Abstract
Aims
For a metal hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii, the recruitment of unique rhizospheric bacterial communities from bulk soils has been well studied. However, in the root-soil interface, the knowledge on the establishment of endospheric microbiomes from rhizospheric soil is still scarce.
Methods
In this study, we combined culture-independent that was 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, and culture-dependent methods that included bacterial isolation, heavy metal tolerance and plant growth-promoting traits.
Results
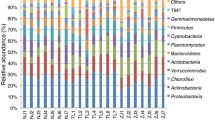
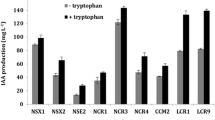
The Cd/Zn concentrations in endosphere were significantly higher than in soil, while Pb concentration in endosphere was significantly lower than in soil. The α-diversity in rhizosphere soils was higher than in root endosphere, and the compartments as a major determinant revealed 85.9% of the taxa variations. The relative abundance of Proteobacteria increased in endosphere compared to rhizosphere. The difference of Cd/Zn tolerance between endospheric and rhizospheric isolates was not obvious, while the Pb tolerance of endospheric isolates significantly decreased compared to rhizosphere.
Conclusions
The results suggest that S. alfredii recruits Cd/Zn-tolerant but not Pb-tolerant endospheric bacterial communities from its rhizospheric soil. The difference in the microbial structure and function in the root-soil interface might be related to the selective absorption of metals in S. alfredii.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai Y, Müller D, Srinivas G, Garrido-Oter R, Potthoff E, Rott M, Dombrowski N, Münch P, Spaepen S, Remus-Emsermann M, Hüttel B, McHardy A, Vorholt J, Schulze-Lefert P (2015) Functional overlap of the Arabidopsis leaf and root microbiota. Nature 528:364–369
Barret M, Briand M, Bonneau S, Preveaux A, Valiere S, Bouchez O, Hunault G, Simoneau P, Jacques M (2015) Emergence shapes the structure of the seed microbiota. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:1257–1266
Beckers B, Op De Beeck M, Weyens N, Boerjan W, Vangronsveld J (2017) Structural variability and niche differentiation in the rhizosphere and endosphere bacterial microbiome of field-grown poplar trees. Microbiome 5:25
Bolyen E, Rideout J, Dillon M et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotech 37:848–857
Bulgarelli D, Rott M, Schlaeppi K, Ver Loren Van Themaat E, Ahmadinejad N, Assenza F, Rauf P, Huettel B, Reinhardt R, Schmelzer E, Peplies J, Gloeckner F, Amann R, Eickhorst T, Schulze-Lefert P (2012) Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota. Nature 488:91–95
Bulgarelli D, Schlaeppi K, Spaepen S, Ver L, Schulze-Lefert P (2013) Structure and functions of the bacterial microbiota of plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 64:807–838
Cao X, Wang X, Tong W, Gurajala H, Lu M, Hamid Y, Feng Y, He Z, Yang X (2019) Distribution, availability and translocation of heavy metals in soil-oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) system related to soil properties. Environ Pollut 252:733–741
Cao X, Luo J, Wang X, Chen Z, Liu G, Khan M, Kang K, Feng Y, He Z, Yang X (2020) Responses of soil bacterial community and cd phytoextraction to a Sedum alfredii-oilseed rape (Brassica napus L. and Brassica juncea L.) intercropping system. Sci Total Environ 723:138152
Castrillo G, Teixeira P, Paredes S, Law T, Lorenzo L, Feltcher M, Finkel O, Breakfield N, Mieczkowski P, Jones C, Paz-ares J, Dangl J (2017) Root microbiota drive direct integration of phosphate stress and immunity. Nature 543:513–518
Cernava T, Erlacher A, Soh J, Sensen C, Grube M, Berg G (2019) Enterobacteriaceae dominate the core microbiome and contribute to the resistome of arugula (Eruca sativa Mill.). Microbiome 7:13
Chen B, Zhang Y, Rafiq M, Khan K, Pan F, Yang X, Feng Y (2014) Improvement of cadmium uptake and accumulation in Sedum alfredii by endophytic bacteria Sphingomonas SaMR12: effects on plant growth and root exudates. Chemosphere 117:367–373
Chen B, Luo S, Wu Y, Ye J, Wang Q, Xu X, Pan F, Khan K, Feng Y, Yang X (2017) The effects of the endophytic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens Sasm05 and IAA on the plant growth and cadmium uptake of Sedum alfredii Hance. Front Microbiol 8:2538
Chen Y, Ding Q, Chao Y, Wei X, Wang S, Qiu R (2018) Structural development and assembly patterns of the root-associated microbiomes during phytoremediation. Sci Total Environ 644:1591–1601
Dominguez-Bello M, Costello E, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Fierer N, Knight R (2010) Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 107:11971–11975
Durán P, Thiergart T, Garrido-Oter R, Agler M, Kemen E, Schulze-Lefert P, Hacquard S (2018) Microbial interkingdom interactions in roots promote Arabidopsis survival. Cell 175:973–983
Edgar R (2013) UPARSE highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996–998
Edwards J, Johnson C, Santos-Medellín C, Lurie E, Podishetty N, Bhatnagar S, Eisen J, Sundaresan V (2015) Structure, variation, and assembly of the root-associated microbiomes of rice. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 112:E911–E920
Gottel N, Castro H, Kerley M, Yang Z, Pelletier D, Podar M, Karpinets T, Uberbacher E, Tuskan G, Vilgalys R, Doktycz M, Schadt C (2011) Distinct microbial communitieswithin the endosphere and rhizosphere of Populus deltoides roots across contrasting soil types. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5934–5944
Grant C, Clarke J, Duguid S, Chaney R (2008) Selection and breeding of plant cultivars to minimize cadmium accumulation. Sci Total Environ 390:301–310
Hou D, Wang K, Liu T, Wang H, Lin Z, Qian J, Lu L, Tian S (2017) Unique rhizosphere micro-characteristics facilitate phytoextraction of multiple metals in soil by the hyperaccumulating plant Sedum alfredii. Environ Sci Technol 51:5675–5684
Hou D, Lin Z, Wang R, Ge J, Wei S, Xie R, Wang H, Wang K, Hu Y, Yang X, Lu L, Tian S (2018) Cadmium exposure-Sedum alfredii planting interactions shape the bacterial community in the hyperaccumulator plant rhizosphere. Appl Environ Microbiol 84:e02797–e02717
Hu Y, Tian S, Foyer C, Hou D, Wang H, Zhou W, Liu T, Ge J, Lu L, Lin X (2019) Efficient phloem transport significantly remobilizes cadmium from old to young organs in a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 365:421–429
Huang A, Jiang T, Liu Y, Bai Y, Reed J, Qu B, Goossens A, Nützmann H, Bai Y, Osbourn A (2019) A specialized metabolic network selectively modulates Arabidopsis root microbiota. Science 364:u6389
Huang L, Wang Q, Zhou Q, Ma L, Wu Y, Liu Q, Wang S, Feng Y (2020) Cadmium uptake from soil and transport by leafy vegetables: a meta-analysis. Environ Pollut 264:114677
Hussain B, Lin Q, Hamid Y, Sanaullah M, Di L, Hashmi MLUR, Khan MB, He Z, Yang X (2020) Foliage application of selenium and silicon nanoparticles alleviates Cd and Pb toxicity in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci Total Environ 712:136497
Johnston-Monje D, Lundberg D, Lazarovits G, Reis V, Raizada M (2016) Bacterial populations in juvenile maize rhizospheres originate from both seed and soil. Plant Soil 405:337–355
Kabagale A, Cornu B, Vliet F, Meyer C, Mergeay M, Simbi J, Droogmans L, Wauven C, Verbruggen N (2010) Diversity of endophytic bacteria from the cuprophytes Haumaniastrum katangense and Crepidorhopalon tenuis. Plant Soil 334:461–474
Krämer U (2010) Metal hyperaccumulation in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 61:517–534
Larousse M, Rancurel C, Syska C, Palero F, Etienne C, Industri B, Nesme X, Bardin M, Galiana E (2017) Tomato root microbiota and Phytophthora parasitica-associated disease. Microbiome 5:56
Lebeis S (2014) The potential for give and take in plant-microbiome relationships. Front Plant Sci 5:287
Lebeis S, Rott M, Dangl J, Schulze-Lefert P (2012) Culturing a plant microbiome community at the cross-Rhodes. New Phytol 196:341–344
Lebeis S, Paredes S, Lundberg D, Breakfield N, Gehring J, McDonald M, Malfatti S, Rio T, Jones C, Tringe S, Dangl J (2015) Salicylic acid modulates colonization of the root microbiome by specific bacterial taxa. Science 349:860–864
Li J, Gurajala H, Wu L, van der Ent A, Qiu R, Baker A, Tang Y, Yang X, Shu W (2018) Hyperaccumulator plants from China: a synthesis of the current state of knowledge. Environ Sci Technol 52:11980–11994
Liu M, He X, Feng T, Zhuo R, Qiu W, Han X, Qiao G, Zhang D (2019) cDNA library for mining functional genes in Sedum alfredii Hance related to cadmium tolerance and characterization of the roles of a novel SaCTP2 gene in enhancing cadmium hyperaccumulation. Environ Sci Technol 53:10926–10940
Lopes K, Carpentieri-Pipolo V, Oro T, Pagliosa E, Degrassi G (2016) Culturable endophytic bacterial communities associated with field-grown soybean. J Appl Microbiol 120:740–755
Lundberg D, Lebeis S, Paredes S, Yourstone S, Gehring J, Malfatti S, Tremblay J, Engelbrektson A, Kunin V, Rio T, Edgar R, Eickhorst T, Ley R, Hugenholtz P, Tringe S, Dangl J (2012) Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome. Nature 488:86–90
Luo S, Chen L, Chen J, Xiao X, Xu T, Wan Y, Rao C, Liu C, Liu Y, Lai C, Zeng G (2011) Analysis and characterization of cultivable heavy metal-resistant bacterial endophytes isolated from Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. and their potential use for phytoremediation. Chemosphere 85:1130–1138
Luo J, Tao Q, Wu K, Li J, Qian J, Liang Y, Yang X, Li T (2017) Structural and functional variability in root-associated bacterial microbiomes of cd/Zn hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:7961–7976
Luo J, Tao Q, Jupa R, Liu Y, Wu K, Song Y, Li J, Huang Y, Zou L, Liang Y, Li T (2019a) Role of vertical transmission of shoot endophytes in root-associated microbiome assembly and heavy metal hyperaccumulation in Sedum alfredii. Environ Sci Technol 53:6954–6963
Luo J, Liu Y, Tao Q, Hou Q, Wu K, Song Y, Liu Y, Guo X, Li J, Hashmi M, Liang Y, Li T (2019b) Successive phytoextraction alters ammonia oxidation and associated microbial communities in heavy metal contaminated agricultural soils. Sci Total Environ 664:616–625
Magoč T, Salzberg S (2011) FLASH fast length adjustment of short reads to improve genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 27:2957–2963
Massoni J, Bortfeld-Miller M, Jardillier L, Salazar G, Sunagawa S, Vorholt J (2020) Consistent host and organ occupancy of phyllosphere bacteria in a community of wild herbaceous plant species. ISME J 14:245–258
Mendes R, Garbeva P, Raaijmakers J (2013) The rhizosphere microbiome: significance of plant beneficial, plant pathogenic, and human pathogenic microorganisms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 37:634–663
Mitter E, de Freitas J, Germida J (2017) Bacterial root microbiome of plants growing in oil sands reclamation covers. Front Microbiol 8:849
Muehe E, Weigold P, Adaktylou I, Planer-Friedrich B, Kraemer U, Kappler A, Behrens S (2015) Rhizosphere microbial community composition affects cadmium and zinc uptake by the metal-hyperaccumulating plant Arabidopsis halleri. Appl Environ Microbiol 81:2173–2181
Niu B, Paulson J, Zheng X, Kolter R (2017) Simplified and representative bacterial community of maize roots. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 114:E2450–E2459
Palmer C, Bik E, DiGiulio D, Relman D, Brown P (2007) Development of the human infant intestinal microbiota. PLoS Biol 5:e177
Penrose D, Glick B (2003) Methods for isolating and characterizing ACC deaminase-containing plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria. Physiol Plant 118:10–15
Perez-Jaramillo J, Carrion V, Bosse M, Ferrao L, de Hollander M, Garcia A, Ramirez C, Mendes R, Raaijmakers J (2017) Linking rhizosphere microbiome composition of wild and domesticated Phaseolus vulgaris to genotypic and root phenotypic traits. The ISME Journal 11:2244–2257
Plociniczak T, Choclor M, Pacwa-Plociniczak M, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2019) Metal-tolerant endophytic bacteria associated with Silene vulgaris support the Cd and Zn phytoextraction in non-host plants. Chemosphere 219:250–260
Quast C, Pruesse E, Yilmaz P, Gerken J, Schweer T, Yarza P, Peplies J, Glockner F (2013) The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D590–D596
Rehman M, Zafar M, Waris A, Rizwan M, Ali S, Sabir M, Usman M, Ayub M, Ahmad Z (2020) Residual effects of frequently available organic amendments on cadmium bioavailability and accumulation in wheat. Chemosphere 244:125548
Rognes T, Flouri T, Nichols B, Quince C, Mahé F (2016) VSEARCH a versatile open source tool for metagenomics. PeerJ 4:e2584
Roman-Ponce B, Ramos-Garza J, Vasquez-Murrieta M, Rivera-Orduna F, Chen W, Yan J, Estrada-de los Santos P, Wang E (2016) Cultivable endophytic bacteria from heavy metal(loid)-tolerant plants. Arch Microbiol 198:941–956
Sarwar M, Kremer R (1995) Enhanced suppression of plant-growth through production of L-tryptophan-derived compounds by deleteriou rhizobacteria. Plant Soil 172:261–269
Schwyn B, Neilands J (1987) Universal chemical-assay for the detection and determination of siderophores. Anal Biochem 160:47–56
Sessitsch A, Kuffner M, Kidd P, Vangronsveld J, Wenzel W, Fallmann K, Puschenreiter M (2013) The role of plant-associated bacteria in the mobilization and phytoextraction of trace elements in contaminated soils. Soil Biol Biochem 60:182–194
Shin M, Shim J, You Y, Myung H, Bang K, Cho M, Kamala-Kannan S, Oh B (2012) Characterization of lead resistant endophytic Bacillus sp. MN3-4 and its potential for promoting lead accumulation in metal hyperaccumulator Alnus firma. J Hazard Mater 199-200:314–320
Tao Q, Zhao J, Li J, Liu Y, Luo J, Yuan S, Li B, Li Q, Xu Q, Yu X, Huang H, Li T, Wang C (2020) Unique root exudate tartaric acid enhanced cadmium mobilization and uptake in Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 383:121177
Tian S, Xie R, Wang H, Hu Y, Hou D, Liao X, Brown P, Yang H, Lin X, Labavitch J, Lu L (2017) Uptake, sequestration and tolerance of cadmium at cellular levels in the hyperaccumulator plant species Sedum alfredii. J Exp Bot 68:2387–2398
Tkacz A, Cheema J, Chandra G, Grant A, Poole P (2015) Stability and succession of the rhizosphere microbiota depends upon plant type and soil composition. The ISME Journal 9:2349–2359
Turner T, James E, Poole P (2013) The plant microbiome. Genome Biol 14:209
Ullah I, Al-Johny B, AL-Ghamdi K, Al-Zahrani H, Anwar Y, Firoz A, AL-Kenani N, Almatry M (2019) Endophytic bacteria isolated from Solanum nigrum L., alleviate cadmium (Cd) stress response by their antioxidant potentials, including SOD synthesis by sodA gene. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 174:197–207
Veach A, Morris R, Yip D, Yang Z, Engle N, Cregger M, Tschaplinski T, Schadt C (2019) Rhizosphere microbiomes diverge among Populus trichocarpa plant-host genotypes and chemotypes, but it depends on soil origin. Microbiome 7:76
Visioli G, D'Egidio S, Sanangelantoni A (2015) The bacterial rhizobiome of hyperaccumulators: future perspectives based on omics analysis and advanced microscopy. Front Plant Sci 5:752
Wang Q, Ge C, Xu S, Wu Y, Sahito Z, Ma L, Pan F, Zhou Q, Huang L, Feng Y, Yang X (2020a) The endophytic bacterium Sphingomonas SaMR12 alleviates Cd stress in oilseed rape through regulation of the GSH-AsA cycle and antioxidative enzymes. BMC Plant Biology 20:63
Wang X, Wang M, Xie X, Guo S, Zhou Y, Zhang X, Yu N, Wang E (2020b) An amplification-selection model for quantified rhizosphere microbiota assembly. Sci Bull 65:983–986
Wang R, Hou D, Li J, Chen J, Fu Y, Wang S, Zheng W, Lu L, Tian S (2020c) Distinct rhizobacterial functional assemblies assist two Sedum alfredii ecotypes to adopt different survival strategies under lead stress. Environ Int 143:105912
Wu Y, Ma L, Liu Q, Sikder M, Vestergård M, Zhou K, Wang Q, Yang X, Feng Y (2020a) Pseudomonas fluorescens promote photosynthesis, carbon fixation and cadmium phytoremediation of hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii. Sci Total Environ 726:138554
Wu Y, Ma L, Liu Q, Vestergård M, Topalovic O, Wang Q, Zhou Q, Huang L, Yang X, Feng Y (2020b) The plant-growth promoting bacteria promote cadmium uptake by inducing a hormonal crosstalk and lateral root formation in a hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. J Hazard Mater 395:122661
Wu Y, Ma L, Liu Q, Topalovic O, Wang Q, Yang X, Feng Y (2020c) Pseudomonas fluorescens accelerates a reverse and long-distance transport of cadmium and sucrose in the hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii. Chemosphere 256:127156
Xia Y, Mucci C, Williams M, Debolt S (2013) Characterization of culturable bacterial endophytes of switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) and their capacity to influence plant growth. Phytopathology 103:163–163
Xv L, Ge J, Tian S, Wang H, Yu H, Zhao J, Lu L (2020) A cd/Zn co-hyperaccumulator and Pb accumulator, Sedum alfredii, is of high cu tolerance. Environ Pollut 263:114401
Yang X, Long X, Ye H, He Z, Calvert D, Stoffella P (2004) Cadmium tolerance and hyperaccumulation in a new Zn-hyperaccumulating plant species (Sedum alfredii Hance). Plant Soil 259:181–189
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh B, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64:991–997
Zgadzaj R, Garrido-Oter R, Jensen DB, Koprivova A, Schulze-Lefert P, Radutoiu S (2016) Root nodule symbiosis in Lotus japonicus drives the establishment of distinctive rhizosphere, root, and nodule bacterial communities. Proc Nati Acad Sci USA 113:E7996–E8005
Zhalnina K, Louie K, Hao Z, Mansoori N, Da Rocha U, Shi S, Cho H, Karaoz U, Loqué D, Bowen B, Firestone M, Northen T, Brodie E (2018) Dynamic root exudate chemistry and microbial substrate preferences drive patterns in rhizosphere microbial community assembly. Nat Microbiol 3:470–480
Zhang H, Xie X, Kim M, Kornyeyev D, Holaday S, Paré P (2008) Soil bacteria augment Arabidopsis photosynthesis by decreasing glucose sensing and abscisic acid levels in planta. Plant J 56:264–273
Zhang W, Huang Z, He L, Sheng X (2012) Assessment of bacterial communities and characterization of lead-resistant bacteria in the rhizosphere soils of metal-tolerant Chenopodium ambrosioides grown on lead–zinc mine tailings. Chemosphere 87:1171–1178
Zhang Y, Xu J, Riera N, Jin T, Li J, Wang N (2017) Huanglongbing impairs the rhizosphere-to-rhizoplane enrichment process of the citrus root-associated microbiome. Microbiome 5:97
Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhang N, Hu B, Jin T, Xu H, Qin Y, Yan P, Zhang X, Guo X, Hui J, Cao S, Wang X, Wang C, Wang H, Qu B, Fan G, Yuan L, Garrido-Oter R, Chu C, Bai Y (2019) NRT1.1B is associated with root microbiota composition and nitrogen use in field-grown rice. Nature Biotech 37:676–684
Acknowledgements
The National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 41771345) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2020FZZX001-06) financially supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Antony Van der Ent.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 284 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Ma, L., Zhang, X. et al. A hyperaccumulator plant Sedum alfredii recruits Cd/Zn-tolerant but not Pb-tolerant endospheric bacterial communities from its rhizospheric soil. Plant Soil 455, 257–270 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04684-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-020-04684-0