Abstract
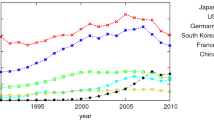
We set out in the present study to examine 1997–2007 data on inventors, based upon country of residence, and on the process of co-invention, with the ultimate aim of undertaking analysis of the main partner countries currently collaborating with China in global technological production. Through our focus on China, we are able to demonstrate the evolving trend towards the establishment of collaborative patenting networks within an emerging market. In addition to exploring the pattern of joint international inventions, we link the patent data to other macro-economic factors for empirical analysis. Our results indicate that the relative manufacturing strength, the international trade exposure, and the respective economy standing have positive effect on the propensity for engaging in such international co-invention activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
These technological fields are based upon the technological classification scheme proposed by Hall et al. (2001); i.e., chemicals (Class 1); ‘computers and communications’ (Class 2); ‘drugs and medical’ (Class 3); electrical and electronics (Class 4); mechanical (Class 5); and ‘others’ (Class 6).
References
Almeida, P. A., & Phene, (2004). Subsidiaries and knowledge creation: the influence of the MNC and host country on innovation. Strategic Management Journal, 25(8–9), 847–864.
Chen, Y., & Puttitanun, T. (2005). Intellectual property rights and innovation in developing countries. Journal of Development Economics, 78, 474–493.
Cheung, K. Y., & Lin, P. (2004). Spillover effects of FDI on innovation in China: evidence from the provincial data. China Economic Review, 15, 25–44.
Du, D-b. (2009). Multinational corporation’s R&D investment in China—policy, trend and impact. Beijing: China Science Publishing Group.
Ejermo, O., & Karlsson, C. (2006). Interregional inventor networks as studied by patent coinventorships. Research Policy, 35, 412–430.
Furman, J. L., Porter, M. E., & Stern, S. (2002). The determinants of national innocative capacity. Research Policy, 31, 899–933.
Guellec, D., & De La Potterie, Bv P. (2001). The internationalisation of technology analyzed with patent data. Research Policy, 30, 1253–1266.
Hall, B., Jaffe, A., Trajtenberg M. (2001) The NBER patent citations data file: lessons, insights and methodological tools. National Bureau of Economic Research working paper no 8498 presented at NBER, Cambridge.
Hicks, D. (2000). 360 degree linkage analysis. Research Evaluation, 9, 133–143.
Hu, A. G., & Jefferson, G. H. (2009). A great wall of patens: what is behind China’s recent patent explosion? Journal of Development Economics, 90, 57–68.
Hu, M. C., & Mathews, J. A. (2008). China’s national innovative capacity. Research Policy, 37, 1465–1479.
Huang, Y.-F., & Chen, C.-J. (2010). The impact of technological diversity and organizational slack on innovation. Technovation, 30, 420–428.
Kim, C., & Song, J. (2007). Creating new technology through alliances: an empirical investigation of joint patents. Technovation, 27, 461–470.
Kostoff, R. N., Briggs, M. B., Rushenberg, R. L., Bowles, C. A., Icenhour, A. S., Nikodym, K. F., et al. (2007). Chinese science and technology—structure and infrastructure. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 74, 1539–1573.
Ma, Z., & Lee, Y. (2008). Patent application and technological collaboration in inventive activities: 1980–2005. Technovation, 28, 379–390.
Ma, Z., Lee, Y., & Chen, C.-F. P. (2009). Booming or emerging? China’s technology capacity and international collaboration in patent activities. Technology Forecasting and Social Change, 76, 787–796.
OECD. (2005). Patents with foreign co-inventor, Compendium of Patent Statistics. OECD, Paris.
Paravantis, J. A., & Georgakellos, D. A. (2007). Trends in energy consumption and carbon dioxide emissions of passenger cars and buses. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 74, 682–707.
Studenmund, AH. (1992). Using econometrics, 2nd edition. New York: Harper Collins.
Yang, C. H., & Kuo, N. F. (2008). Trade-related influences, foreign intellectual property rights and outbound international patenting. Research Policy, 37, 446–459.
Yueh, LY. (2006). Patent laws and innovation in China, China and the world economy, Oxford.
Zedtwitz, V. M., Ikeda, T., Gong, L., Carpenter, R., & Hämäläinen, S. (2007). Managing foreign R&D in China. Research-Technology Management, 50, 19–27.
Zhou, P., & Glanzel, W. (2010). In-depth analysis on China’s international cooperation in science. Scientometrics, 82, 597–612.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, J.H., Jang, SL. & Chang, CH. The patterns and propensity for international co-invention: the case of China. Scientometrics 94, 481–495 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0821-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-012-0821-7