Abstract
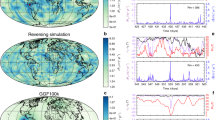
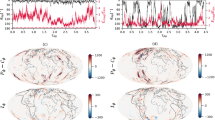
Recent advances in the study of geomagnetic field reversals are reviewed. These include studies of the transitional field during the last geomagnetic reversal and the last geomagnetic excursion based on paleomagnetic observations, and analysis of reversals in self-consistent 3D numerical dynamo simulations. Field models inferred from observations estimate reversal duration in the range of 1–10 kyr (depending on site location). The transitional fields during both the Matuyama/Brunhes reversal and the Laschamp excursion are characterized by low-latitude reversed flux formation and subsequent poleward migration. During both events the dipole as well as the non-dipole field energies decrease. However, while the non-dipole energy dominates the dipole energy for a period of 2 kyr in the reversal, the non-dipole energy merely exceeds the dipole energy for a very brief period during the excursion. Numerical dynamo simulations show that stronger convection, slower rotation, and lower electrical conductivity provide more favorable conditions for reversals. A non-dimensional number that depends on the typical length scale of the flow and represents the relative importance of inertial effects, termed the local Rossby number, seems to determine whether a dynamo will reverse or not. Stable polarity periods in numerical dynamos may last about 1 Myr, whereas reversals may last about 10 kyr. Numerical dynamo reversals often involve prolonged dipole collapse followed by shorter directional instability of the dipole axis, with advective processes governing the field variation. Magnetic upwellings from the equatorial inner-core boundary that produce reversed flux patches at low-latitudes of the core-mantle boundary could be significant in triggering reversals. Inferences from the observational and modeling sides are compared. We summarize with an outlook on some open questions and future prospects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Alldredge, Harmonics required in main field and secular variation models. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 36, 63–72 (1984)
H. Amit, P. Olson, Geomagnetic dipole tilt changes induced by core flow. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 166, 226–238 (2008)
H. Amit, P. Olson, A dynamo cascade interpretation of the geomagnetic dipole decrease. Geophys. J. Int. 181, 1411–1427 (2010)
H. Amit, J. Aubert, G. Hulot, P. Olson, A simple model for mantle-driven flow at the top of Earth’s core. Earth Planets Space 60, 845–854 (2008)
J. Aubert, H. Amit, G. Hulot, Detecting thermal boundary control in surface flows from numerical dynamos. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 160, 143–156 (2007)
J. Aubert, H. Amit, G. Hulot, P. Olson, Thermo-chemical wind flows couple Earth’s inner core growth to mantle heterogeneity. Nature 454, 758–761 (2008a)
J. Aubert, J. Aurnou, J. Wicht, The magnetic structure of convection-driven numerical dynamos. Geophys. J. Int. 172, 945–956 (2008b)
J. Aubert, S. Labrosse, C. Poitou, Modelling the paleo-evolution of the geodynamo. Geophys. J. Int. 179, 1414–1428 (2009)
J. Aurnou, S. Andreadis, L. Zhu, P. Olson, Experiments on convection in Earth’s core tangent cylinder. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 212, 119–134 (2003)
S. Baumgartner, J. Beer, J. Masarik, G. Wagner, L. Meynadier, H.A. Synal, Geomagnetic modulation of the 36cl flux in the grip ice core, greenland. Science 279(5355), 1330–1332 (1998)
M. Berhanu, R. Monchaux, S. Fauve, N. Mordant, F. Petrelis, A. Chiffaudel, F. Daviaud, B. Dubrulle, L. Marie, F. Ravelet, M. Bourgoin, P. Odier, J.-F. Pinton, R. Volk, Magnetic fld reversals in an experimental turbulent dynamo. Europhys. Lett. 77 (2007). doi:10.1209/0295–5075/77/59001
C.L. Blanchet, N. Thouveny, T. de Garidel-Thoron, Evidence for multiple paleomagnetic intensity lows between 30 and 50 ka bp from a western equatorial pacific sedimentary sequence. Quat. Sci. Rev. 25, 1039–1052 (2006)
U. Bleil, T.V. Dobeneck, Geomagnetic events and relative paleointensity records; clues to high-resolution paleomagnetic chronostratigraphies of late quaternary marine sediments?, in Use of Proxies in Paleoceanography; Examples from the South Atlantic, ed. by G. Fischer, G. Wefer (Springer, Berlin, 1999), pp. 635–654
J. Bloxham, The expulsion of magnetic flux from the Earth’s core. Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 87, 669–678 (1986)
J. Bloxham, D. Gubbins, Geomagnetic field analysis—iv. Testing the frozen-flux hypothesis. Geophys. J. R. Astr. Soc. 84, 139–152 (1986)
J. Bloxham, A. Jackson, Fluid flow near the surface of the Earth’s outer core. Rev. Geophys. 29, 97–120 (1991)
N. Bonhommet, J. Babkine, Sur la presence daimentations inversees dans la chaine des puys. C. R. Acad. Sci. Ser. B 264, 92 (1967)
M.B. Brown, R. Holme, A. Bargery, Exploring the influence of the non-dipole field on magnetic records for field reversals and excursions. Geophys. J. Int. 168, 541–550 (2007)
B. Brunhes, Recherches sur le direction d’aimantation des roches volcaniques. J. Phys. 5, 705–724 (1906)
F. Busse, R. Simitev, Toroidal flux oscillation as possible cause of geomagnetic excursions and reversals. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 168, 237–243 (2008)
S.C. Cande, D.V. Kent, Revised calibration of the geomagnetic polarity timescale forthe late cretaceous and cenozoic. J. Geophys. Res. 100, 6093–6095 (1995)
W.S. Cassata, B.S. Singer, J. Cassidy, Laschamp and mono lake geomagnetic excursions recorded in new zealand. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 268, 76–88 (2008)
J.E.T. Channell, Late brunhes polarity excursions (mono lake, laschamp, iceland basin and pringle falls) recorded at odp site 919 (Irminger basin). Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 244, 378–393 (2006)
U. Christensen, J. Aubert, Scaling properties of convection-driven dynamos in rotating spherical shells and application to planetary magnetic fields. Geophys. J. Int. 166, 97–114 (2006)
U. Christensen, P. Olson, Secular variation in numerical geodynamo models with lateral variations of boundary heat flow. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 138, 39–54 (2003)
U. Christensen, J. Wicht, Numerical dynamo simulations, in Treatise on Geophysics, ed. by P. Olson, vol. 8 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2007)
U. Christensen, P. Olson, G. Glatzmaier, Numerical modelling of the geodynamo: a systematic parameter study. Geophys. J. Int. 138, 393–409 (1999)
A. Chulliat, N. Olsen, Observation of magnetic diffusion in the Earth’s outer core from Magsat, Ørsted and CHAMP data. J. Geophys. Res. 115, B05105 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009JB006994
B.M. Clement, Geographical distribution of transitional VGPs: evidence for non-zonal symmetry during the matuyama-brunhes geomagnetic reversal. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 104, 48–58 (1991)
B.M. Clement, Dependence of the duration of geomagnetic polarity reversals on site latitude. Nature 428, 637–640 (2004)
B.M. Clement, D.V. Kent, A southern hemisphere record of the matuyama-brunhes polarity reversal. Geophys. Res. Lett. 18, 81–84 (1991)
R. Coe, G. Glatzmaier, Symmetry and stability of the geomagnetic field. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L21311 (2006)
R.S. Coe, L. Hongre, G.A. Glatzmaier, An examination of simulated geomagnetic reversals from a palaeomagnetic perspective. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 358, 1141–1170 (2000)
A. Cox, Reversed flux as reversal mechanism. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 13, 35–51 (1975)
A. Cox, J. Hillhouse, M. Fuller, Paleomagnetic records of polarity transitions, excursions, and secular variation. Rev. Geophys. Space Phys. 13, 185–189 (1975)
P. Davidson, An Introduction to Magnetohydrodynamics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2001)
E. Dormy, J.-P. Valet, V. Courtillot, Numerical models of the geodynamo and observational constraints. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 1(10), 1037 (2000). doi:10.1029/2000GC000062
P. Driscoll, P. Olson, Polarity reversals in geodynamo models with core evolution. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 282, 24–33 (2009)
G. Glatzmaier, Numerical simulation of stellar convective dynamos. 1: The model and method. J. Comp. Phys. 55, 461–484 (1984)
G. Glatzmaier, Dynamo models: how realistic are they? Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 30, 237–257 (2002)
G. Glatzmaier, P. Roberts, A three-dimensional convective dynamo solution with rotating and finitely conducting inner core and mantle. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 91, 63–75 (1995a)
G. Glatzmaier, P. Roberts, A three-dimensional self-consistent computer simulation of a geomagnetic field reversal. Nature 377, 203–209 (1995b)
G. Glatzmaier, P. Roberts, Simulating the geodynamo. Comput. Phys. 38, 269–288 (1997)
G. Glatzmaier, R. Coe, L. Hongre, P. Roberts, The role of the earth’s mantle in controlling the frequency of geomagnetic reversals. Nature 401, 885–890 (1999)
D. Gubbins, Mechanism for geomagnetic polarity reversals. Nature 326, 167–169 (1987)
D. Gubbins, The distinction between geomagnetic excursions and reversals. Geophys. J. Int. 137, F1–F3 (1999)
D. Gubbins, A. Jones, C. Finlay, Fall in Earth’s magnetic field is erratic. Science 312, 900–902 (2006)
D. Gubbins, P. Willis, B. Sreenivasan, Correlation of Earth’s magnetic field with lower mantle thermal and seismic structure. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 162, 256–260 (2007)
H. Guillou, B.S. Singer, C. Laj, C. Kissel, S. Scailleta, B.R. Jicha, On the age of the laschamp geomagnetic excursion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 227, 331–341 (2004)
Y. Guyodo, J.-P. Valet, Global changes in intensity of the earth’s field during the past 800 kyr. Nature 399, 249–252 (1999)
F. Heller, Self-reversal of natural remanent magnetisation in the olby-laschamp lavas. Nature 284(5754), 334–335 (1980)
K.A. Hoffman, Palaeomagnetic excursions, aborted reversals and transitional fields. Nature 294, 67–69 (1981)
K.A. Hoffman, Dipolar reversal states of the geomagnetic field and core mantle dynamics. Nature 359, 789–794 (1992)
K.A. Hoffman, Transitional paleomagnetic field behavior: Preferred paths or patches? Surv. Geophys. 17, 207–211 (1996)
K. Hori, J. Wicht, U. Christensen, The effect of thermal boundary conditions on dynamos driven by internal heating. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. (2010). doi:10.1016/j.pepi.2010.06.011
G. Hulot, F. Lhuillier, J. Aubert, Earth’s dynamo limit of predictability. Geophys. Res. Let. 37, L06305 (2010). doi:10.1029/2009GL041869
M. Hyodo, Possibility of reconstruction of the past geomagnetic field from homogeneous sediments. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 36, 45–62 (1984)
M. Ingham, G. Turner, Behaviour of the geomagnetic field during the matuyama-brunhes polarity transition. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 168, 163–178 (2008)
A. Jackson, A. Jonkers, M. Walker, Four centuries of geomagnetic secular variation from historical records. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A358, 957–990 (2000)
D. Jault, Axial invariance of rapidly varying diffusionless motions in the Earth’s core interior. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 166, 67–76 (2008)
A. Jonkers, Long-range dependence in the cenozoic reversal record. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 135, 253–266 (2003)
C. Kissel, C. Laj, L. Labeyrie, T. Dokken, A. Voelker, D. Blamart, Rapid climatic variations during marine isotope stage 3: magnetic analyses of sediments from Nordic seas and north Atlantic. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 171, 489–502 (1999)
M.F. Knudsen, P.M. Holm, N. Abrahamsen, Paleomagnetic results from a reconnaissance study of Santiago (cape verde islands): Identification of cryptochron c2r.2r-1. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 173, 279–289 (2009)
M. Korte, C. Constable, Continuous geomagnetic field models for the past 7 millennia: 2, cals7k. Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 6, Q02H16 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004GC000801
D. Krása, V.P. Shcherbakov, T. Kunzmann, N. Petersen, Self-reversal of remanent magnetization in basalts due to partially oxidized titanomagnetites. Geophys. J. Int. 162, 115–136 (2005)
C. Kutzner, U. Christensen, Effects of driving mechanisms in geodynamo models. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27, 29–32 (2000)
C. Kutzner, U. Christensen, From stable dipolar towards reversing numerical dynamos. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 131, 29–45 (2002)
C. Kutzner, U. Christensen, Simulated geomagnetic reversals and preferred virtual geomagnetic pole paths. Geophys. J. Int. 157, 1105–1118 (2004)
C. Laj, J.E.T. Channell, Geomagnetic excursions, in Treatise in Geophysics, ed. by M. Kono, vol. 5 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2007), pp. 373–416
C. Laj, A. Mazaud, R. Weeks, M. Fuller, E. Herrero-Bevera, Geomagnetic reversal paths. Nature 351, 447 (1991)
C. Laj, N. Szeremeta, C. Kissel, H. Guillou, Geomagnetic paleointensities at Hawaii between 3.9 and 2.1 ma: preliminary results. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 179, 191–204 (2000)
C. Laj, C. Kissel, V. Scao, J. Beer, D.M. Thomas, H. Guillou, R. Muscheler, G. Wagner, Geomagnetic intensity and inclination variations at Hawaii for the past 98 kyr from core soh-4: a new study and a comparison with existing contemporary data. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 129, 205–243 (2002)
C. Laj, C. Kissel, A.P. Roberts, Geomagnetic field behavior during the iceland basin and laschamp geomagnetic excursions: a simple transitional field geometry? Geochem. Geophys. Geosyst. 7(3), Q03004 (2006). doi:10.1029/2005GC001122
L. Lanci, C. Kissel, R. Leonhardt, C. Laj, Morphology of the iceland basin excursion from a spherical harmonics analysis and an iterative bayesian inversion procedure of sedimentary records. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 169, 131–139 (2008)
C.G. Langereis, Excursions in geomagnetism. Nature 399, 207–208 (1999)
C.G. Langereis, A.A.M.V. Hoof, P. Rochette, Longitudinal confinement of geomagnetic reversal paths as a possible sedimentary artifact. Nature 358, 226–230 (1992)
C.G. Langereis, M.J. Dekkers, G.J. De Lange, M. Paterne, P.J.M. Van Santvoort, Magnetostratigraphy and astronomical calibration of the: Last 1.1 myr from an eastern Mediterranean piston core and dating of short events in the brunhes. Geophys. J. Int. 129(1), 75–94 (1997)
R. Leonhardt, K. Fabian, Paleomagnetic reconstruction of the global geomagnetic field evolution during the matuyama/brunhes transition: Iterative bayesian inversion and independent verification. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 253, 172–195 (2007)
R. Leonhardt, H.C. Soffel, A reversal of the earth’s magnetic field recorded in midmiocene lava flows of Gran canaria: Paleointensities. J. Geophys. Res. 107(B11), 2299 (2002). doi:10.1029/2001JB000949
R. Leonhardt, K. Fabian, M. Winklhofer, A. Ferk, C. Kissel, C. Laj, Geomagnetic field evolution during the laschamp excursion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 278, 87–95 (2009)
S. Levi, H. Audunsson, R.A. Duncan, L. Kristjansson, P.-Y. Gillot, S.P. Jakobsson, Late pleistocene geomagnetic excursion in icelandic lavas: confirmation of the laschamp excursion. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 96, 443–457 (1990)
J. Li, T. Sato, A. Kageyama, Repeated and sudden reversals of the dipole field generated by spherical dynamo action. Science 295, 1887–1890 (2002)
L.E. Lisiecki, M.E. Raymo, A pliocene-pleistocene stack of 57 globally distributed benthic d18o records. Paleoceanography 20, PA1003 (2005). doi:10.1029/2004PA001071
J. Love, Paleomagnetic volcanic data and geometric regularity of reversals and excursions. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 12,435–12,452 (1998)
J.J. Love, Statistical assessment of preferred transitional vgp longitudes on palaeomagnetic lava data. Geophys. J. Int. 140, 211–221 (2000)
J.J. Love, A. Mazaud, A database for the matuyama-brunhes magnetic reversal. Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 103, 207–245 (1997)
S.P. Lund, M. Schwartz, L. Keigwin, T. Johnson, Deep-sea sediment records of the laschamp geomagnetic field excursion (<41,000 calender years before present). J. Geophys. Res. 110, B04101 (2005). doi:10.1029/2003JB002943
G. Masters, G. Laske, H. Bolton, A. Dziewonski, The relative behavior of shear velocity, bulk sound velocity, and compressional velocity in the mantle: implications for chemical and thermal structure, in Earth’s Deep Interior, ed. by S. Karato, A. Forte, R. Liebermann, G. Masters, L. Stixrude. AGU Monograph, vol. 117 (AGU, Washington D.C., 2000)
A. Mazaud, An attempt at reconstructing the geomagnetic field at the core-mantle boundary during the upper Olduvai polarity transition (1.66 myear). Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 90, 211–219 (1995)
A. Mazaud, ‘Sawtooth’ variation in magnetic intensity profiles and delayed acquisition of magnetization in deep sea cores. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 139, 379–386 (1996)
A. Mazaud, C. Laj, M. Bender, A geomagnetic chronology for antarctic ice accumulation. Geophys. Res. Lett. 21(5), 337–340 (1994)
R.T. Merrill, P.L. McFadden, Geomagnetic polarity transitions. Rev. Geophys. 37, 201–226 (1999)
R. Merrill, M. McElhinny, P. McFadden, The Magnetic Field of the Earth: Paleomagnetism, the Core, and the Deep Mantle (Academic Press, San Diego, 1998)
H. Moffatt, Magnetic Field Generation in Electrically Conducting Fluids (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1978)
F. Nimmo, Energetics of the core, in Treatise on Geophysics, ed. by P. Olson, vol. 8 (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2007)
N. Nishikawa, K. Kusano, Simulation study of symmetry-breaking instability and the dipole field reversal in a rotating spherical shell dynamo. Phys. Plasmas 15, 082903 (2008)
N. Olsen, M. Mandea, Rapidly changing flows in the Earth’s core. Nature Geosci. 1, 390–394 (2008)
P. Olson, Gravitational dynamos and the low frequency geomagnetic secular variation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 104, 20159–20166 (2007)
P. Olson, H. Amit, Changes in earth’s dipole. Naturwissenschaften 93, 519–542 (2006)
P. Olson, U. Christensen, The time averaged magnetic field in numerical dynamos with nonuniform boundary heat flow. Geophys. J. Int. 151, 809–823 (2002)
P. Olson, U. Christensen, Dipole moment scaling for convection-driven planetary dynamos. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 250, 561–571 (2006)
P. Olson, U. Christensen, G. Glatzmaier, Numerical modeling of the geodynamo: Mechanisms of field generation and equilibration. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 10383–110404 (1999)
P. Olson, P. Driscoll, H. Amit, Dipole collapse and reversal precursors in a numerical dynamo. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 173, 121–140 (2009)
P. Olson, R. Coe, P. Driscoll, G. Glatzmaier, P. Roberts, Geodynamo reversal frequency and heterogeneous core-mantle boundary heat flow. Phys. Earth Planer. Inter. 180, 66–79 (2010)
E. Parker, Hydromagnetic dynamo models. Astrophys. J. 121, 293–314 (1955)
M. Prévot, P. Camps, Absence of preferred longitude sectors for poles from volcanic records of geomagnetic reversals. Nature 366, 53–57 (1993)
M. Prévot, E.A. Mankinen, R.S. Coe, S. Grommé, The Steens mountain (Oregon) geomagnetic polarity transition 2. field intensity variations and discussion of reversal models. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 10417–10448 (1985)
A.P. Roberts, Geomagnetic excursions: Knowns and unknowns. Geophys. Res. Lett. 35, L17307 (2008)
P. Roberts, S. Scott, On analysis of the secular variation, 1, a hydromagnetic constraint: Theory. J. Geomagn. Geoelectr. 17, 137–151 (1965)
A.P. Roberts, M. Winklhofer, Why are geomagnetic excursions not always recorded in sediments? Constraints from post-depositional remanent magnetization lock-in modelling. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 227, 345–359 (2004)
J. Rotvig, An investigation of reversing numerical dynamos driven by either differential or volumetric heating. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 176, 69–82 (2009)
D. Ryan, G. Sarson, Are geomagnetic field reversals controlled by turbulence within the Earth’s core? Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L02307 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006GL028291
G. Sarson, C. Jones, A convection driven geodynamo reversal model. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 111, 3–20 (1999)
A. Schult, Self-reversal of magnetization and chemical composition of titanomagnetites in basalts. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 4(1), 57–63 (1968)
J.C. Shao, M. Fuller, T. Tanimoto, J.R. Dunn, D.B. Stone, Spherical harmonic analyses of paleomagnetic data: The time-averaged geomagnetic field for the past 5 myr and the brunhes-matuyama reversal. J. Geophys. Res. 104(B3), 5015–5030 (1999)
R. Simitev, F. Busse, Prandtl-number dependence of convection-driven dynamos in rotating spherical fluid shells. J. Fluid Mech. 532, 365–388 (2005)
B.S. Singer, K.A. Hoffman, R.S. Coe, L.L. Brown, B.R. Jicha, M.S. Pringle, A. Chauvin, Structural and temporal requirements for geomagnetic field reversal deduced from lava flows. Nature 434, 633–636 (2005)
P.J. Smith, Field reversal or self-reversal? Nature 229(5284), 378–380 (1971)
B. Sreenivasan, C. Jones, Azimuthal winds, convection and dynamo action in the polar regions of planetary cores. Geophys. Astrophys. Fluid Dyn. 100, 319–339 (2006)
F. Stacey, Physics of the Earth (Brookfield Press, Brisbane, 1992)
J. Stoner, J. Channell, D. Hodell, C.D. Charles, A 580 kyr paleomagnetic record from the sub-antarctic south Atlantic (ocean drilling program site 1089). J. Geophys. Res. 108, 2244 (2003). doi:10.1029/2001JB001390
F. Takahashi, M. Matsushima, Y. Honkura, Simulations of a quasi-Taylor state geomagnetic field including polarity reversals on the Earth simulator. Science 309, 459–461 (2005)
F. Takahashi, M. Matsushima, Y. Honkura, A numerical study on magnetic polarity transition in an MHD dynamo model. Earth Planets Space 59, 665–673 (2007)
F. Takahashi, M. Matsushima, Y. Honkura, Scale variability in convection-driven MHD dynamos at low Ekman number. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 167, 168–178 (2008)
F. Theyer, E. Herrero-Bervera, V. Hsu, The zonal harmonic model of polarity transitions: a test using successive reversals. J. Geophys. Res. 90, 1963–1982 (1985)
J.-P. Valet, E. Herrero-Bervera, Some characteristics of geomagnetic reversals inferred from detailed volcanic records. Compt. Ren. Geosci. 335, 79–90 (2003)
J.-P. Valet, L. Tauxe, B.M. Clement, Equatorial and mid-latitude records of the last geomagnetic reversal from the Atlantic ocean. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 94, 371–384 (1989)
J.-P. Valet, P. Tucholka, V. Courtillot, L. Meynadier, Palaeomagnetic constraints on the geometry of the geomagnetic field during reversals. Nature 356, 400–407 (1992)
J.-P. Valet, L. Meynadier, Y. Guyodo, Geomagnetic dipole strength and reversal rate over the past two million years. Nature 435, 802–805 (2005)
J.-P. Valet, G. Plenier, E. Herrero-Bervera, Geomagnetic excursions reflect an aborted polarity state. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 274, 472–478 (2008)
J. Vogt, B. Zieger, K.-H. Glassmeier, A. Stadelmann, M.-B. Kallenrode, M. Sinnhuber, H. Winkler, Energetic particles in the paleomagnetosphere: Reduced dipole configurations and quadrupolar contributions. J. Geophys. Res. 112, A06216 (2007). doi:10.1029/2006JA012224
J. Wicht, Inner-core conductivity in numerical dynamo simulations. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 132, 281–302 (2002)
J. Wicht, Palaeomagnetic interpretation of dynamo simulations. Geophys. J. Int. 162, 371–380 (2005)
J. Wicht, P. Olson, A detailed study of the polarity reversal mechanism in a numerical dynamo model. Geophys. Geochem. Geosyst. 5 (2004). doi:10.1029/2003GC000602
J. Wicht, A. Tilgner, Theory and modeling of planetary dynamos. Space Sci. Rev. 152, 501–542 (2010)
J. Wicht, S. Stellmach, H. Harder, Numerical models of the geodynamo: From fundamental Cartesian models to 3D simulations of field reversals, in Geomagnetic Field Variations—Space-Time Structure, Processes, and Effects on System Earth, ed. by H. Glassmeier, H. Soffel, J. Negendank (Springer, Berlin, 2009)
J. Wicht, S. Stellmach, H. Harder, Numerical dynamo simulations–from basic concepts to realistic models, in Handbook of Geomathematics (Springer, Berlin, 2010)
I. Williams, M. Fuller, Zonal harmonic models of reversal transition fields. J. Geophys. Res. 86(B12), 11657–11665 (1981)
P. Willis, B. Sreenivasan, D. Gubbins, Thermal core-mantle interaction: Exploring regimes for ‘locked’ dynamo action. Phys. Earth Planet. Inter. 165, 83–92 (2007)
H.-U. Worm, A link between geomagnetic reversals and events and glaciations. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 147, 55–67 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amit, H., Leonhardt, R. & Wicht, J. Polarity Reversals from Paleomagnetic Observations and Numerical Dynamo Simulations. Space Sci Rev 155, 293–335 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-010-9695-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-010-9695-2