. In VTC. IEEE.
Lee, J. H., Han, Y. H., Gundavelli, S., & Chung, T. M. (2009). A comparative performance analysis on Hierarchical Mobile IPv6 and Proxy Mobile IPv6. Telecommunication Systems, 41(4), 279–292.
Wang, Q., & Abu-Rgheff, M. A. (2006). Signalling analysis of cost-efficient mobility support by integrating Mobile IP and SIP in all IP wireless networks. International Journal of Communication Systems, 19(2), 225–247.
Makaya, C., & Pierre, S. (2008). An analytical framework for performance evaluation of IPv6-based mobility management protocols. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 7(3), 972–983.
Munir, K., Lagrange, X., Bertin, P., Ouzzif, M., & Guillouard, K. (2015). Performance analysis of mobility management architectures in cellular networks. Telecommunication Systems, 59(2), 211–227.
Lee, J. H., Bonnin, J. M., You, I., & Chung, T. M. (2013). Comparative handover performance analysis of IPv6 mobility management protocols. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 60(3), 1077–1088.
Lee, K. H., Lee, H. W., Ryu, W., & Han, Y. H. (2013). A scalable network-based mobility management framework in heterogeneous IP-based networks. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 1989–2002.
Giust, F., Bernardos, C. J., & de la Oliva, A. (2014). Analytic evaluation and experimental validation of a network-based IPv6 distributed mobility management solution. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 13(11), 2484–2497.
Condeix, T., & Sargento, S. (2014). Studying the integration of distributed and dynamic schemes in the mobility management. Computer Networks, 60, 46–59.
Ali-Ahmad, H., Ouzzif, M., Bertin, P., & Lagrange, X. (2014). Performance analysis on network-based distributed mobility management. Wireless Personal Communications (WPC), 74(4), 1245–1263.
Bertin, P., Bonjour, S., & Bonnin, J.M. (2009). An evaluation of dynamic mobility anchoring. In VTC. IEEE.
Louin, P., & Bertin, P. (2011). Network and host based distributed mobility. In WPMC IEEE:.
Ali-Ahmad, H., Ouzzif, M., Bertin, P., & Lagrange, X. (2013). Distributed mobility management: approaches and analysis. In Proceedings of the IEEE ICC—telecommunication standards.
Gohar, M., & Koh, S. J. (2012). Network-based distributed mobility control in localized mobile LISP networks. IEEE Communications Letters, 16(1), 104–107.
Hossain, M. S., & Atiquzzaman, M. (2013). Cost analysis of mobility protocols. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 2271–2285.
IETF RFC 3261. (2002). SIP: Session initiation protocol.
Bertin, P., Bonjour, S., & Bonnin, J. M. (2008). A distributed dynamic mobility management scheme designed for flat IP architectures. In NTMS. IEEE.
Bertin, P., Bonjour, S., & Bonnin, J.M. (2009). Distributed or centralized mobility? In GLOBECOM. IEEE.
Seite, P., & Bertin, P. (2014). Distributed mobility anchoring, draft-seite-dmm-dma-07, IETF.
Sadhukhan, P., Das, P. K., & Saha, S. (2013). Hybrid mobility management schemes integrating mobile IP and SIP for seamless invocation of services in All-IP network. Telecommunication Systems, 52(4), 2027–2046.
Cisco. (2010). Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update, 2009–2014.
Schulzrinne, H., & Wedlund, E. (2000). Application-layer mobility using SIP. ACM Mobile Computing and Communications Review, 4(3), 47–57.
RFC 7333. (2014). Requirements for distributed mobility management.
Akyildiz, I. F., & Wang, W. (2002). A dynamic location management scheme for next-generation multitier PCS systems. IEEE Transactions Wireless Communications, 1(1), 178–189.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ali-Ahmad, H., Munir, K., Bertin, P. et al. Processing loads analysis of distributed mobility management and SIP-based reachability. Telecommun Syst 63, 681–696 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0148-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11235-016-0148-4