Abstract
Background and aims
Phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria can colonize the surface of plant roots under natural conditions and may enter plant tissues to form endophytic symbiosis. They can convert unavailable phosphorus in the soil into available phosphorus, which can be utilized by plants. The aims of this study were to investigate the chemotaxis of Bacillus cereus YL6 and its migration and colonization sites in Chinese cabbage and to provide some technical support for the subsequent investigation of the physiological regulation mechanism of phosphate-dissolving bacteria in plants.
Methods
This study demonstrated that the green fluorescent protein marker did not affect the physiological and biochemical properties of YL6. Through the chemotaxis test and pot experiment, the colonization and growth promoting mechanism of YL6 in Chinese cabbage was explored.
Results
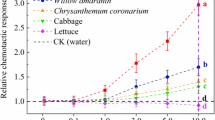
YL6 showed a strong positive chemotactic response to cabbage roots. The addition of organic acids to the soil promotes the colonization of YL6 in Chinese cabbage roots. Colonization of YL6 in Chinese cabbage is a dynamic process that moves from the root surface to root tissues and then up to stems and leaves. Fluorescence microscopy showed that YL6 mainly colonized cortical cells and vascular bundles of various plant tissues and was also observed in mesophyll cells. The proliferative effect of YL6 resulted from the interaction of effective phosphorus, and exuded auxin and gibberellin in the rhizosheath.
Conclusion
This study enhanced our understanding of the interaction mechanisms between phosphate-dissolving bacteria YL6 and Chinese cabbage. YL6 has the potential for future development into bio-fertilizer for agricultural production.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adesemoye AO, Kloepper JW (2009) Plant-microbes interactions in enhanced fertilizer-use efficiency. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85(1):1–12
Bacilio-Jiménez M, Aguilar-Flores S, Ventura-Zapata E et al (2003) Chemical characterization of root exudates from rice ( Oryza sativa) and their effects on the chemotactic response of endophytic bacteria. Plant Soil 249(2):271–277
Barrett M, Morissey JP, O'Gara F (2011) Functional genomics analysis of plant growth-promoting rhizobacterial traits involved in rhizosphere competence. Biol Fertil Soils 47:729–744
Bemier SP, Ha DG, Khan W et al (2011) Modulation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa surface-associated group behaviors by individual amino acids through c-di—GMP signaling. Res Microbiol 162:680–688
Cao Y, Zhang ZH, Ling N et al (2011) Bacillus subtilis SQR9 can control Fusarium wilt in cucumber by colonizing plant roots. Biol Fertil Soils 47:495–506
Chaiharn M, Lumyong S (2011) Screening and optimization of indole-3-acetic acid production and phosphate solubilization from rhizobacteria aimed at improving plant growth. Curr Microbiol 62(1):173–181
Che JM, Liu P, Zhang Y et al (2010) Tagging of bacterial-wilt-disease biocontrol bacteria ANTI-8098A (Bacillus cereus) with the green fluorescence protein gene and its biological characteristics. J Agric Biotechnol 18(2):337–345
Chen Y, Cao S, Chai Y, Clardy J, Kolter R, Guo JH, Losick R (2012) A Bacillus subtilis sensor kinase involved in triggering biofilm formation on the roots of tomato plants. Mol Microbiol 85(3):418–430
Compant S, Clément C, Sessitsch A. (2010). Plant growth-promoting bacteria in the rhizo- and endosphere of plants: their role, colonization, mechanisms involved and prospects for utilization[J]. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 42(5):669–678
Compant S, Duffy B, Nowak J, Clément C, Barka EA (2005) Use of plant growth-promoting Bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Appl Environ Microbiol 71(9):4951–4959
Dietel K, Beator B, Budiharjo A, et al (2013) Bacterial traits involved in colonization of Arabidopsis thaliana roots by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42. The Plant Pathology Journal 29(1):59–66
Du F, He PF, Wu YZ, et al (2015) GFP-labeled endophytic Bacillus subtilis Y10 and its colonization in Chinese cabbage. Chinese Journal of Ecology 34(7):2064–2070
Egamberdieva D, Jabborova D, Wirth S (2013) Alleviation of salt stress in legumes by co-inoculation with Pseudomonas and rhizobium. Fundamentals and Advances. Springer India, Plant Microbe Symbiosis, pp 291–303
Fan B, Borriss R, Bleiss W, et al. (2012). Gram-positive rhizobacterium Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 colonizes three types of plants in different patterns[J]. The Journal of Microbiology, 50(1):38–44.
Flávia MVL, Czajkowski R, de Souza RM et al (2014) Studies on the colonization of axenically grown tomato plants by a GFP-tagged strain of Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. michiganensis. Eur J Plant Pathol 139(1):53–66
Glickmann E, Dessaux Y (1995) A critical examination of the specificity of the salkowski reagent for indolic compounds produced by phytopathogenic bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol 61(2):793–796
Gordillo F, Chávez FP, Jerez CA (2010) Motility and chemotaxis of Pseudomonas sp. B4 towards polychlorobiphenyls and chlorobenzoates. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 60(2):322–328
Gotz M, Gomes N, Dratwinski A et al (2010) Survival of gfp-tagged antagonistic bacteria in the rhizosphere of tomato plants and their effects on the indigenous bacterial community. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56(2):207–218
Grimm AC, Harwood CS (1997) Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas spp. to the polyaromatic hydrocarbon naphthalene. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4111–4115
Gu JG, Fang DH, Li TF et al (2004) Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas fluorescens RB-42 and RB-89 and colonization of tobacco roots. Chin J Soil Fertil 4:34–36
Gupta M, Kiran S, Gulati A, Singh B, Tewari R (2012) Isolation and identification of phosphate solubilizing bacteria able to enhance the growth and aloin-a biosynthesis of Aloe barbadensis miller. Microbiol Res 167(6):358–363
Han J, Xie H, Zhao JH (2007) Rapid determination of exopolysaccharide from Bacillus Subtilis and optimization of fermentation conditions. Food Sci Technol 6:210–213
Hao X, Cho CM, Racz GJ et al (2002) Chemical retardation of phosphate diffusion in an acid soil as affected by liming. Nutr Cycl Agroecosyst 64(3):213–224
Hardoim PR, Overbeek LSV, Elsas JDV (2008) Properties of bacterial endophytes and their proposed role in plant growth. Trends Microbiol 16(10):463–471
Hedden P, Sponsel V (2015) A century of gibberellin research. J Plant Growth Regul 34(4):740–760
Hu XJ, Xie LH, Yu CB et al (2011) Chemotaxis of acid and sugar in the root exudates of Brassica napus L. Chin J Oil Crop Sci 33(4):416–419
Isherword KF (1998) Fertilizer use and environment. In: N.Ahmed and A. Hamid (eds.), Proc. Symp. Plant Nutrition Management for Sustainable Agricultural Growth. NFDC, Islamabad, 57–76.
Jin X, Yang R, Yan X (2016) Chemotactic responses of Phytophthora sojae zoospores to amino acids and sugars in root exudates. J Gen Plant Pathol 82(3):142–148
Khan K, Joergensen R (2009) Changes in microbial biomass and P fractions in biogenic household waste compost amended with inorganic P fertilizers. Bioresour Technol 100(1):303–309
Lavania M, Chauhan PS, Chauhan SVS, Singh HB, Nautiyal CS (2006) Induction of plant defense enzymes and Pheno-lics by treatment with plant growth–promoting Rhizobacteria Serratia marcescens NBRI1213. Curr Microbiol 52(5):363–368
Ling N, Raza W, Ma J et al (2011) Identification and role of organic acids in watermelon root exudates for recruiting Paenibacillus polymyxa SQR-21 in the rhizosphere. Eur J Soil Biol 47(6):374–379
Lu ZY, Yang XF, Feng YJ (2006) Isolation, classification, colonization and application of Endophytic Bacteria in plants. Life Sci 18(1):90–94
Mehta P, Walia A, Chauhan A, Shirkot CK (2013) Plant growth promoting traits of phosphate-solubilizing rhizobacteria isolated from apple trees in trans Himalayan region of Himachal Pradesh. Arch Microbiol 195(5):357–369
Murphy J, Riley JP (1962) Modified solution method for determination of phosphate in natural water. Anal Chim Acta 27:31–36
Neal AL, Ahmad S, Gordonweeks R et al (2012) Benzoxazinoids in root exudates of maize attract Pseudomonas putida to the Rhizosphere. PLoS One 7(4):e35498
Padda KP, Puri A, Chanway CP (2016) Effect of GFP tagging of Paenibacillus polymyxa P2b-2R on its ability to promote growth of canola and tomato seedlings. Biol Fertil Soils 52(3):1–11
Pan H (2015) Isolation and identification of PSB and their impact on inorganic phosphorus fractionation of calcareous soil. Thesis for M.S.,Chin.Northwest A&F University, Supervisor: Cao C L. pp. 8–20
Pascale BB, Yunrong C, Hera V et al (2013) Bacillus subtilis biofilm induction by plant polysaccharides. PNAS 110(17):E1621–E1630
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with the vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Premono ME, Moawad AM, Vleck PLG (1996) Effect of phosphate solubilizing Pseudmonas putida on the growth of maize and its survival in the rhizosphere. Indonasian J Crop Sci 11:3–23
Price RE (2012) The effect of various alnJno acids as nitrogen source on biofilm formation of Aero. monas spp. Texas Tech University, Lubbock
Rudrappa T, Czymmek KJ, Paré PW, Bais HP (2008) Root-secreted malic acid recruits beneficial soil bacteria. Plant Physiol 148(3):1547–1556
Shen YF, E YY, Yang F, et al. (2017) Effects of amino acid composition in root exudates of watermelon on the chemotaxis and rhizosphere colonization of Bacillus polymyxa SQR-21[J]. J Nanjing Agric Univ, (1)
Shirmardi M, Savaghebi GR, Khavazi K et al (2010) Effect of microbial inoculants on uptake of nutrient elements in two cultivars of sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) in saline soils. Notulae Scientia Biologicae 2(3):57–66
Sindhu SS, Parmar P, Phour M (2014) Nutrient cycling: potassium Solubilization by microorganisms and improvement of crop growth. Geomicrobiol Biogeochem:175–198
Sorroche FG, Rinaudi LV, Zorreguieta Á, Giordano W (2010) EPS II-dependent autoaggregation of Sinorhizobium meliloti planktonic cells. Curr Microbiol 61(5):465–470
Steel R, Torrie JH (1997) Principles and Procedures of Statistics: A Biometrical Approach. McGraw-Hil, New York
Sudisha J, Niranjana SR, Sukanya SL et al (2010) Relative efficacy of strobilurin formulations in the control of downy mildew of sunflower. J Pest Sci 83(4):461–470
Wang GH, Zhao Y, Zhou DR et al (2003) Research status and prospects of phosphate solubilizing Bacteria. Ecol Environ 12(1):96–101
Wang Z, Xu G, Ma P, et al. (2017) Isolation and characterization of a phosphorus-solubilizing bacterium from Rhizosphere soils and its colonization of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis)[J]. Front Microbiol, 8
Weert DE, Dekkers LC, et al (2006) The two-component coIR/S system of Pseudomonas fluorescens WCS365 plays a role in rhizosphere competence through maintaining the structure and function of the outer membrane. Fems Microbiol Ecol 58(2):205–213
Wei CY, Xing YX, Mo Y et al (2014) Colonization of nitrogen-fixing Bacteria DX120E marked by green fluorescent protein gene in sugarcane plants. Acta Agron Sin 40(6):1132–1139
Xu WH, Liu ZP, Fu CM et al (2018) The promoting effect of Bacillus Rhizopus on Rice roots. J Henan Agric Sci 47(4):59–63
Xue QH, Li D, Tang L (2000) Improvement of gibberellin fluorescence assay. JNorthwest A&F Uniy (Natural Science Edition) 28(4):34–39
Yaryura PM, León M, Correa OS, Kerber NL, Pucheu NL, García AF (2008) Assessment of the role of chemotaxis and biofilm formation as requirements for colonization of roots and seeds of soybean plants by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens BNM339. Curr Microbiol 56(6):625–632
Yi YM, Huang WY, Ge Y (2008) Exopolysaccharide:a novel important factor in the microbial dissolution of tricalcium phosphate. World J MicrobiolBiotech 24:1059–1065
Yssel A, Reva O, Tastan BO (2011) Comparative structural bioinformatics analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens chemotaxis proteins within Bacillus subtilis group. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92(5):997–1008
Zhang SM, Wang YX, Li J et al (2006) Colonization of Bacillus subtilis BS-68A on cucumber. Biotechnology 16(4):73–74
Zhang N, Wang D, Liu Y et al (2014) Effects of different plant root exudates and their organic acid components on chemotaxis, biofilm formation and colonization by beneficial rhizosphere-associated bacterial strains. Plant Soil 374(1–2):689–700
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Matthew G. Bakker.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 309 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Xie, H., Ku, Y. et al. Chemotaxis of Bacillus cereus YL6 and its colonization of Chinese cabbage seedlings. Plant Soil 447, 413–430 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04344-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04344-y