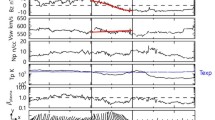
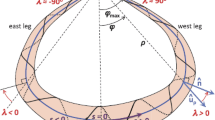
Abstract
This work extends recent efforts on the force-free modeling of large flux rope-type structures (magnetic clouds, MCs) to much smaller spatial scales. We first select small flux ropes (SFRs) by eye whose duration is unambiguous and which were observed by the Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) or Wind spacecraft during solar maximum years. We inquire into which analytical technique is physically most appropriate, augmenting the numerical modeling with considerations of magnetic twist. The observational fact that these SFRs typically do not expand significantly into the solar wind makes static models appropriate for this study. SFRs can be modeled with force-free methods during the maximum phase of solar activity. We consider three models: (i) a linear force-free field (\(\nabla\times \mathbf{B} = \alpha \mathbf{B}\)) with a specific, prescribed constant \(\alpha\) (Lundquist solution), and (ii) with \(\alpha\) as a free constant parameter (“Lundquist-alpha” solution), and (iii) a uniform twist field (Gold–Hoyle solution). We retain only those cases where the impact parameter is less than one-half the flux rope (FR) radius, \(R\), so the results should be robust (29 cases). The SFR radii lie in the range \([{\approx}\,0.003, 0.059]~\mbox{AU}\). Comparing results, we find that the Lundquist-alpha and uniform twist solutions yielded comparable and small normalized \(\chi^{2}\) values in most cases. This means that analytical modeling alone cannot distinguish which of these two is better in reproducing their magnetic field geometry. We then use Grad–Shafranov (GS) reconstruction to analyze these events further in a model-independent way. The orientations derived from GS are close to those obtained from the uniform twist field model. We then considered the twist per unit length, \(\tau\), both its profile through the FR and its absolute value, applying a graphic approach to obtain \(\tau\) from the GS solution. The results are in better agreement with the uniform twist model. We find \(\tau\) to lie in the range \([5.6, 34]~\mbox{turns}/\mbox{AU}\), i.e. much higher than typical values for MCs. The GH model-derived \(\tau\) values are comparable to those obtained from GS reconstruction. We find that the twist per unit length, \(L\), is inversely proportional to \(R\), as \(\tau\approx0.17/R\). We combine MC and SFR results on \(\tau(R)\) and give a relation that is approximately valid for both sets. Using this, we find that the axial and azimuthal fluxes, \(F_{z}\) and \(F_{\phi}\), vary as \({\approx}\,2.1 B_{0} R^{2}\) (\({\times}10^{21}~\mbox{Mx}\)) and \(F_{\phi}/L \approx0.36 B_{0} R\) (\({\times}10^{21}~\mbox{Mx}/\mbox{AU}\)). The relative helicity per unit length is \(H/L \approx0.75 B_{0}^{2} R^{3}\) (\({\times}10^{42}~\mbox{Mx}^{2}/\mbox{AU}\)).















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Haddad, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Savani, N.P., Möstl, C., Marubashi, K., Hidalgo, M.A., et al.: 2013, Magnetic field configuration models and reconstruction methods for interplanetary coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 284, 129. DOI .
Al-Haddad, N., Nieves-Chinchilla, T., Savani, N.P., Lugaz, N., Roussev, I.: 2018, Fitting and reconstruction of thirteen simple coronal mass ejections. Solar Phys. 293, 73. DOI .
Aulanier, G., Janvier, M., Schmieder, B.: 2012, The standard flare model in three dimensions – I. Strong-to-weak shear transition in post-flare loops. Astron. Astrophys. 543, A110. DOI .
Burlaga, L.F.: 1988, Magnetic clouds: Constant alpha force-free configurations. J. Geophys. Res. 93, 7217. DOI .
Burlaga, L., Sittler, E., Mariani, F., Schwenn, R.: 1981, Magnetic loop behind an interplanetary shock: Voyager, Helios, and IMP 8 observations. J. Geophys. Res. 86, 6673. DOI .
Dasso, S., Mandrini, C.H., Démoulin, P., Luoni, M.L.: 2006, A new model-independent method to compute magnetic helicity in magnetic clouds. Astron. Astrophys. 455, 349. DOI .
Démoulin, P.: 2010, Interaction of ICMEs with the solar wind. AIP Conf. Proc. 1216, 229. DOI .
Farrugia, C.J., Burlaga, L.F., Osherovich, V.A., Richardson, I.G., Freeman, M.P., Lepping, R.P., et al.: 1993, A study of an expanding interplanetary magnetic cloud and its interaction with the Earth’s magnetosphere: The interplanetary aspect. J. Geophys. Res. 98, 7621. DOI .
Farrugia, C.J., Janoo, L.A., Torbert, R.B., Quinn, J.M., Ogilvie, K.W., Lepping, R.P., et al.: 1999, A uniform-twist magnetic flux rope in the solar wind. AIP Conf. Proc. 471, 745. DOI .
Galvin, A.B., Kistler, L.M., Popecki, M.A., Farrugia, C.J., Simunac, K.D.C., Ellis, L., et al.: 2008, The plasma and suprathermal ion composition (PLASTIC) investigation on the STEREO observatories. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 437. DOI .
Gold, T., Hoyle, F.: 1960, On the origin of solar flares. Mon. Not. Roy. Astron. Soc. 120, 89. ADS .
Hau, L.-N., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö: 1999, Two-dimensional coherent structures in the magnetopause: Recovery of static equilibria from single-spacecraft data. J. Geophys. Res. 104, 6899. DOI .
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Krucker, S.: 2015, Magnetic field line lengths inside interplanetary magnetic flux ropes. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 5266. DOI .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö: 2001, Reconstruction of magnetic flux ropes in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 28(3), 467. DOI .
Hu, Q., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö: 2002, Reconstruction of magnetic clouds in the solar wind: Orientations and configurations. J. Geophys. Res. 107, 1142. DOI .
Hu, Q., Qiu, J., Dasgupta, B., Khare, A., Webb, G.M.: 2014, Structures of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes and comparison with their solar sources. Astrophys. J. 793, 53. DOI .
Janvier, M., Démoulin, P., Dasso, S.: 2013, Global axis shape of magnetic clouds deduced from the distribution of their local axis orientation. Astron. Astrophys. 556, A50. DOI .
Kahler, S.W., Haggerty, D.K., Richardson, I.G.: 2011, Magnetic field-line lengths in interplanetary coronal mass ejections inferred from energetic electron events. Astrophys. J. 736, 106. DOI .
Khrabrov, A.V., Sonnerup, B.U.Ö.: 1998, deHoffmann–Teller analysis. In: Analysis Methods for Multi-Spacecraft Data, International Space Science Institute, Bern, 221.
Larson, D.E., Lin, R.P., McTieman, J.M., McFadden, J.P., Ergun, R.E., McCarthy, M., et al.: 1997, Tracing the topology of the October 18 – 20, 1995, magnetic cloud with \({\sim}\,0.1\,\mbox{--}\,10^{2}~\mbox{keV}\) electrons. Geophys. Res. Lett. 24(15), 1911. DOI .
Lepping, R.P., Jones, J.A., Burlaga, L.F.: 1990, Magnetic field structure of interplanetary magnetic clouds at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 95, 11957. DOI .
Lepping, R.P., Acũna, M.H., Brulaga, L.F., Farrell, W.M., Slavin, J.A., Schatten, K.H., et al.: 1995, The Wind Magnetic Field Investigation. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 207. DOI .
Lepping, R.P., Berdichevsky, D.B., Wu, C.-C., Szabo, A., Narock, T., Mariani, F., et al.: 2006, A summary of WIND magnetic clouds for years 1995 – 2003: Model-fitted parameters, associated errors and classifications. Ann. Geophys. 24, 215. DOI .
Liu, Y., Luhmann, J.G., Huttunen, K.E.J., Lin, R.P., Bale, S.D., Russell, C.T., et al.: 2008, Reconstruction of the 2007 May 22 magnetic cloud: How much can we trust the flux-rope geometry of CMEs? Astrophys. J. 677, L133. DOI .
Luhmann, J.G., Curtis, D.W., Schroeder, P., McCauley, J., Lin, R.P., Larson, D.E., et al.: 2008, STEREO IMPACT investigation goals, measurements, and data products overview. Space Sci. Rev. 136, 117. DOI .
Lundquist, S.: 1950, Magnetohydrostatic fields. Ark. Fys. 2, 361.
Mandrini, C.H., Pohjolainen, S., Dasso, S., Green, L.M., Démoulin, P., van Driel-Gesztelyi, L., et al.: 2005, Interplanetary flux rope ejected from an X-ray bright point – The smallest magnetic cloud source-region ever observed. Astron. Astrophys. 434(2), 725. DOI .
Markwardt, C.B.: 2009, Non-linear least squares fitting in IDL with MPFIT. In: Bohlender, D., Dowler, P., Durand, D. (eds.) Proc. ADASS XVIII. ASP Conf. Ser., 411, Astronomical Society of the Pacific, San Francisco, 251.
Marubashi, K., Lepping, R.P.: 2007, Long-duration magnetic clouds: A comparison of analyses using torus- and cylinder-shaped flux rope models. Ann. Geophys. 25, 2453. DOI .
Moldwin, M.B., Ford, S., Lepping, R., Slavin, J., Szabo, A.: 2000, Small-scale magnetic flux ropes in the solar wind. Geophys. Res. Lett. 27(1), 57. DOI .
Möstl, C., Miklenic, C., Farrugia, C.J., Temmer, M., Veronig, A., Galvin, A.B., et al.: 2008, Two-spacecraft reconstruction of a magnetic cloud and comparison to its solar source. Ann. Geophys. 26, 3139. DOI .
Möstl, C., Farrugia, C.J., Biernat, H.K., Leitner, M., Kilpua, E.K.J., Galvin, A.B., et al.: 2009, Optimized Grad–Shafranov reconstruction of a magnetic cloud using STEREO-Wind observations. Solar Phys. 256, 427. DOI .
Newbury, J.A., Russell, C.T., Phillips, J.L., Gary, S.P.: 1998, Electron temperature in the ambient solar wind: Typical properties and a lower bound at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 103, 9553. DOI .
Ogilvie, K.W., Chornay, D.J., Fritzenreiter, R.J., Hunsaker, F., Keller, J., Lobell, J., et al.: 1995, SWE, A comprehensive plasma instrument for the Wind spacecraft. Space Sci. Rev. 71, 55. DOI .
Riley, P., Linker, J.A., Lionello, R., Mikić, Z., Odstrcil, D., Hidalgo, M.A., et al.: 2004, Fitting flux ropes to a global MHD solution: A comparison of techniques. J. Atmos. Solar-Terr. Phys. 66, 1321. DOI .
Sonnerup, B.U.Ö., Scheible, M.: 1998, Minimum and maximum variance analysis. In: Analysis Methods for Multi-Spacecraft Data, 185. ADS .
Sonnerup, B.U.Ö., Hasegawa, H., Teh, W.-L., Hau, L.-N.: 2006, Grad–Shafranov reconstruction: An overview. J. Geophys. Res. 111, A09204. DOI .
Sturrock, P.A.: 1994, Plasma Physics: An Introduction to the Theory of Astrophysical, Geophysical and Laboratory Plasmas, Cambridge University Press, New York, 209. ADS .
van Ballegooijen, A.A., Mackay, D.H.: 2007, Model for the coupled evolution of subsurface and coronal magnetic fields in solar active regions. Astrophys. J. 659, 1713. DOI .
Vemareddy, P., Möstl, C., Amerstorfer, T., Mishra, W., Farrugia, C.J., Leitner, M.: 2016, Comparison of magnetic properties in a magnetic cloud and its solar source on 2013 April 11 – 14. Astrophys. J. 828(12), 3139. DOI .
Wang, Y., Zhou, Z., Shen, C., Liu, R., Wang, S.: 2015, Investigating plasma motion of magnetic clouds at 1 AU through a velocity-modified cylindrical force-free flux rope model. J. Geophys. Res. 120, 1543. DOI .
Wang, Y., Zhuang, B., Hu, Q., Liu, R., Shen, C., Chi, Y.: 2016, On the twists of interplanetary magnetic flux ropes observed at 1 AU. J. Geophys. Res. 121, 9316. DOI .
Yu, W., Farrugia, C.J., Lugaz, N., Galvin, A.B., Kilpua, E.K.J., Kucharek, H., et al.: 2014, A statistical analysis of properties of small transients in the solar wind 2007 – 2009: STEREO and Wind observations. J. Geophys. Res. 119, 689. DOI .
Yu, W., Farrugia, C.J., Galvin, A.B., Lugaz, N., Luhmann, J.G., Simunac, K.D.C., et al.: 2016, Small solar wind transients at 1 AU: STEREO observations (2007 – 2014) and comparison with near-Earth wind results (1995 – 2014). J. Geophys. Res. 121, 5005. DOI .
Acknowledgements
Support for this work came from the following grants: NASA STEREO Quadrature grant, NSF AGS-1435785, AGS-1433086 and AGS-1433213, and NASA NNX16AO04G, NNX15AB87G, and NNX15AU01G. C.M. thanks the Austrian Science Fund (FWF): [P26174-N27]. P.V. is supported by an INSPIRE grant of AORC scheme under Department of Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, W., Farrugia, C.J., Lugaz, N. et al. The Magnetic Field Geometry of Small Solar Wind Flux Ropes Inferred from Their Twist Distribution. Sol Phys 293, 165 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1385-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11207-018-1385-3