Abstract
Aims
The symbiosis between Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 and its host legumes is influenced by the type 3 secretion system (T3SS), which delivers proteins (effectors) directly into the host cells to promote infection. GunA, one of the predicted HH103 effectors, potentially codes for a cellulase. In this work we tried to characterise GunA and elucidate its role in symbosis with soybean and cowpea.
Methods
A GunA::HA fusion protein was constructed to study T3SS-dependent secretion. Cellulase activity of GunA was measured and gunA::uidA-GFP and gunA::cyA fusions were constructed to monitor gunA expression in nodules and to study translocation to the host cells, respectively. Finally, the symbiotic performance of a gunA mutant was studied in soybean and cowpea.
Results
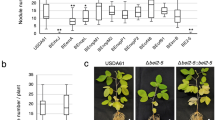
GunA from S. fredii HH103 shows cellulase activity and is secreted through the T3SS in response to the inducer flavonoid genistein. Interestingly, at the beggining of the symbiotic process, GunA was partially responsible for the induction of the expression of the soybean GmPR1 gene, a gene used as a marker for plant defense responses. However, GunA was also detected in soybean and cowpea developed nodules. Finally, nodulation assays indicate that GunA is beneficial for symbiosis with soybean but detrimental with cowpea.
Conclusion
Secretion of GunA through the S. fredii HH103 T3SS clearly and differentially impacts the symbiotic performance of this strain with soybean and cowpea. GunA, or its cellulase activity, is recognised by soybean root cells very early in the symbiotic process but, curiously, its secretion can also be detected in mature nodules. This suggests different symbiotic roles at different symbiotic stages that need to be further elucidated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bellincampi D, Cervone F, Lionetti V (2014) Plant cell wall dynamics and wall-related susceptibility in plant-pathogen interactions. Front Plant Sci 5:228
Beringer JE (1974) R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol 84:188–198
Caldelari Baumberger I, Fraefel N, Göttfert M, Hennecke H (2003) New NodW- or NifA-regulated Bradyrhizobium japonicum genes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 16:342–351
Deakin WJ, Broughton WJ (2009) Symbiotic use of pathogenic strategies: rhizobial protein secretion systems. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:312–320
de Lyra MCCP, López-Baena FJ, Madinabeitia N, Vinardell JM, Espuny MR, Cubo MT, Bellogín RA, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Ollero FJ (2006) Inactivation of the Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 rhcJ gene abolishes nodulation outer proteins (Nops) secretion and decreases the symbiotic capacity with soybean. Int Microbiol 9:125–133
Denoux C, Galletti R, Mammarella N, Gopalan S, Werck D, de Lorenzo G, Ferrari S, Ausubel FM, Dewdney J (2008) Activation of defense response pathways by OGs and Flg22 elicitors in Arabidopsis seedlings. Mol Plant 1:423–445
Downie JA (2010) The roles of extracellular proteins, polysaccharides and signals in the interactions of rhizobia with legume roots. FEMS Microbiol Rev 34:150–170
Fåhraeus G (1957) The infection of clover root hairs by nodule bacteria studied by a simple glass slide technique. J Gen Microbiol 16:374–381
Gage DJ (2004) Infection and invasion of roots by symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing rhizobia during nodulation of temperate legumes. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:280–300
Galan JE, Waksman G (2018) Protein-injection machines in bacteria. Cell 172:1306–1318
Glazebrook J (2005) Contrasting mechanisms of defense against biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens. Annu Rev Phytopathol 43:205–227
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77:51–59
Jiménez-Guerrero I, Pérez-Montaño F, Medina C, Ollero FJ, López-Baena FJ (2015a) NopC is a Rhizobium-specific type 3 secretion system effector secreted by Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii HH103. PLoS One 10:e0142866
Jiménez-Guerrero I, Pérez-Montaño F, Monreal JA, Preston GM, Fones H, Vioque B, Ollero FJ, López-Baena FJ (2015b) Rhizobial type 3 secretion system effectors suppress the early soybean defense responses induced by its natural symbiont Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii HH103. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 28:790–799
Jiménez-Guerrero I, Pérez-Montaño F, Medina C, Ollero FJ, López-Baena FJ (2017) The Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii HH103 nodulation outer protein NopI is a determinant for efficient nodulation of soybean and cowpea. Appl Environ Microbiol 83:e02770–e02716
Jimenéz-Zurdo JI, Mateos PF, Dazzo FB, Martínez-Molina E (1996) Cell-bound cellulase and polygalacturonase production by Rhizobium and Bradyrhizobium species. Soil Biol Biochem 28:917–921
Krause A, Doerfel A, Göttfert M (2002) Mutational and transcriptional analysis of the type III secretion system of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 5:1228–1235
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
López-Baena FJ, Monreal JA, Pérez-Montaño F, Guasch-Vidal B, Bellogín RA, Vinardell JM, Ollero FJ (2009) The absence of Nops secretion in Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 increases GmPR1 expression in Williams soybean. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 22:1445–1454
López-Baena FJ, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Rodríguez-Carvajal MA, Vinardell JM (2016) Bacterial molecular signals in the Sinorhizobium fredii-soybean symbiosis. Int J Mol Sci 17:E755
López-Baena FJ, Vinardell JM, Pérez-Montaño F, Crespo-Rivas JC, Bellogín RA, Espuny MR, Ollero FJ (2008) Regulation and symbiotic significance of nodulation outer proteins secretion in Sinorhizobium fredii HH103. Microbiology 154:1825–1836
Margaret I, Becker A, Blom J, Bonilla I, Goesmann A, Göttfert M, Lloret J, Mittard-Runte V, Rückert C, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Vinardell JM, Weidner S (2011) Symbiotic properties and first analyses of the genomic sequence of the fast growing model strain Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 nodulating soybean. J Biotechnol 155:11–19
Mazarei M, Elling AA, Maier TR, Puthoff DP, Baum TJ (2007) GmEREBP1 is a transcription factor activating defense genes in soybean and Arabidopsis. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:107–119
Murray JD (2011) Invasion by invitation: rhizobial infection in legumes. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 24:631–639
Okazaki S, Kaneko T, Sato S, Saeki K (2013) Hijacking of leguminous nodulation signalling by the rhizobial type III secretion system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:17131–17136
Pallen MJ, Chaudhuri RR, Henderson IR (2003) Genomic analysis of secretion systems. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:519–527
Pérez-Montaño F, Jiménez-Guerrero I, Acosta-Jurado S, Navarro-Gómez P, Ollero FJ, Ruiz-Sainz JE, López-Baena FJ, Vinardell JM (2016) A transcriptomic analysis of the effect of genistein on Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 reveals novel rhizobial genes putatively involved in symbiosis. Sci Rep 6:31592
Pessi G, Ahrens CH, Rehrauer H, Lindemann A, Hauser F, Fischer HM, Hennecke H (2007) Genome-wide transcript analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum bacteroids in soybean root nodules. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 20:1353–1363
Poole P, Ramachandran V, Terpolilli J (2018) Rhizobia: from saprophytes to endosymbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol 16:291–303. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2017.171
Robledo M, Rivera L, Menéndez E, Martínez-Hidalgo P, Rivas R, Velázquez E, Dazzo FB, Martínez-Molina E, Mateos PF (2015) Role of Rhizobium cellulase CelC2 in host root colonization and infection. In: de Bruijn FJ (ed) Biological Nitrogen Fixation. Wiley, USA, pp 525–532
Rodrigues JA, López-Baena FJ, Ollero FJ, Vinardell JM, Espuny MR, Bellogín RA, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Thomas JR, Sumpton D, Ault J, Thomas-Oates J (2007) NopM and NopD are rhizobial nodulation outer proteins: identification using LC-MALDI and LC-ESI with a monolithic capillary column. J Proteome Res 6:1029–1037
Sambrook J, Russell D (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor (USA)
Schechter LM, Guenther J, Olcay EA, Jang S, Krishnan HB (2010) Translocation of NopP by Sinorhizobium fredii USDA257 into Vigna unguiculata root nodules. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:3758–3761
Schirrmeister J, Friedrich L, Wenzel M, Hoppe M, Wolf C, Göttfert M, Zehner S (2011) Characterization of the self-cleaving effector protein NopE1 of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol 193:3733–3739
Simon R (1984) High frequency mobilization of gram-negative bacterial replicons by the in vivo constructed Tn5-mob transposon. Mol Gen Genet 196:413–420
Sinha D, Gupta MK, Patel HK, Ranjan A, Sonti RV (2013) Cell wall degrading enzyme induced rice innate immune responses are suppressed by the type 3 secretion system effectors XopN, XopQ, XopX and XopZ of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. PLoS One 8:e75867
Sory MP, Cornelis GR (1994) Translocation of a hybrid YopE-adenylate cyclase from Yersinia enterocolitica into HeLa cells. Mol Microbiol 14:583–594
Staehelin C, Krishnan HB (2015) Nodulation outer proteins: double-edged swords of symbiotic rhizobia. Biochem J 470:263–274
Süß C, Hempel J, Zehner S, Krause A, Patschkowski T, Göttfert M (2006) Identification of genistein-inducible and type III-secreted proteins of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Biotechnol 126:69–77
Teather RM, Wood PJ (1982) Use of Congo red-polysaccharide interactions in enumeration and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from the bovine rumen. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:777–780
Tu JC (1974) Rhizobial root nodules of soybean as revealed by scanning and transmission electron microscopy. Phytopatol 65:447–454
Verma DPS, Zogbi V, Bal AK (1978) A cooperative action of plant and Rhizobium to dissolve the host cell wall during development of root nodule symbiosis. Plant Sci Lett 13:137–142
Vinardell JM, Acosta-Jurado S, Zehner S, Göttfert M, Becker A, Baena I, Blom J, Crespo-Rivas JC, Goesmann A, Jaenicke S, Krol E, McIntosh M, Margaret I, Pérez-Montaño F, Schneiker-Bekel S, Serranía J, Szczepanowski R, Buendía AM, Lloret J, Bonilla I, Pühler A, Ruiz-Sainz JE, Weidner S (2015) The Sinorhizobium fredii HH103 genome: a comparative analysis with S. fredii strains differing in their symbiotic behavior with soybean. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 28:811–824
Vincent JM (1970) The modified Fåhræus slide technique. In: Vincent JM (ed) A manual for the practical study of root nodule bacteria. Blackwell scientific publications. United Kingdom, Oxford, pp 144–145
Wassem R, Kobayashi H, Kambara K, Le Quéré A, Walker GC, Broughton WJ, Deakin WJ (2008) TtsI regulates symbiotic genes in Rhizobium sp. NGR234 by binding to tts boxes. Mol Microbiol 78:736–748
Zehner S, SchoberG WM, Lang K, Göttfert M (2008) Expression of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum type III secretion system in legume nodules and analysis of the associated tts box promoter. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 21:1087–1093
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the Junta de Andalucía (project P11-CVI-7050) and the Spanish Ministerio de Economía y Competitividad (project BIO2016-78409-R). We also would like to thank the Servicio General de Biología (CITIUS) of the Universidad de Sevilla for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Ulrike Mathesius
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Figure 1
GunA translocation assays. cAMP levels measured in soybean nodules harvested 18 dpi from plants inoculated with the HH103 RifR and the HH103 RifRrhcJ::Ω strains carrying the gunA::cya fusion. The HH103 RifR strain was used as a control. Data shown are the mean (± standard deviation of the mean) for two biological replicates. Each cAMP value was individually compared to that obtained in plants inoculated with the HH103 RifR strain using the Mann-Whitney non-parametrical test. None of the treatments were significantly different at the level α = 5% (p < 0.05). (PNG 64 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 21 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
(DOCX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiménez-Guerrero, I., Pérez-Montaño, F., Zdyb, A. et al. GunA of Sinorhizobium (Ensifer) fredii HH103 is a T3SS-secreted cellulase that differentially affects symbiosis with cowpea and soybean. Plant Soil 435, 15–26 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3875-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3875-3