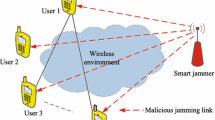
Abstract
In this paper, we study the anti-jamming power control problem of secondary users (SUs) in a large-scale cooperative cognitive radio network attacked by a smart jammer with the capability to sense the ongoing transmission power. The interactions between cooperative SUs and a jammer are investigated with game theory. We derive the Stackelberg equilibrium of the anti-jamming power control game consisting of a source node, a relay node and a jammer and compare it with the Nash equilibrium of the game. Power control strategies with reinforcement learning methods such as Q-learning and WoLF-PHC are proposed for SUs without knowing network parameters (i.e., the channel gains and transmission costs of others and so on) to achieve the optimal powers against jamming in this cooperative anti-jamming game. Simulation results indicate that the proposed power control strategies can efficiently improve the anti-jamming performance of SUs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiao L, Dai H, Ning P (2012) Jamming-resistant collaborative broadcast using uncoordinated frequency hopping. IEEE Trans Inf Forensics Secur 7(1):297–309
Yang D, Xue G, Zhang J, Richa A, Fang X (2013) Coping with a smart jammer in wireless networks: a stackelberg game approach. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 12(8):4038–4047
Chen C, Song M, Xin C, Backens J (2013) A game-theoretical anti-jamming scheme for cognitive radio networks. IEEE Netw 27(3):22–27
Zhu Q, Li H, Han Z, Basar T (2010) A stochastic game model for jamming in multi-channel cognitive radio systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications (ICC), pp 1–6
El-Bardan R, Brahma S, Varshney P (2014) Power control with jammer location uncertainty: a game theoretic perspective. In: Proceedings of the annual conference on information sciences and systems (CISS), pp 1–6
Wang B, Wu Y, Liu K, Clancy T (2011) An anti-jamming stochastic game for cognitive radio networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 29(4):877–889
Bkassiny M, Li Y, Jayaweera S (2013) A survey on machine-learning techniques in cognitive radios. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 15(3):1136–1159
Amuru S, Buehrer RM (2014) Optimal jamming using delayed learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE military communications conference (MILCOM), pp 1528–1533
Bhunia S, Sengupta S, Vazquez-Abad F (2014) Cr-honeynet: a learning and decoy based sustenance mechanism against jamming attack in CRN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE military communications conference (MILCOM), pp 1173–1180
Li Y, Xiao L, Liu J, Tang Y (2014) Power control stackelberg game in cooperative anti-jamming communications. In: Proceedings of the international conference on game theory for networks, pp 93–98
Watkins C, Dayan P (1992) Q-learning. Mach Learn 8(3–4):279–292
Bowling M, Veloso M (2002) Multiagent learning using a variable learning rate. Artif Intell 136(2):215–250
Altman E, Avrachenkov K, Garnaev A (2007) A jamming game in wireless networks with transmission cost. Netw Control Optim Lect Notes Comput Sci 4465:1–12
DeBruhl B, Kroer C, Datta A, Sandholm T, Tague P (2014) Power napping with loud neighbors: optimal energy-constrained jamming and anti-jamming. In: Proceedings of the ACM conference on security and privacy in wireless and mobile networks, pp 117–128
Seredynski M, Bouvry P (2013) Analysing the development of cooperation in manets using evolutionary game theory. J Supercomput 63(3):854–870
Khan S (2011) Mosaic-net: a game theoretical method for selection and allocation of replicas in ad hoc networks. J Supercomput 55(3):321–366
Wu Y, Wang B, Liu K, Clancy T (2012) Anti-jamming games in multi-channel cognitive radio networks. IEEE J Sel Areas Commun 30(1):4–15
Gwon Y, Dastangoo S, Fossa C, Kung H (2013) Competing mobile network game: embracing antijamming and jamming strategies with reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE conference on communications and network security, pp 28–36
Lo B, Akyildiz I (2012) Multiagent jamming-resilient control channel game for cognitive radio ad hoc networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on communications, pp 1821–1826
Dastangoo S, Fossa C, Gwon Y (2014) Competing cognitive tactical networks. Linc Lab J 20(2):16–35
Conley W, Miller A (2013) Cognitive jamming game for dynamically countering ad hoc cognitive radio networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE military communications conference (MILCOM), pp 1176–1182
Busoniu L, Babuska R, Schutter B (2008) A comprehensive survey of multiagent reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C: Appl Rev 38(2):156–172
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by NSFC (No. 61271242, 61301097, 61440002) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2013121023).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, L., Li, Y., Liu, J. et al. Power control with reinforcement learning in cooperative cognitive radio networks against jamming. J Supercomput 71, 3237–3257 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1420-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-015-1420-1