Abstract
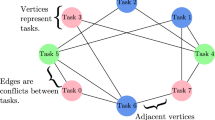
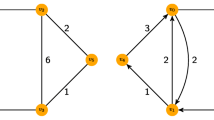
We report on a case study in programming an early quantum annealer to attack optimization problems related to operational planning. While a number of studies have looked at the performance of quantum annealers on problems native to their architecture, and others have examined performance of select problems stemming from an application area, ours is one of the first studies of a quantum annealer’s performance on parametrized families of hard problems from a practical domain. We explore two different general mappings of planning problems to quadratic unconstrained binary optimization (QUBO) problems, and apply them to two parametrized families of planning problems, navigation-type and scheduling-type. We also examine two more compact, but problem-type specific, mappings to QUBO, one for the navigation-type planning problems and one for the scheduling-type planning problems. We study embedding properties and parameter setting and examine their effect on the efficiency with which the quantum annealer solves these problems. From these results, we derive insights useful for the programming and design of future quantum annealers: problem choice, the mapping used, the properties of the embedding, and the annealing profile all matter, each significantly affecting the performance.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rieffel, E.G., Polak, W.: A Gentle Introduction to Quantum Computing. MIT Press, Cambridge, MA (2011)
Nielsen, M., Chuang, I.L.: Quantum Computing and Quantum Information. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2001)
Farhi, E., Goldstone, J., Gutmann, S., Sipser, M.: Quantum computation by adiabatic evolution. arXiv:quant-ph/0001106 (2000)
Das, A., Chakrabarti, B.K.: Colloquium: quantum annealing and analog quantum computation. Rev. Mod. Phys. 80, 1061 (2008)
Smelyanskiy, V.N., Rieffel, E.G., Knysh, S.I., Williams, C.P., Johnson, M.W., Thom, M.C., Macready, W.G., Pudenz, K.L.: A near-term quantum computing approach for hard computational problems in space exploration. arXiv:1204.2821 (2012)
Johnson, M., Amin, M., Gildert, S., Lanting, T., Hamze, F., Dickson, N., Harris, R., Berkley, A., Johansson, J., Bunyk, P., et al.: Quantum annealing with manufactured spins. Nature 473(7346), 194 (2011)
Boixo, S., Albash, T., Spedalieri, F.M., Chancellor, N., Lidar, D.A.: Experimental signature of programmable quantum annealing. Nat. Commun. (2013). doi:10.1038/ncomms3067
Smolin, J.A., Smith, G.: Classical signature of quantum annealing. arXiv:1305.4904 (2013)
Wang, L., Rønnow, T.F., Boixo, S., Isakov, S.V., Wang, Z., Wecker, D., Lidar, D.A., Martinis, J.M., Troyer, M.: Comment on “Classical signature of quantum annealing”. arXiv:1305.5837 (2013)
Boixo, S., Rønnow, T.F., Isakov, S.V., Wang, Z., Wecker, D., Lidar, D.A., Martinis, J.M., Troyer, M.: Evidence for quantum annealing with more than one hundred qubits. Nat. Phys. 10(3), 218 (2014)
Shin, S.W., Smith, G., Smolin, J.A., Vazirani, U.: How “quantum” is the D-Wave machine? arXiv:1401.7087 (2014)
Vinci, W., Albash, T., Mishra, A., Warburton, P.A., Lidar, D.A.: Distinguishing classical and quantum models for the D-Wave device. arXiv:1403.4228 (2014)
Shin, S.W., Smith, G., Smolin, J.A., Vazirani, U.: Comment on “Distinguishing classical and quantum models for the D-Wave device”. arXiv:1404.6499 (2014)
Rieffel, E.G., Venturelli, D., Hen, I., Do, M., Frank, J.: Parametrized families of hard planning problems from phase transitions. In: Proceedings of the Twenty-Eighth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI-14), pp. 2337–2343,(2014)
Wang, Z., Boixo, S., Albash, T., Lidar, D.: Benchmarking the D-Wave adiabatic quantum optimizer via 2D-Ising spin glasses. APS Meeting Abstr. 1, 27005 (2013)
Rønnow, T.F., Wang, Z., Job, J., Boixo, S., Isakov, S.V., Wecker,D., Martinis, J.M., Lidar, D.A., Troyer, M.: Defining and detectingquantum speedup. Science 345(6195), 420 (2014)
Wang, Z., Job, J., Troyer, M., Lidar, D.A. et al.: Performance of quantum annealing on random Ising problems implemented using the D-wave two. Bull. Am. Phys. Soc. (2014)
Venturelli, D., Mandra, S., Knysh, S., OGorman, B., Biswas, R., Smelyanskiy, V.: Quantum optimization of fully-connected spin glasses. arXiv:1406.7553 (2014)
Kassal, I., Whitfield, J.D., Perdomo-Ortiz, A., Yung, M.H., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Simulating chemistry using quantum computers. arXiv:1007.2648 (2010)
Perdomo-Ortiz, A., Dickson, N., Drew-Brook, M., Rose, G., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Finding low-energy conformations of lattice protein models by quantum annealing. Sci. Rep. (2012). doi:10.1038/srep00571
Babbush, R., Perdomo-Ortiz, A., O’Gorman, B., Macready, W., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Construction of energy functions for lattice heteropolymer models: a case study in constraint satisfaction programming and adiabatic quantum optimization. arXiv:1211.3422 (2012)
Babbush, R., Love, P.J., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Adiabatic quantum simulation of quantum chemistry. arXiv:1311.3967 (2013)
Perdomo-Ortiz, A., Fluegemann, J., Narasimhan, S., Smelyanskiy, V., Biswas, R.: A quantum approach to diagnosis of multiple faults in electrical power systems. In: 5th IEEE International Conference on Space Mission Challenges for Information Technology. (To appear.) (2014)
O’Gorman, B., Perdomo-Ortiz, A., Babbush, R., Aspuru-Guzik, A., Smelyanskiy, V.: Bayesian network structure learning using quantum annealing. Eur. Phys. J. Spec. Top. arXiv:1407.3897 (2014)
Perdomo-Ortiz, A., Fluegemann, J., Narasimhan, S., Biswas, R., Smelyanskiy, V.: Programming and solving real-world applications on a quantum annealing device. arXiv:1406.7601 (2014)
Fikes, R.E., Nilsson, N.J.: STRIPS: a new approach to the application of theorem proving to problem solving. Artif. Intell. 2(3), 189 (1972)
Ghallab, M., Nau, D., Traverso, P.: Automated Planning: Theory and Practice. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2004)
Long, D., Fox, M.: PDDL2. 1: an extension to PDDL for expressing temporal planning domains. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 20, 1 (2003)
Helmert, M.: Complexity results for standard benchmark domains in planning. Artifi. Intell. J. 143(2), 219–262 (2003)
Hoffmann, J.: Local search topology in planning benchmarks: an empirical analysis. J. Artif. Intell. Res. 24, 685 (2005)
Komlós, J., Szemerédi, E.: Limit distribution for the existence of Hamiltonian cycles in a random graph. Discrete Math. 43(1), 55 (1983)
Cheeseman, P., Kanefsky, B., Taylor, W.M.: Where the really hard problems are. IJCAI 91, 331–337 (1991)
Chien, S., Johnston, M., Frank, J., Giuliano, M., Kavelaars, A., Lenzen, C., Policella, N., Verfailie, G.: A generalized timeline representation, services, and interface for automating space mission operations. In: 12th International Conference on Space Operations (2012)
Achlioptas, D., Friedgut, E.: A sharp threshold for k-colorability. Random Struct. Algorithm. 14(1), 63 (1999)
Coja-Oghlan, A.: Upper-bounding the k-colorability threshold by counting covers. arXiv:1305.0177 (2013)
Achlioptas, D., Moore, C.: Almost all graphs with average degree 4 are 3-colorable. J. Comput. Syst. Sci. 67(2), 441 (2003)
Dubois, O., Mandler, J.: On the non-3-colourability of random graphs. arXiv:math/0209087 (2002)
Culberson, J., Beacham, A., Papp, D.: Hiding our colors. In: Proceedings of the CP95 Workshop on Studying and Solving Really Hard Problems, pp. 31–42, (1995)
Choi, V.: Minor-embedding in adiabatic quantum computation: II. Minor-universal graph design. Quantum Inf. Process. 7(5), 193 (2008)
Lucas, A.: Ising formulations of many NP problems. arXiv:1302.5843 (2013)
Blum, A., Furst, M.: Fast planning through planning graph analysis. Artif. Intell. J. 90, 281 (1997)
Kautz, H.: Working Notes on the Fourth International Planning Competition (IPC-2004) pp. 44–45 (2004)
Boros, E., Hammer, P.L.: Pseudo-boolean optimization. Discrete Appl. Math. 123(1), 155 (2002)
Babbush, R., O’Gorman, B., Aspuru-Guzik, A.: Resource efficient gadgets for compiling adiabatic quantum optimization problems. Ann. Phys. 525(10–11), 877 (2013)
Klymko, C., Sullivan, B.D., Humble, T.S.: Adiabatic quantum programming: minor embedding with hard faults. Quantum Inf. Process. 13(3), 709 (2014)
Cai, J., Macready, B., Roy, A.: A practical heuristic for finding graph minors. arXiv:1406.2741 (2014)
Pudenz, K.L., Albash, T., Lidar, D.A.: Error-corrected quantum annealing with hundreds of qubits. Nat. Commun. (2014). doi:10.1038/ncomms4243
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Jeremy Frank, Alejandro Perdomo-Ortiz, Sergey Knysh, Itay Hen, Ross Beyer, and Chris Henze for helpful discussions, and to D-Wave for technical support and for discussions related to the calibration issue and our results before and after. This work was supported in part by the Office of the Director of National Intelligence (ODNI), the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA), via IAA 145483; by the AFRL Information Directorate under grant F4HBKC4162G001. The views and conclusions contained herein are those of the authors and should not be interpreted as necessarily representing the official policies or endorsements, either expressed or implied, of ODNI, IARPA, AFRL, or the U.S. Government. The U.S. Government is authorized to reproduce and distribute reprints for Governmental purpose notwithstanding any copyright annotation thereon. The authors also would like to acknowledge support from the NASA Advanced Exploration Systems program and NASA Ames Research Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rieffel, E.G., Venturelli, D., O’Gorman, B. et al. A case study in programming a quantum annealer for hard operational planning problems. Quantum Inf Process 14, 1–36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0892-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11128-014-0892-x