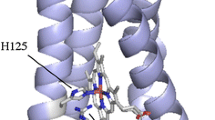
Abstract
The cytochrome (Cyt) c-554 in thermophilic green photosynthetic bacterium Chlorobaculum tepidum serves as an intermediate electron carrier, transferring electrons to the membrane-bound Cyt c z from various enzymes involved in the oxidations of sulfide, thiosulfate, and sulfite compounds. Spectroscopically, this protein exhibits an asymmetric α-absorption band for the reduced form and particularly large paramagnetic 1H NMR shifts for the heme methyl groups with an unusual shift pattern in the oxidized form. The crystal structure of the Cyt c-554 has been determined at high resolution. The overall fold consists of four α-helices and is characterized by a remarkably long and flexible loop between the α3 and α4 helices. The axial ligand methionine has S-chirality at the sulfur atom with its CεH3 group pointing toward the heme pyrrole ring I. This configuration corresponds to an orientation of the lone-pair orbital of the sulfur atom directed at the pyrrole ring II and explains the lowest-field 1H NMR shift arising from the 181 heme methyl protons. Differing from most other class I Cyts c, no hydrogen bond was formed between the methionine sulfur atom and polypeptide chain. Lack of this hydrogen bond may account for the observed large paramagnetic 1H NMR shifts of the heme methyl protons. The surface-exposed heme pyrrole ring II edge is in a relatively hydrophobic environment surrounded by several electronically neutral residues. This portion is considered as an electron transfer gateway. The structure of the Cyt c-554 is compared with those of other Cyts c, and possible interactions of this protein with its electron transport partners are discussed.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cba :
-
Chlorobaculum
- Chl :
-
Chlorobium
- CD:
-
Circular dichroism
- COSY:
-
Correlation spectroscopy
- HMQC:
-
Heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence
- MALDI-TOF:
-
Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight
- MCD:
-
Magnetic circular dichroism
- NOESY:
-
Nuclear Overhauser effect spectroscopy
- RC:
-
Reaction center
- RR:
-
Resonance Raman
- Tch :
-
Thermochromatium
- TOMES:
-
Thiosulfate oxidizing multi-enzyme system
References
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Arslan E, Schulz H, Zufferey R, Künzler P, Thöny-Meyer L (1998) Overproduction of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum c-type cytochrome subunits of the cbb 3 oxidase in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:744–747
Azai C, Tsukatani Y, Itoh S, Oh-oka H (2010) C-type cytochromes in the photosynthetic electron transfer pathways in green sulfur bacteria and heliobacteria. Photosynth Res 104:189–199
Benini S, Borsari M, Ciurli S, Dikiy A, Lamborghini M (1998) Modulation of Bacillus pasteurii cytochrome c 553 reduction potential by structural and solution parameters. J Biol Inorg Chem 3:371–382
Brune DC (1995) Sulfur compounds as photosynthetic electron donors. In: Blankenship RE, Madigan MT, Bauer CE (eds) Anoxyenic photosynthetic bacteria. Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands, pp 847–870
Carter DC, Melis KA, O’Donnell SE, Burgess BK, Furey WF Jr, Wang B-C, Stout CD (1985) Crystal structure of Azotobacter cytochrome c 5 at 2.5 Å resolution. J Mol Biol 184:279–295
Davidson MW, Meyer TE, Cusanovich MA, Knaff DB (1986) Complex formation between Chlorobium limicola f. thiosulfatophilum c-type cytochromes. Biochim Biophys Acta 850:396–401
Desbois A (1994) Resonance Raman spectroscopy of c-type cytochromes. Biochimie 76:693–707
Emsley P, Lohkamp B, Scott WG, Cowtan K (2010) Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr D D66:486–501
Gorst CM, Wilks A, Yeh DC, de Montellano PRO, La Mar GN (1998) Solution 1H NMR investigation of the molecular and electronic structure of the active site of substrate-bound human heme oxygenase: the nature of the distal hydrogen bond donor to bound ligands. J Am Chem Soc 120:8875–8884
Higuchi M, Hirano Y, Kimura Y, Oh-oka H, Miki K, Wang Z-Y (2009) Overexpression, characterization, and crystallization of the functional domain of cytochrome c z from Chlorobium tepidum. Photosynth Res 102:77–84
Hirano Y, Higuchi M, Oh-oka H, Miki K, Wang Z-Y (2010) Crystal structure of the electron carrier domain of the reaction center cytochrome c z subunit from green photosynthetic bacterial Chlorobium tepidum. J Mol Biol 397:1175–1187
Hirano Y, Kimura Y, Suzuki H, Miki K, Wang Z-Y (2012) Structure analysis and comparative characterization of the cytochrome c’ and flavocytochrome c from thermophilic purple photosynthetic bacterium Thermochromatium tepidum. Biochemistry 51:6556–6567
Holm L, Rosenström P (2010) Dali server: conservation mapping in 3D. Nucleic Acids Res 38:W545–W549
Hu S, Morris IK, Singh JP, Smith KM, Spiro TG (1993) Complete assignment of cytochrome c resonance Raman spectra via enzymic reconstitution with isotopically labeled hemes. J Am Chem Soc 115:12446–12458
Itoh M, Seo D, Sakurai H, Sétif P (2002) Kinetics of electron transfer between soluble cytochrome c-554 and purified reaction center complex from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum. Photosynth Res 71:125–135
Korszun ZR, Salemme FR (1977) Structure of cytochrome c 555 of Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum: primitive low-potential cytochrome c. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5244–5247
Kusai A, Yamanaka T (1973) Cytochrome c (553, Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum) is a sulfide-cytochrome c reductase. FEBS Lett 34:235–237
Lewis MA, Timkovich R, Cotton TM (1985) A comparative study of the resonance Raman spectra of bacterial cytochromes. Arch Biochem Biophys 236:515–525
Lyskov S, Gray JJ (2008) The RosettaDock server for local protein–protein docking. Nucleic Acids Res 36:W233–W238
McLachlan SJ, La Mar GN, Lee K-B (1988) One- and two-dimensional nuclear Overhauser effect studies of the electronic/molecular structure of the heme cavity of ferricytochrome b 5. Biochim Biophys Acta 957:430–445
Miroux B, Walker JE (1996) Over-production of proteins in Escherichia coli: mutant hosts that allow synthesis of some membrane proteins and globular proteins at high levels. J Mol Biol 260:289–298
Moore GR, Pettigrew GW (1990) Cytochromes c: evolutionary structural and physicochemical aspects. Springer, Berlin
Morelle N, Simorre J-P, Caffrey M, Meyer T, Cusanovich M, Marion D (1995) 1H and 13C NMR assignment and secondary structure of Chlorobium limicola f. thiosulfatophilum ferrocytochrome c 555. FEBS Lett 365:172–178
Murshudov GN, Levedev A, Vagin AA, Wilson KS, Dodson EJ (1999) Efficient anisotropic refinement of macromolecular structure using FFT. Acta Crystallogr D D55:247–255
Nojiri M, Koteishi H, Nakagami T, Kobayashi K, Inoue T, Yamaguchi K, Suzuki S (2009) Structural basis of inter-protein electron transfer for nitrite reduction in denitrification. Nature 462:117–120
Ogawa T, Furusawa T, Nomura R, Seo D, Hosoya-Matsuda N, Sakurai H, Inoue K (2008) SoxAX binding protein, a novel component of the thiosulfate-oxidizing multienzyme system in the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum. J Bacteriol 190:6097–6110
Ogawa T, Furusawa T, Shiga M, Seo D, Sakurai H, Inoue K (2010) Biochemical studies of a soxF-encoded monomeric flavoprotein purified from the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobaculum tepidum that stimulates in vitro thiosulfate oxidation. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 74:771–780
Oh-oka H, Iwaki M, Itoh S (1998) Membrane -bound cytochrome c z couples quinol oxidoreductase to the P840 reaction center complex in isolated membranes of the green sulfur bacterium Chlorobium tepidum. Biochemistry 37:12293–12300
Otwinowski Z, Minor W (1997) Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. In: Charles W, Carter J, Robert MS (eds) Methods in enzymology macromolecular crystallography part A, vol 276. Academic Press, New York, pp 307–326
Sakurai H, Ogawa T, Shiga M, Inoue K (2010) Inorganic sulfur oxidizing system in green sulfur bacteria. Photosynth Res 104:163–176
Senn H, Wüthrich K (1983) A new spatial structure for the axial methionine observed in cytochrome c 5 from Pseudomonas mendocina. Biochim Biophys Acta 747:16–25
Senn H, Wüthrich K (1985) Amino acid sequence, haem-iron co-ordination geometry and functional properties of mitochondrial and bacterial c-type cytochromes. Quart Rev Biophys 18:111–134
Senn H, Cusanovich MA, Wüthrich K (1984) 1H NMR assignments for the heme group and electronic structure in Chlorobium thiosulfatophilum cytochrome c-555. Biochim Biophys Acta 785:46–53
Shao W, Sun H, Yao Y, Tang W (1995) 1H NMR studies of the imidazole complex of cytochrome c: resonance assignment and structural characterization of the heme cavity. Inorg Chem 34:680–687
Shelnutt JA, Rousseau DL, Dethmers JK, Margoliash E (1981) Protein influences on porphyrin structure in cytochrome c. Biochemistry 20:6485–6497
Shokhirev NV, Walker FA (1998) The effect of axial ligand plane orientation on the contact and pseudocontact shifts of low-spin ferriheme proteins. J Biol Inorg Chem 3:581–594
Spiro TG, Stong JD, Stein P (1979) Porphyrin core expansion and doming in heme proteins. New evidence from resonance Raman spectra of six-coordinate high-spin ion(III) hemes. J Am Chem Soc 101:2648–2655
Tsukatani Y, Azai C, Kondo T, Itoh S, Oh-oka H (2008) Parallel electron donation pathways to cytochrome cz in the type I homodimeric photosynthetic reaction center complex of Chlorobium tepidum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1777(9):1211–1217. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2008.05.002
Vagin A, Teplyakov A (1997) MOLREP: an automated program for molecular replacement. J Appl Cryst 30:1022–1025
Wang Z-Y, Kadota T, Kobayashi M, Kasuya A, Nozawa T (2004) NMR relaxation study of the bacteriochlorophyll c in solutions. J Phys Chem B 108:15422–15428
Wei X, Ming L-J, Cannons AC, Solomonson LP (1998) 1H and 13C NMR studies of a truncated heme domain from Chlorella vulgaris nitrate reductase: signal assignment of the heme moiety. Biochim Biophys Acta 1382:129–136
Worrall JAR, Schlarb-Ridley BG, Reda T, Marcaida MJ, Moorlen RJ, Wastl J, Hirst J, Bendall DS, Luisi BF, Howe CJ (2007) Modulation of heme redox potential in the cytochrome c 6 family. J Am Chem Soc 129:9468–9475
Wüthrich K (1976) NMR in biological research: peptides and proteins. North-Holland, Amsterdam
Yamanaka T, Okunuki K (1968) Comparison of Chlorobium thiosulphatophilum cytochrome c-555 with c-type cytochromes derived from algae and nonsulphur purple bacteria. J Biochem 63:341–346
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Higuchi for technical assistance. This work was supported by Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research on Priority Areas “Structures of Biological Macromolecular Assemblies” (to Z.-Y.W-O.) and Grants-in-aid for Scientific Research (C) (No. 24570183 to H. O.), from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan, and partially supported by The Kurata Memorial Hitachi Science and Technology Foundation. The X-ray experiments were performed under the approval of the Photon Factory Program Advisory Committee (Proposal No. 2009G525 and 2011G514), and we thank the beamline staff for their help in data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Long-Jiang Yu and Masaki Unno have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, LJ., Unno, M., Kimura, Y. et al. Structure analysis and characterization of the cytochrome c-554 from thermophilic green sulfur photosynthetic bacterium Chlorobaculum tepidum . Photosynth Res 118, 249–258 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9922-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11120-013-9922-2