Abstract
Background and aims
Anthropogenic activities have increased nitrogen (N) and phosphorus (P) inputs to terrestrial ecosystems, which may significantly alter P cycle through accumulation and resorption.
Methods
We measured the concentrations of four different P fractions (inorganic, nucleic, sugar, and residual P) in both live leaves and senescent leaves in N and P additions in an evergreen plantation forest of subtropical China.
Results
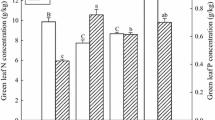
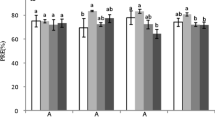
Adding moderate N plus P increased total, inorganic, and sugar P concentrations, which sustained the leaf N/P balance and alleviated P limitation in Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantation. Nitrogen and P (total, nucleic, and residue P) resorption proficiencies did but P (each of various fractions) resorption efficiency did not respond to nutrient addition. The concentrations and resorption efficiencies of most P fractions were lower in the old than young leaves, but their resorption proficiencies except for sugar P weren’t different.
Conclusions
Internal P cycles of Chinese fir could be strongly altered through increasing accumulation of inorganic P and sugar P factions in respond to soil P enrichment when combined with suitable N addition. The easily degradable P (inorganic and sugar P) were preferentially resorbed regardless of nutrient addition. Leaf age was a key-factor influencing the resorption extent of P fractions in Chinese fir.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aerts R (1996) Nutrient resorption from senescing leaves of perennials: are there general patterns? J Ecol 84:597–608. https://doi.org/10.2307/2261481
Allen SE (1989) Chemical analysis of ecological materials. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford
Chapin FS, Kedrowski RA (1983) Seasonal changes in nitrogen and phosphorus fractions and autumn retranslocation in evergreen and deciduous taiga trees. Ecology 64:376–391. https://doi.org/10.2307/1937083
Chapin FS III, Moilanen L (1991) Nutritional controls over nitrogen and phosphorus resorption from Alaskan birch leaves. Ecology 72:709–715. https://doi.org/10.2307/2937210
Chen FS, Niklas KJ, Liu Y, Fang XM, Wan SZ, Wang HM (2015) Nitrogen and phosphorus additions alter nutrient dynamics but not resorption efficiencies of Chinese fir leaves and twigs differing in age. Tree Physiol 35:1106–1117. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpv076
Cheng Y, Wang J, Sun N, Xu M, Zhang J, Cai Z, Wang S (2018) Phosphorus addition enhances gross microbial N cycling in phosphorus-poor soils: a 15N study from two long-term fertilization experiments. Biol Fert Soils 54:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-018-1299-0
Cleveland CC, Townsend AR, Schmidt SK (2002) Phosphorus limitation of microbial processes in moist tropical forests: evidence from short-term laboratory incubations and field studies. Ecosystems 5:0680–0691. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-002-0202-9
Close DC, Beadle CL (2004) Total, and chemical fractions, of nitrogen and phosphorus in Eucalyptus seedling leaves: effects of species, nursery fertiliser management and transplanting. Plant Soil 259:85–95. https://doi.org/10.1023/b:plso.0000020942.97995.f3
Denton MD, Veneklaas EJ, Freimoser FM, Lambers H (2007) Banksia species (Proteaceae) from severely phosphorus-impoverished soils exhibit extreme efficiency in the use and re-mobilization of phosphorus. Plant Cell Environ 30:1557–1565. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01733.x
de Oliveira LB, Marques ACR, de Quadros FLF, Farias JG, Piccin R, Brunetto G, Nicoloso FT (2018) Phosphorus allocation and phosphatase activity in grasses with different growth rates. Oecologia 186:633–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-018-4059-9
Dong WY, Zhang XY, Liu XY, Fu XL, Chen FS, Wang HM, Sun X, Wen X (2015) Responses of soil microbial communities and enzyme activities to nitrogen and phosphorus additions in Chinese fir plantations of subtropical China. Biogeosciences 12:5537–5546. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-12-5537-2015
Elser JJ, Dobberfuhl DR, MacKay NA, Schampel JH (1996) Organism size, life history, and N: P stoichiometry. BioScience 46:674–684. https://doi.org/10.2307/1312897
Feller IC, Lovelock CE, McKee KL (2007) Nutrient addition differentially affects ecological processes of Avicennia germinans in nitrogen versus phosphorus limited mangrove ecosystems. Ecosystems 10:347–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-007-9025-z
Feller IC, Whigham DF, O’Neill JP, McKee KL (1999) Effects of nutrient enrichment on within-stand cycling in a mangrove forest. Ecology 80:2193–2205. https://doi.org/10.1890/0012-9658(1999)080[2193:EONEOW]2.0.CO;2
Güsewell S (2004) N: P ratios in terrestrial plants: variation and functional significance. New Phytol 164:243–266. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2004.01192.x
Güsewell S (2005) Nutrient resorption of wetland graminoids is related to the type of nutrient limitation. Funct Ecol 19:344–354. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0269-8463.2005.00967.x
Helmisaari HS (1992) Nutrient retranslocation within the foliage of Pinus sylvestris. Tree Physiol 10:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/10.1.45
Hidaka A, Kitayama K (2011) Allocation of foliar phosphorus fractions and leaf traits of tropical tree species in response to decreased soil phosphorus availability on mount Kinabalu, Borneo. J Ecol 99:849–857. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2745.2011.01805.x
Hidaka A, Kitayama K (2013) Relationship between photosynthetic phosphorus-use efficiency and foliar phosphorus fractions in tropical tree species. Ecol Evol 3:4872–4880. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.861
Hom JL, Oechel WC (1983) The photosynthetic capacity, nutrient content, and nutrient use efficiency of different needle age-classes of black spruce (Picea mariana) found in interior Alaska. Can J For Res 13:834–839. https://doi.org/10.1139/x83-113
Hu XF, Chen FS, Wine ML, Fang XM (2017) Increasing acidity of rain in subtropical tea plantation alters aluminum and nutrient distributions at the root-soil interface and in plant tissues. Plant Soil 417:261–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-017-3256-3
Huang J, Yu H, Lin H, Zhang Y, Searle EB, Yuan Z (2016) Phosphorus amendment mitigates nitrogen addition-induced phosphorus limitation in two plant species in a desert steppe, China. Plant Soil 399:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2649-4
Killingbeck KT (1996) Nutrients in senesced leaves: keys to the search for potential resorption and resorption proficiency. Ecology 77:1716–1727. https://doi.org/10.2307/2265777
Kitajima K, Mulkey SS, Samaniego M, Wright SJ (2002) Decline of photosynthetic capacity with leaf age and position in two tropical pioneer tree species. Am J Bot 89:1925–1932. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.89.12.1925
Lambers H, Chapin FS III, Pons TL (2008) Plant physiological ecology. Springer Science & Business Media. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-0-387-78341-3
Lambers H, Cawthray GR, Giavalisco P, Kuo J, Laliberté E, Pearse SJ, Scheible WR, Stitt M, Teste F, Turner BL (2012) Proteaceae from severely phosphorus-impoverished soils extensively replace phospholipids with galactolipids and sulfolipids during leaf development to achieve a high photosynthetic phosphorus-use-efficiency. New Phytol 196:1098–1108. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04285.x
Lambers H, Finnegan PM, Jost R, Plaxton W, Shane M, Stitt M (2015a) Phosphorus nutrition in Proteaceae and beyond. Nat Plants 1:15109. https://doi.org/10.1038/nplants.2015.109
Lambers H, Clode PL, Hawkins HJ, Laliberté E, Oliveira RS, Reddell P, Shane MW, Stitt M, Weston P (2015b) Metabolic adaptations of the non-mycotrophic proteaceae to soils with low phosphorus. Annu Plant Rev 48:289. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118958841.ch11
Li R, Yang Q, Zhang W, Zheng W, Chi Y, Xu M, Wang S (2016b) Thinning effect on photosynthesis depends on needle ages in a Chinese fir (Cunninghamia lanceolata) plantation. Sci Total Environ 580:900–906. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.12.036
Li R, Yang Q, Zhang W, Zheng W, Wang S (2018) Response of nonstructural carbohydrates to thinning and understory removal in a Chinese fir [Cunninghamia lanceolata (lamb.) hook] plantation. Trees 32:801–808. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-018-1673-4
Li Y, Niu S, Yu G (2016a) Aggravated phosphorus limitation on biomass production under increasing nitrogen loading: a meta-analysis. Glob Change Biol 22:934–943. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.13125
Liu J, Li Y, Xu Y, Liu S, Huang W, Fang X, Yin G (2017) Phosphorus uptake in four tree species under nitrogen addition in subtropical China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:20005–20014. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-9633-x
Liu X, Duan L, Mo J, Du E, Shen J, Lu X, Zhang Y, Zhou X, He C, Zhang F (2011) Nitrogen deposition and its ecological impact in China: an overview. Environ Pollut 159:2251–2264. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.j.1227.2010.00137
Lü XT, Reed SC, Yu Q, Han XG (2016) Nutrient resorption helps drive intra-specific coupling of foliar nitrogen and phosphorus under nutrient-enriched conditions. Plant Soil 398:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-015-2642-y
Marklein AR, Houlton BZ (2012) Nitrogen inputs accelerate phosphorus cycling rates across a wide variety of terrestrial ecosystems. New Phytol 193:696–704. https://doi.org/10.3410/f.14267334.15779539
Mayor JR, Wright SJ, Turner BL (2014) Species-specific responses of foliar nutrients to long-term nitrogen and phosphorus additions in a lowland tropical forest. J Ecol 102:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2745.12190
Millard P, Grelet G (2010) Nitrogen storage and remobilization by trees: ecophysiological relevance in a changing world. Tree Physiol 30:1083–1095. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpq042
Mimura T (1995) Homeostasis and transport of inorganic phosphate in plants. Plant Cell Physiol 36:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a078724
Nambiar EKS, Fife DN (1987) Growth and nutrient retranslocation in needles of radiata pine in relation to nitrogen supply. Ann Bot 60:147–156. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.aob.a087431
Olsen SR (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate[M]. United States Department Of Agriculture; Washington 82:457–464. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-195612000-00002
Ostertag R (2010) Foliar nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation responses after fertilization: an example from nutrient-limited Hawaiian forests. Plant Soil 334:85–98. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-010-0281-x
Reed SC, Seastedt TR, Mann CM, Suding KN, Townsend AR, Cherwin KL (2007) Phosphorus fertilization stimulates nitrogen fixation and increases inorganic nitrogen concentrations in a restored prairie. App Soil Ecol 36:238–242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsoil.2007.02.002
Reed SC, Townsend AR, Davidson EA, Cleveland CC (2012) Stoichiometric patterns in foliar nutrient resorption across multiple scales. New Phytol 196:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04249.x
Soudzilovskaia NA, Onipchenko VG, Cornelissen JH, Aerts R (2007) Effects of fertilisation and irrigation on ‘foliar afterlife’ in alpine tundra. J Veg Sci 18:755–766. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1654-1103.2007.tb02591.x
Sterner RW, Elser JJ (2002) Ecological stoichiometry: the biology of elements from molecules to the biosphere. Princeton University Press, Princeton, New Jersey
Stitt M, Lunn J, Usadel B (2010) Arabidopsis and primary photosynthetic metabolism–more than the icing on the cake. Plant J 61:1067–1091. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2010.04142.x
Tang Y, Zhang X, Li D, Wang H, Chen F, Fu X, Yu G (2016) Impacts of nitrogen and phosphorus additions on the abundance and community structure of ammonia oxidizers and denitrifying bacteria in Chinese fir plantations. Soil Biol Biochem 103:284–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.09.001
Tsujii Y, Onoda Y, Kitayama K (2017) Phosphorus and nitrogen resorption from different chemical fractions in senescing leaves of tropical tree species on mount Kinabalu, Borneo. Oecologia 185:171–180. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-017-3938-9
Turner BL, Brenes-Arguedas T, Condit R (2018) Pervasive phosphorus limitation of tree species but not communities in tropical forests. Nature 555:367–370. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0099-x
Vergutz L, Manzoni S, Porporato A, Novais RF, Jackson RB (2012) Global resorption efficiencies and concentrations of carbon and nutrients in leaves of terrestrial plants. Ecol Monogr 82:205–220. https://doi.org/10.1890/11-0416.1
Vitousek PM, Porder S, Houlton BZ, Chadwick OA (2010) Terrestrial phosphorus limitation: mechanisms, implications, and nitrogen–phosphorus interactions. Ecol Appl 20:5–15. https://doi.org/10.1890/08-0127.1
Wang FC, Chen FS, Wang GG, Mao R, Fang XM, Wang HM, Bu WS (2019) Effects of experimental nitrogen addition on nutrients and nonstructural carbohydrates of dominant understory plants in a Chinese fir plantation. Forests 10:155. https://doi.org/10.3390/f10020155
Wang M, Murphy MT, Moore TR (2014) Nutrient resorption of two evergreen shrubs in response to long-term fertilization in a bog. Oecologia 174:365–377. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00442-013-2784-7
Warren C (2006) Why does photosynthesis decrease with needle age in Pinus pinaster? Trees 20:157–164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-005-0021-7
Wyka TP, Żytkowiak R, Oleksyn J (2016) Seasonal dynamics of nitrogen level and gas exchange in different cohorts of scots pine needles: a conflict between nitrogen mobilization and photosynthesis? Eur J Forest Res 135:483–493. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-016-0947-x
Yan Z, Kim N, Han W, Guo Y, Han T, Du E, Fang J (2015) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus supply on growth rate, leaf stoichiometry, and nutrient resorption of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Soil 388:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-014-2316-1
Yang H (2018) Effects of nitrogen and phosphorus addition on leaf nutrient characteristics in a subtropical forest. Trees 32:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-017-1636-1
Yuan ZY, Chen HY (2015) Negative effects of fertilization on plant nutrient resorption. Ecology 96:373–380. https://doi.org/10.1890/14-0140.1
Yuan Z, Shi X, Jiao F, Han F (2017) N and P resorption as functions of the needle-age class in two conifer trees. J Plant Ecol 11:780–788. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpe/rtx055
Zheng L, Zhao Q, Yu Z, Zhao S, Zeng D (2017) Altered leaf functional traits by nitrogen addition in a nutrient-poor pine plantation: a consequence of decreased phosphorus availability. Sci Rep 7:7415. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07170-3
Zhang G, Zhang L, Wen D (2018) Photosynthesis of subtropical forest species from different successional status in relation to foliar nutrients and phosphorus fractions. Sci Rep 8:10455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28800-4
Zhu J, He N, Wang Q, Yuan G, Wen D, Yu G, Jia Y (2015) The composition, spatial patterns, and influencing factors of atmospheric wet nitrogen deposition in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems. Sci Total Environ 511:777–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.12.038
Zhu J, Wang Q, He N, Smith MD, Elser JJ, Du J, Yuan G, Yu G, Yu Q (2016) Imbalanced atmospheric nitrogen and phosphorus depositions in China: implications for nutrient limitation. J Geophys Res Biogeosci 121:1605–1616. https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jg003393
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 31730014, 31870427 and 31760200); and Jiangxi Provincial Department of Science and Technology (grant numbers 20165BCB19006 & 20181ACH80006). We thank Yu Liu, Liqun Zou and Xiulan Zhang for their help with field sampling and laboratory measurement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Hans Lambers.
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 2699 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, FC., Fang, XM., Wang, G.G. et al. Effects of nutrient addition on foliar phosphorus fractions and their resorption in different-aged leaves of Chinese fir in subtropical China. Plant Soil 443, 41–54 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04221-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-019-04221-8