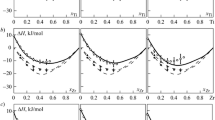
The partial mixing enthalpies of titanium, zirconium, and hafnium with liquid copper and iron alloys are studied by high-temperature calorimetry. The studies are carried out at a temperature of 1873 K along the sections with constant ratios x Cu/x Fe = 3, 1, and 1/3. Along all the studied sections, these functions are negative. The integral mixing enthalpies of components in the Cu–Fe–(Ti, Zr, Hf) systems along the studied sections are calculated by integrating the Gibbs–Duhem equation. The ΔH functions for ternary Cu–Fe–(Ti, Zr, Hf) melts are characterized by positive values in the vicinity of the binary Cu–Fe system and show negative values in a range of compositions with x Me > 0.1 (Me = = Ti, Zr, Hf).


Similar content being viewed by others
References
B. J. Park, H. J. Chang, D. H. Kim, et al., “Phase separating bulk metallic glass: a hierarchical composite,” Phys. Rev. Lett., 96, No. 24, 245503-1–245503-4 (2006).
H. J. Chang, W. Yook, E. S. Park, et al., “Synthesis of metallic glass composites using phase separation phenomena,” Acta Mater., 58, No. 7, 2483–2491 (2010).
N. Mattern, T. Gemming, J. Thomas, et al., “Phase separation in Ni–Nb–Y metallic glasses,” J. Alloys Compd., 495, No. 2, 299–304 (2010).
S. W. Sohn, W. Yook, W. T. Kim, et al., “Phase separation in bulk-type Gd–Zr–Al–Ni metallic glass,” Intermetallics, 23, 57–62 (2012).
J. Pan, L. Liu, and K. C. Chan, “Enhanced plasticity by phase separation in CuZrAl bulk metallic glass with micro-addition of Fe,” Scr. Mater., 60, No. 9, 822–825 (2009).
D. V. Louzguine-Luzgin, G. Xie, Q. Zhang, et al., “Effect of Fe on the glass-forming ability, structure and devitrification behavior of Zr–Cu–Al bulk glass-forming alloys,” Philos. Mag., 90, No. 14, 1955–1968 (2010).
J. Pan, K. C. Chan, Q. Chen, et al., “The effect of microalloying on mechanical properties in CuZrAl bulk metallic glass,” J. Alloys Compd., 504, S74–S77 (2010).
T. Nagase, A. Yokoyama, and Y. Umakoshi, “Multi-scale crystalline Cu globule dispersed Fe-based metallic glass formation by multi-step liquid phase separation,” J. Alloys Compd., 494, No. 1, 295–300 (2010).
D. H. Kim, W. T. Kim, E. S. Park, et al., “Phase separation in metallic glasses,” Prog. Mater. Sci., 58, No. 8, 1103–1172 (2013).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu–Ti–Zr system. I. Cu–Ti system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 5–6, 344–360 (2008).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamic assessment of the Cu–Ti–Zr system. II. Cu–Zr and Ti–Zr systems,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 7–8, 428–446 (2008).
M. A. Turchanin and P. G. Agraval, “Thermodynamic assessment of the copper–hafnium system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 47, No. 3–4, 223–233 (2008).
M. A. Turchanin, A. R. Abdulov, P. G. Agraval, et al., “Thermodynamic functions of mixing for Fe–Ti melts,” Russian Metallurgy (Metally), No. 5, 370–376 (2008).
P. G. Agraval, L. A. Dreval, and M. A. Turchanin, “Thermodynamic properties of iron melts with titanium, zirconium, and hafnium,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 55, No. 11–12, 707–716 (2017).
Y. Nakagawa, “Liquid immiscibility in copper–iron and copper–cobalt systems in the supercooled state,” Acta Metall., 6, No. 11, 704–711 (1958).
S. P. Elder, A. Munitz, and G. J. Abbashian, “Metastable liquid immiscibility in iron–copper and cobalt–copper alloys,” Mater. Sci. Forum, 50, 137–150 (1989).
G. Wilde, R. Willnecker, R.-N. Singh, et al., “The metastable miscibility gap in the system Fe–Cu,” Z. Metallkd., 88, No. 10, 804–809 (1997).
S.-E. Amara, A. Belhadj, R. Kesri, et al., “Stable and metastable equilibria in the binary Fe–Cu and ternary Fe–Cu–C systems,” Z. Metallkd., 90, No. 2, 116–123 (1999).
R. A. Dunlap, G. Stroink, Z. M. Stadnik, et al., “Properties of as-quenched and hydrogenated copper–iron–titanium alloys,” Mater. Sci. Eng., 99, 543–546 (1988).
T. L. Wang and B. X. Liu, “Glass forming ability of the Fe–Zr–Cu system studied by thermodynamic calculation and ion beam mixing,” J. Alloys Compd., 481, 156–160 (2009).
L. Ma, L. Wang, T. Zhang, et al., “Bulk glass formation of Ti–Zr–Hf–Cu–M (M = Fe, Co, Ni) alloys,” Mater. Trans., 43, No. 2, 277–280 (2002).
K. Jin and J. F. Löffler, “Bulk metallic glass formation in Zr–Cu–Fe–Al alloys,” Appl. Phys. Lett., 86, 241909-1–241909-3 (2005).
M. A. Turchanin and I. V. Nikolaenko, “Enthalpies of formation of liquid (copper + manganese) alloys,” Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 28, No. 3, 473–478 (1997).
P. Agraval, L. Dreval, M. Turchanin, et al., “Enthalpy of mixing of liquid Ni–Ti–Zr alloys at 1873 K,” J. Chem. Thermodyn., 106, 309–316 (2017).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, A. N. Fesenko, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamics of liquid alloys and metastable phase transformations in the copper–titanium system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 44, No. 5–6, 259–270 (2005).
A. A. Turchanin, I. A. Tomilin, M. A. Turchanin, et al., “Enthalpies of formation of liquid and amorphous Zr–Cu alloys,” J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 250–252, 582–585 (1999).
M. A. Turchanin, P. G. Agraval, and A. R. Abdulov, “Thermodynamics of liquid alloys of iron with zirconium,” Rasplavy, No. 6, 25–29 (2006).
P. G. Agraval, L. A. Dreval, and M. A. Turchanin, “Enthalpy of mixing of hafnium in liquid iron by high-temperature calorimetry,” J. Alloys Compd., 604, 273–275 (2014).
M. A. Turchanin and P. G. Agraval, “Thermodynamics of liquid alloys, and stable and metastable phase equilibria in the copper–iron system,” Powder Metall. Met. Ceram., 40, No. 7–8, 337–353 (2001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya, Vol. 56, Nos. 3–4 (514), pp. 143–153, 2017.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agraval, P.G., Dreval, L.A. & Turchanin, M.A. Interaction of Components in Cu–Fe Glass-Forming Melts with Titanium, Zirconium, and Hafnium. I. Calorimetric Study of Mixing Enthalpies. Powder Metall Met Ceram 56, 231–238 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9890-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11106-017-9890-8