Abstract
In this paper, we examine corporate insolvency in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) region between 2004 and 2011. Data comprises 28 financial ratio variables from 112 firms. We use Logit regression with best-subset selection criteria to investigate the predictive value of the ratios in the GCC context, particularly cash flow-based ratios. We also examine the main dimensions of the ratios, and the weights firms attach to them, using 3-way Multidimensional Scaling (MDS). We find that a parsimonious Logit model with the profitability ratio EBITTL, the leverage ratio TLTA and the cash flow ratios CFFOTA and CFFOCL can predict insolvency, ex-ante, with 84.8, 95.6 and 73.9 % overall, type I and II accuracy, respectively. From MDS, we uncover four financial-ratio dimensions: (i) ‘Non-strategic sales activities’, (ii) ‘Profitability and financial stability balance’, (iii) ‘Sales activities against capital conversion’; and (iv) ‘Market value against cash generation’. Insolvent firms appear very specific and attach most salience to the ‘Non-strategic sales activities’ dimension, unlike solvent firms which attach more salience to the other three dimensions. Therefore, the results imply that, to reduce susceptibility to insolvency in the GCC, managers should focus less on non-strategic sales activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abudelrahman N (2004) An Analytical study on some models of predicting financial failure applied on Saudi Arabia corporate companies. King Abdulaziz University, Jeddah
Al-Ajmi J, Kim J (2012) Are Gulf stock markets efficient? Evidence from new multiple variance ratio tests. Appl Econ 44(14):1737–1747
Aldeehani T (1995) An Implementation of Altman’s Model for the prediction of corporate bankruptcy. King Abudelaziz University, Jeddah
Al-Khazali OM, Ding DK, Pyun CS (2007) A new variance ratio test of random walk in emerging markets: a revisit. Finan Rev 42(2):303–317
AlShebani W (2006) An initial role in accounting information by predicting financial failure for Saudi Companies. J Adm Sci 20(2)
Altman E (1968) Financial ratios, discriminant analysis and the prediction of corporate bankruptcy. J Finan 23(4):589–609
Altman EI (1983) Why businesses fail. J Bus Strateg 3(4):15–21
Altman E (2006) Corporate financial distress and bankruptcy: a complete guide to predicting & avoiding distress and profiting from bankruptcy, 3rd edn. Wiley, New Jersey
Altman EI, Lavallee M (1981) Business failure classification in Canada. J Bus Adm 12(1):147–164
Altman EI, Narayanan P (1997) An international survey of business failure classification models. Finan Mark Inst Instrum 6(2):1–57
Altman E, Haldeman R, Narayanan P (1977) ZETA analysis A new model to identify bankruptcy risk of corporations. J Bank Financ 1(1):29–54
Andreev Y (2006) Predicting financial distress of Spanish companies
Arabie P, Carroll DJ, DeSarbo WS (1987) Three-way scaling and clustering, vol 65.Quantitative applications in the social sciences. Sage, London
Arouri MEH, Lahiani A, Nguyen DK (2011) Return and volatility transmission between world oil prices and stock markets of the GCC countries. Econ Model 28(4):1815–1825
Aziz A, Lawson GH (1989) Cash flow reporting and financial distress models: testing of hypotheses. Finan Manag 18:55–63
Aziz A, Emanuel DC, Lawson GH (1988) Bankruptcy prediction—an investigation of cash flow based models. J Manag Stud 25(5):419–437
Balcaen S, Ooghe H (2006) 35 years of studies on business failure: an overview of the classic statistical methodologies and their related problems. B Account Rev 38(1):63–93
Barnes P (1987) The analysis and use of financial ratios: a review article. J Bus Financ Account 14(4):449–461
Basheikh AM (2012) Prediction of financial failure of Saudi listed companies. Int J Manag Financ Account 4(2):195–213
Beaver W (1966) Financial ratios as predictors of failure. J Account Res 4:71–111
Bley J (2011) Are GCC stock markets predictable? Emerg Mark Rev 12(3):217–237
Blum M (1974) Failing company discriminant analysis. J Account Res 12:1–25
Bose I (2006) Deciding the financial health of dot-coms using rough sets. Info Manag 43(7):835–846
Bragg SM (2002) Business ratios and formulas: a comprehensive guide, vol 577. Wiley, New Jersey
Breiman L (1996) Bagging predictors. Mach Learn 24(2):123–140. doi:10.1007/bf00058655
Brigham EF, Ehrhardt MC (2010) Financial management theory and practice. South-Western Publication, Mason
Busing FM, Groenen PJ, Heiser WJ (2005) Avoiding degeneracy in multidimensional unfolding by penalizing on the coefficient of variation. Psycometrika 70(1):71–98
Canbas S, Cabuk A, Kilic SB (2005) Prediction of commercial bank failure via multivariate statistical analysis of financial structures: the Turkish case. Eur J Oper Res 166(2):528–546
Casey C, Bartczak N (1985) Using operating cash flow data to predict financial distress: some extensions. J Account Res 23(1):384–401
CFA Institute (2009) Finiacial reporting and analysis, vol 3. CFA progr curric. PEARSON, Boston
Charan R, Useem J, Harrington A (2002) Why companies fail CEOs offer every excuse but the right one: their own errors. Here are ten mistakes to avoid. Fortune Eur Ed 145(11):36–46
Charitou A, Neophytou E, Charalambous C (2004) Predicting corporate failure: empirical evidence for the UK. Eur Account Rev 13(3):465–497
Chen KH, Shimerda TA (1981) An empirical-analysis of useful financial ratios. Finan Manag 10(1):51–60. doi:10.2307/3665113
Chen J, Marshall BR, Zhang J, Ganesh S (2006) Financial distress prediction in China. Rev Pac Basin Financ Market Policy 9(02):317–336
Chipulu M, Neoh JG, Ojiako U, Williams T (2013) A multidimensional analysis of project manager competences. IEEE Trans Eng Manag 60(7):506–517
Coats PK, Fant LF (1993) Recognizing financial distress patterns using a neural-network tool. Finan Manag 22(3):142–155. doi:10.2307/3665934
Dambolena IG, Khoury SJ (2012) Ratio stability and corporate failure. J Finan 35(4):1017–1026
Deakin E (1972) A discriminant analysis of predictors of business failure. J Account Res 10:167–179
Doumpos M, Zopounidis C, Golfinopoulou V (2007) Additive support vector machines for pattern classification. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part B Cybern 37(3):540–550. doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2006.887427
Edmister RO (1972) An empirical test of financial ratio analysis for small business failure prediction. J Financ Quant Anal 7:1477–1493
Elam R (1975) The effect of lease data on the predictive ability of financial ratios. Account Review 50(1):25–43
Emery DR, Barron FH, Messier WF (1982) Conjoint measurement and the analysis of noisy data: a comment. J Account Res 20(2):450–458
Ezzamel M, Mar Molinero C, Beech A (1987) On the distributional properties of financial ratios. J Bus Financ Account 14(4):463–481
Fasano U, Zubair I (2003) GCC countries: from oil dependence to diversification International Monetary Fund
Fedenczuk LL (2003) To neural or not to neural?—This is the question. In: System. SUGI’27 Proceedings. SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC
Firth D (1993) Bias reduction of maximum likelihood estimates. Biometrika 80(1):27–38
Friedman JH (1977) A recursive partitioning decision rule for nonparametric classification. IEEE Trans Comput 100(4):404–408
Furnival GM, Wilson RW (1974) Regression by Leaps and Bounds. Technometrics 16(4):499–511
Gentry JA, Newbold P, Whitford DT (1985) Classifying bankrupt firms with funds flow components. J Account Res 23(1):146–160
Gentry JA, Newbold P, Whitford DT (1987) Funds flow components, financial ratios, and bankruptcy. J Bus Financ Account 14(4):595–606
Gilbert LR, Menon K, Schwartz KB (1990) Predicting bankruptcy for firms in financial distress. J Bus Financ Account 17(1):161–171
Gloubos G, Grammatikos T (1988) The success of bankruptcy prediction models in Greece. Stud Bank Financ 7(1):37–46
Gombola MJ, Ketz JE (1983) Financial ratio patterns in retail and manufacturing organizations. Finan Manag 12(2):45–56. doi:10.2307/3665210
Goudie AW, Meeks G (1991) The exchange rate and company failure in a macro-micro model of the UK company sector. Econ J 101(406):444–457
Gupta MC, Huefner RJ (1972) A cluster analysis study of financial ratios and industry characteristics. J Account Res 10:77–95
Han L, Han L, Zhao H (2013) Orthogonal support vector machine for credit scoring. Eng Appl Artif Intell 26(2):848–862. doi:10.1016/j.engappai.2012.10.005
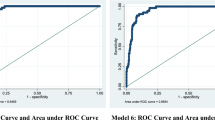
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ (1982) The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristics curve. Radiology 143:29–36
Hasabo H (1987) The use of accounting ratios in predicting financial crises a suggested model for Kuwait stock exchange. J Gulf Arab Peninsul States Stud 13(52)
Hawkins DM (2004) The problem of overfitting. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 44(1):1–12
House RJ, Hanges PJ, Javidan M, Dorfman PW, Gupta V (2004) Culture, leadership and organizations: the GLOBE Study of 62 societies. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA
Hussain M, Islam MM, Gunasekaran A, Maskooki K (2002) Accounting standards and practices of financial institutions in GCC countries. Manag Audit J 17(7):350–362. doi:10.1108/02686900210437453
Jones FL (1987) Current techniques in bankruptcy prediction. J Account Lit 6(1):131–164
Jones S, Hensher DA (2004) Predicting firm financial distress: a mixed logit model. Account Rev 79(4):1011–1038
Joy OM, Tollefson JO (1975) On the financial applications of discriminant analysis. J Financ Quant Anal 10:723–739
Kahya E, Theodossiou P (1999) Predicting corporate financial distress: a time-series CUSUM methodology. Rev Quant Finan Account 13(4):323–345
Karels GV, Prakash AJ (1987) Multivariate normality and forecasting of business bankruptcy. J Bus Financ Account 14(4):573–593
Keasey K, McGuinness P (1990) The failure of UK industrial firms for the period 1976–1984, logistic analysis and entropy measures. J Bus Financ Account 17(1):119–135
Khamis M, Senhadji A (2010) Impact of the Global Financial Crisis on the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries and Challenges Ahead. International Monetary Fund, Washington, DC
Ko C (1982) A delineation of corporate appraisal models and classification of bankruptcy firms in Japan. New York University, New York
Koziol C (2014) A simple correction of the WACC discount rate for default risk and bankruptcy costs. Rev Quant Finan Account 42(4):653–666
Kruskal JB, Wish M (1978) Multidimensional Scaling. Sage, London
Kuwait stock exchange (2010) KSE Committ decision No. (3/2010). http://www.kuwaitse.com/A/KSE/Decision2005.aspx. Accessed 30 March 2011
Laitinen T, Kankaanpaa M (1999) Comparative analysis of failure prediction methods: the finnish case. Eur Account Rev 8(1):67–92
Lane WR, Looney SW, Wansley JW (1986) An application of the Cox proportional hazards model to bank failure. J Bank Financ 10(4):511–531
Lensberg T, Eilifsen A, McKee TE (2006) Bankruptcy theory development and classification via genetic programming. Eur J Oper Res 169(2):677–697
Libby R (1975) Accounting ratios and the prediction of failure: some behavioral evidence. J Account Res 13:150–161
Luoma M, Laitinen EK (1991) Survival analysis as a tool for company failure prediction. Omega 19(6):673–678
Mar Molinero C, Ezzamel M (1991) Multidimensional scaling applied to corporate failure. Omega 19(4):259–274
Mar-Molinero C, Serrano-Cinca C (2001) Bank failure: a multidimensional scaling approach. Eur J Financ 7(2):165–183
Megginson WL, Smart SB (2005) Introduction to corporate finance. Cengage Learning
Mensah YM (1983) The differential bankruptcy predictive ability of specific price level adjustments: some empirical evidence. Account Rev 58:228–246
Mensah YM (1984) An examination of the stationarity of multivariate bankruptcy prediction models: a methodological study. J Account Res 22:380–395
Min JH, Lee Y-C (2005) Bankruptcy prediction using support vector machine with optimal choice of kernel function parameters. Expert Syst Appl 28(4):603–614
Ministry of Industry and Commerce Kingdom of Bahrain (2002) Commercial registration—law no. 9, 2002. http://www.moic.gov.bh/MoIC/Ar/Industry/ResourcesLaws/CommerceLaw/CompanyLaws/CompanyLaw9.htm
Moriarity S, Barron FH (1976) Modeling the materiality judgements of audit partners. J Account Res 14:320–341
Morris R (1997) Early warning indicators of corporate failure: A critical review of previous research and further empirical evidence. Ashgate (Aldershot, Hants, England and Brookfield, Vt.)
Moyer RC, McGuigan JR, Kretlow WJ (2008) Contemporary financial management. South-Western Publication, Mason
Nemes S, Jonasson JM, Genell A, Steineck G (2009) Bias in odds ratios by logistic regression modelling and sample size. BMC Med Res Method 9(1):56
Neophytou E, Molinero C (2004) Predicting corporate failure in the UK: a multidimensional scaling approach. J Bus Financ Account 31 (5–6):677–710
Neophytou E, Molinero C (2005) Financial ratios, size, industry and interest rate issues in company failure: an extended multidimensional scaling analysis. Kent Business School, Canterbury
Ni J, Kwak W, Cheng X, Gong G (2014) The determinants of bankruptcy for Chinese firms. Rev Pac Basin Financ Market Policy 17(02):22 papes. doi:10.1142/S021909151450012X
Ohlson JA (1980) Financial ratios and the probabilistic prediction of bankruptcy. J Account Res 18(1):109–131
Ong CS, Huang JJ, Tzeng GH (2005) Building credit scoring models using genetic programming. Expert Syst Appl 29(1):41–47
Onour I (2010) The global financial crisis and equity markets in middle east oil exporting countries. The Arab Planning Institute, Kuwait
Peduzzi P, Concato J, Kemper E, Holford TR, Feinstein AR (1996) A simulation study of the number of events per variable in logistic regression analysis. J Clin Epidemiol 49(12):1373–1379
Peel M, Peel D, Pope P (1986) Predicting corporate failure—some results for the UK corporate sector. Omega 14(1):5–12
Peeters M (2011) The changing pattern in international trade and capital flows of the Gulf Cooperation Council countries in comparison with other oil-exporting countries. J Knowl Manag Econ Inf Technol 1(7):356–384
Platt HD, Platt MB (1990) Development of a class of stable predictive variables: the case of bankruptcy prediction. J Bus Financ Account 17(1):31–51
Punj G, Stewart DW (1983) Cluster analysis in marketing research: review and suggestions for application. J Mark Res 20:134–148
Ravisankar P, Ravi V, Bose I (2010) Failure prediction of dotcom companies using neural network–genetic programming hybrids. Info Sci 180(8):1257–1267
Richardson FM, Davidson LF (1983) An exploration into bankruptcy discriminant model sensitivity. J Bus Financ Account 10(2):195–207
Rocha R, Farazi S (2011) Financial access and stability. Financial flagship report. World Bank, Washington, DC
Salchenberger LM, Cinar E, Lash NA (1992) Neural Networks: a new tool for predicting thrift failures. Decis Sci 23(4):899–916
Saudi Commerce Ministry (1966) Systems and regulations—companies system. http://beta.mci.gov.sa/Arabic/LawsRegulations/SystemsAndRegulations/Pages/CompaniesSystem.aspx. Accessed 30 March 2011
Schiffman S, Reynolds M, Young F (1981) Introduction to multidimensional scaling theory, methods and applications. Academic Press, London
Serrano-Cinca C (1996) Self organizing neural networks for financial diagnosis. Decis Supp Syst 17(3):227–238
Shin KS, Lee YJ (2002) A genetic algorithm application in bankruptcy prediction modeling. Expert Syst Appl 23(3):321–328
Shumway T (2001a) Forecasting bankruptcy more accurately: a simple hazard model. J Bus 74(1):101–124
Shumway T (2001b) Forecasting bankruptcy more accurately: a simple hazard model. J Bus 74(1):101–124
Smith M, Liou DK (1979) Industrial sector and financial distress. Manag Audit J 22(4):376–391
Sori M, Hasbullah J (2009) Financial ratios, discriminant analysis and the prediction of corporate distress. Cogn Sci 11:5–15
State of Qatar Ministry of Economy and Commerce (2002) The Commercial Companies Law—Law no. (5) of 2002. vol 5
Steyerberg EW, Eijkemans MJC, Harrell FE, Habbema JDF (2001) Prognostic modeling with logistic regression analysis: In search of a sensible strategy in small data sets. Med Decis Mak 21(1):45–56. doi:10.1177/0272989x0102100106
Sultanate of Oman Ministry of Commerce and Industry (1986) Laws and regulations—Commercial Companies Law, vol 4/74
Sung TK, Chang N, Lee G (1999) Dynamics of modeling in data mining: interpretive approach to bankruptcy prediction. J Manag Inf Syst 16(1):63–85
Ta HP, Seah LH (1988) Business failure prediction in Singapore. Stud Bank Financ 7:105–113
Taffler R (1982) Forecasting company failure in the UK using discriminant analysis and financial ratio data. J R Stat Soc Ser A 145(3):342–358
Thomas LC, Edelman DB, Crook JN (2002) Credit scoring and its applications. Siam
United Arab Emirate Ministry of Economy (1984) Commercial Regulations—Companies Law, vol 8
Uttamchandani M, Nasser SN, Batra S, Sanderson R, Koldertsova A, Helmy O (2009) Study on Insolvency Systems in the middle east and north Africa. Hawkamah/World Bank/OECD/INSOL International
Varetto F (1998) Genetic algorithms applications in the analysis of insolvency risk. J Bank Financ 22(10):1421–1439
Ward TJ (1994) Cash flow information and the prediction of financially distressed mining, oil and gas firms: a comparative study. J Appl Bus Res 10(3):78–86
Warner JB (1977) Bankruptcy costs: some evidence. J finan 32(2):337–347
White M (1996) The costs of corporate bankruptcy: A US-European comparison. In: Corporate bankruptcy: economic and legal perspectives, pp 467–500
Wilcox J (1973) A prediction of business failure using accounting data. J Account Res 11:163–179
Zavgren C (1983) The prediction of corporate failure: the state of the art. J Account Lit 2(1):1–37
Zavgren C (1985) Assessing the vulnerability to failure of American industrial firms: a logistic analysis. J Bus Financ Account 12(1):19–45
Zhu X, Li J, Wu D, Wang H, Liang C (2013) Balancing accuracy, complexity and interpretability in consumer credit decision making: a C-TOPSIS classification approach. Knowl Based Syst 52:258–267
Zmijewski ME (1984) Methodological issues related to the estimation of financial distress prediction models. J Account Res 22:59–82
Acknowledgments
I would like to thank anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendices
Appendix 1
See Table 10.
Appendix 2: Logit prediction model results
Appendix 3: Probit prediction model results
Appendix 4
See Table 15.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khoja, L., Chipulu, M. & Jayasekera, R. Analysing corporate insolvency in the Gulf Cooperation Council using logistic regression and multidimensional scaling. Rev Quant Finan Acc 46, 483–518 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11156-014-0476-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11156-014-0476-y
Keywords
- Gulf Cooperation Council
- Corporate insolvency
- Multidimensional scaling
- Cluster analysis
- Logit
- Probit
- Financial ratio